Chonnam Med J.
2011 Aug;47(2):127-129. 10.4068/cmj.2011.47.2.127.
First Fatal Oseltamivir-Resistant 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Case in an Adult in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. haroc153@naver.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2048798
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2011.47.2.127
Abstract
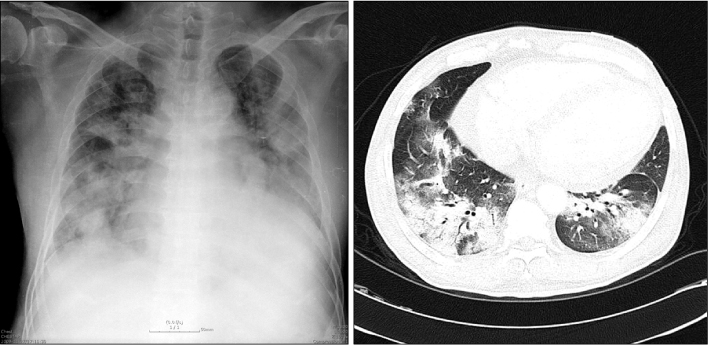
- It has been suggested that oseltamivir-resistant influenza viruses harboring the H274/275Y mutation are less virulent than are those that are oseltamivir-sensitive, and fatality attributed to infection with an oseltamivir-resistant virus is very rare. Here we report the first fatal adult case of oseltamivir-resistant 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) in Korea. A 60-year-old Korean male who had hypertension, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and dilated cardiomyopathy visited Chonnam National University Hospital because of a 7-day history of chest pain and dyspnea. The patient was at another clinic and had been medicated with oseltamivir (75 mg twice daily) beginning 7 days before admission. Empirical antibiotics were started on the first day of hospitalization. Reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) was reported to be positive, and a double dose of oseltamivir (150 mg twice per day) was started on day four of hospitalization. However, the pneumonia worsened and the patient died, despite 3 days of high-dose antiviral therapy and 6 days of antibacterial therapy. An H275Y mutation was detected in the neuraminidase gene sequence. This case shows that oseltamivir resistance after short-term drug exposure is possible and can be fatal, emphasizing that early use of zanamivir should be considered in suspicious cases.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Cardiomyopathy, Dilated
Chest Pain
Diabetes Mellitus
Drug Resistance, Viral
Dyspnea
Hospitalization
Humans
Hypertension
Influenza A Virus, H1N1 Subtype
Influenza, Human
Korea
Male
Middle Aged
Neuraminidase
Orthomyxoviridae
Oseltamivir
Pandemics
Pneumonia
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic
Viruses
Zanamivir
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Neuraminidase
Oseltamivir
Zanamivir
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Was 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Mild Among Pregnant Korean Women?
Joon Hwan An, Ha-Na Kim, Ok-Ja Choi, Gwang-Sook Kim, Uh Jin Kim, Mi Ok Jang, Seung Ji Kang, Kyung-Hwa Park, Sook-In Jung, Yong Soo Kwon, Hee-Chang Jang
Chonnam Med J. 2013;49(2):96-99. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2013.49.2.96.
Reference
-
1. Update on oseltamivir resistance to influenza A(H1N1) 2009 viruses. World Health Organization. Accessed 21 April 2011. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/influenza/2011_02_11_weekly_web_update_oseltamivir_resistance.pdf.2. Ives JA, Carr JA, Mendel DB, Tai CY, Lambkin R, Kelly L, et al. The H274Y mutation in the influenza A/H1N1 neuraminidase active site following oseltamivir phosphate treatment leave virus severely compromised both in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 2002. 55:307–317.
Article3. Duan S, Boltz DA, Seiler P, Li J, Bragstad K, Nielsen LP, et al. Oseltamivir-resistant pandemic H1N1/2009 influenza virus possesses lower transmissibility and fitness in ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2010. 6:e1001022.
Article4. Baz M, Abed Y, Simon P, Hamelin ME, Boivin G. Effect of the neuraminidase mutation H274Y conferring resistance to oseltamivir on the replicative capacity and virulence of old and recent human influenza A(H1N1) viruses. J Infect Dis. 2010. 201:740–745.
Article5. van der Vries E, van den Berg B, Schutten M. Fatal oseltamivir-resistant influenza virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:1074–1076.
Article6. Renaud C, Boudreault AA, Kuypers J, Lofy KH, Corey L, Boeckh MJ, et al. H275Y mutant pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus in immunocompromised patients. Emerg Infect Dis. 2011. 17:653–660.
Article7. Wolfe C, Greenwald I, Chen L. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 and oseltamivir resistance in hematology/oncology patients. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. 16:1809–1811.
Article8. Hong HL, Kim JH, Yi HJ, Kwon HH. A case of oseltamivir-resistant pandemic influenza (H1N1 2009). Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:103–106.
Article9. Lee YH, Kim HY, Kim HS, Uh Y, Kim YK, Kim BR, et al. A case of oseltamivir-resistant pandemic influenza (H1N1 2009) in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:107–111.
Article10. Yi H, Lee JY, Hong EH, Kim MS, Kwon D, Choi JH, et al. Oseltamivir-resistant pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2010. 16:1938–1942.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Oseltamivir-Resistant Pandemic Influenza (H1N1 2009)
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Influenza
- A Case of Oseltamivir-Resistant Pandemic Influenza (H1N1 2009) in a Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and management of pandemic novel Influenza A (H1N1)
- The Emergence of Oseltamivir-Resistant Seasonal Influenza A (H1N1) Virus in Korea During the 2008-2009 Season