Anat Cell Biol.
2015 Mar;48(1):66-74. 10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.66.
Cisplatin induces primary necrosis through poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 activation in kidney proximal tubular cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical Course, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Anatomy, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. jinu.kim@jejunu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Biomedicine and Drug Development, Jeju National University, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2046077
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.66
Abstract
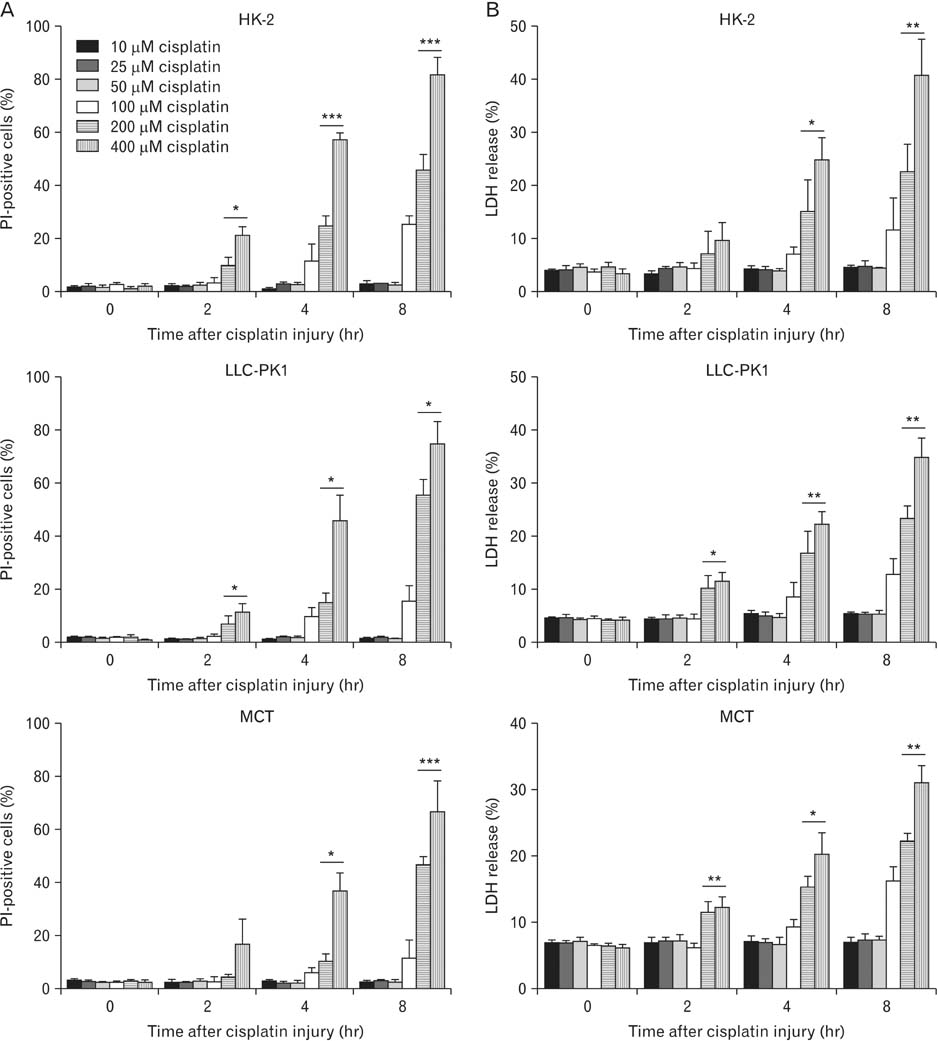
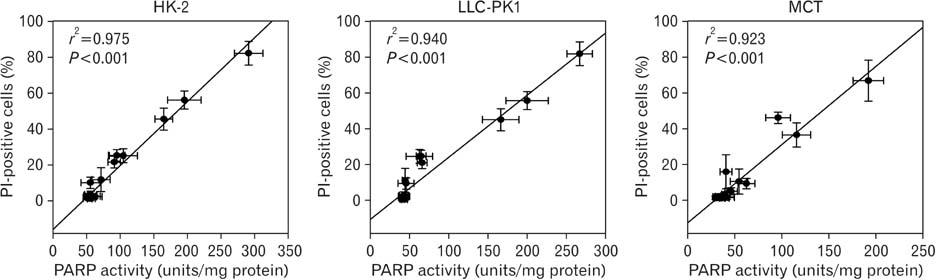
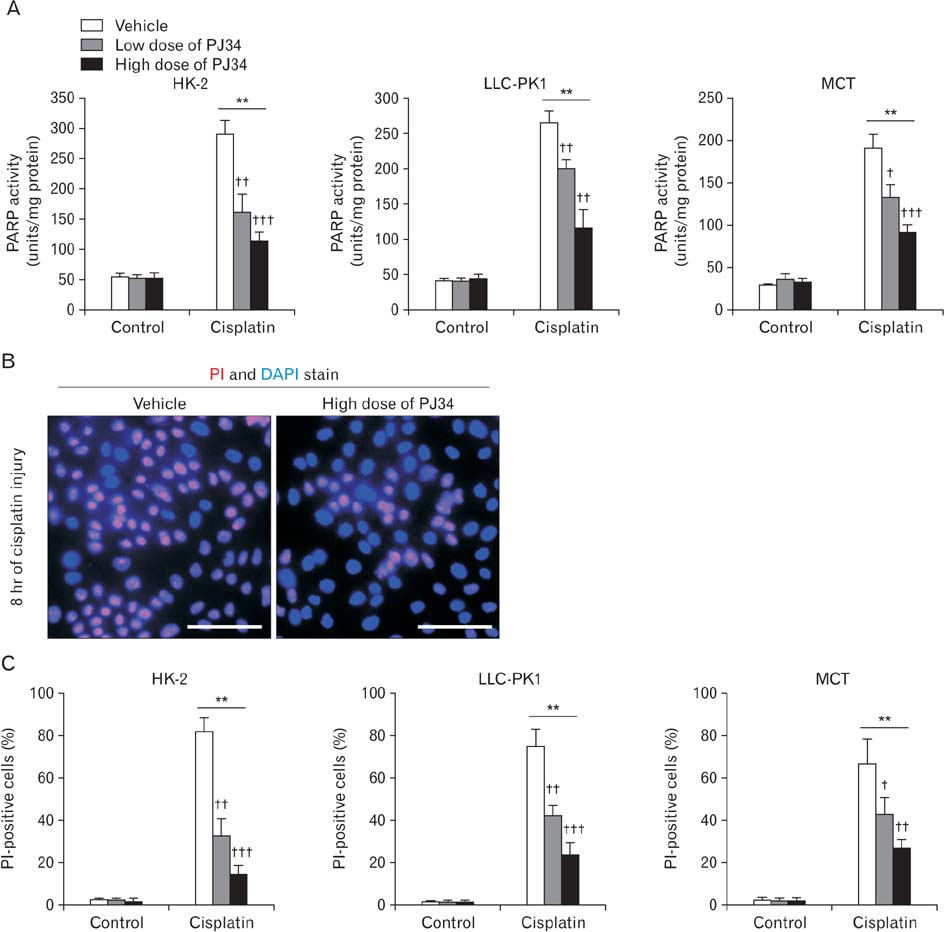
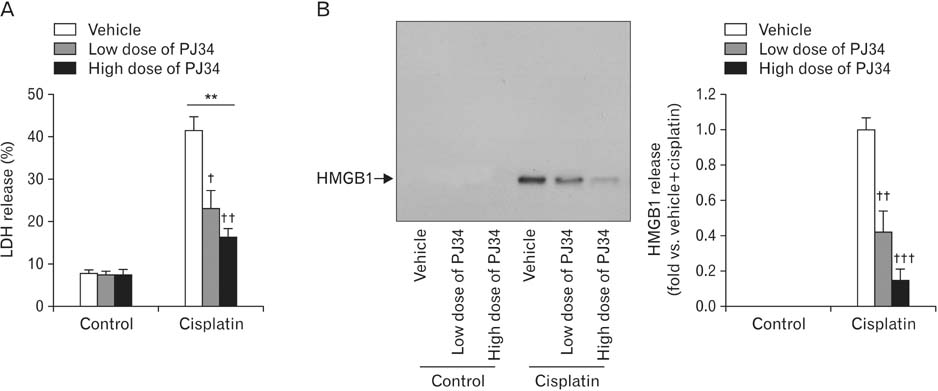
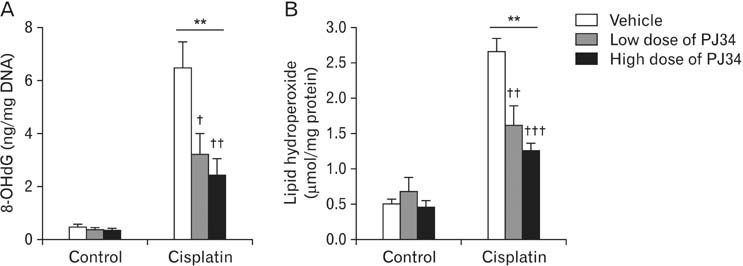
- Treatment with cisplatin for cancer therapy has a major side effect such as nephrotoxicity; however, the role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) in necrosis in response to cisplatin nephrotoxicity remains to be defined. Here we report that cisplatin induces primary necrosis through PARP1 activation in kidney proximal tubular cells derived from human, pig and mouse. Treatment with high dose of cisplatin for 4 and 8 hours induced primary necrosis, as represented by the percentage of propidium iodide-positive cells and lactate dehydrogenase release. The primary necrosis was correlated with PARP1 activation during cisplatin injury. Treatment with PJ34, a potent PARP1 inhibitor, at 2 hours after injury attenuated primary necrosis after 8 hours of cisplatin injury as well as PARP1 activation. PARP1 inhibition also reduced the release of lactate dehydrogenase and high mobility group box protein 1 from kidney proximal tubular cells at 8 hours after cisplatin injury. Oxidative stress was increased by treatment with cisplatin for 8 hours as shown by 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine and lipid hydroperoxide assays, but PARP1 inhibition at 2 hours after injury reduced the oxidative damage. These data demonstrate that cisplatin-induced PARP1 activation contributes to primary necrosis through oxidative stress in kidney proximal tubular cells, resulting in the induction of cisplatin nephrotoxicity and inflammation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Exogenous spermidine ameliorates tubular necrosis during cisplatin nephrotoxicity
Sang Pil Yoon, Jinu Kim
Anat Cell Biol. 2018;51(3):189-199. doi: 10.5115/acb.2018.51.3.189.Cyclosporin A aggravates hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells
Daeun Moon, Jinu Kim
Anat Cell Biol. 2019;52(3):312-323. doi: 10.5115/acb.18.192.Extraneural CGRP Induces Oxidative Stress in Kidney Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells
Daeun Moon, Sang-Pil Yoon, Hee-Seong Jang, Mi Ra Noh, Ligyeom Ha, Babu J. Padanilam, Jinu Kim
Anat Biol Anthropol. 2019;32(4):121-128. doi: 10.11637/aba.2019.32.4.121.
Reference
-
1. Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003; 22:7265–7279.2. Wang D, Lippard SJ. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005; 4:307–320.3. Stark JJ, Howel SB. Nephrotoxicity of cis-platinum (II) dichlorodiammine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978; 23:461–466.4. Arany I, Safirstein RL. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol. 2003; 23:460–464.5. Megyesi J, Safirstein RL, Price PM. Induction of p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1 in kidney tubule cells affects the course of cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1998; 101:777–782.6. Li S, Basnakian A, Bhatt R, Megyesi J, Gokden N, Shah SV, Portilla D. PPAR-alpha ligand ameliorates acute renal failure by reducing cisplatin-induced increased expression of renal endonuclease G. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004; 287:F990–F998.7. Wei Q, Dong G, Franklin J, Dong Z. The pathological role of Bax in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2007; 72:53–62.8. Pabla N, Murphy RF, Liu K, Dong Z. The copper transporter Ctr1 contributes to cisplatin uptake by renal tubular cells during cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 296:F505–F511.9. Lieberthal W, Triaca V, Levine J. Mechanisms of death induced by cisplatin in proximal tubular epithelial cells: apoptosis vs. necrosis. Am J Physiol. 1996; 270(4 Pt 2):F700–F708.10. Pabla N, Dong Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 2008; 73:994–1007.11. Pabla N, Huang S, Mi QS, Daniel R, Dong Z. ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:6572–6583.12. Dong G, Luo J, Kumar V, Dong Z. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases suppress cisplatin-induced p53 activation and apoptosis in renal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010; 298:F293–F300.13. Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV, Kaushal GP. Autophagy is associated with apoptosis in cisplatin injury to renal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008; 294:F777–F787.14. Kraus WL, Lis JT. PARP goes transcription. Cell. 2003; 113:677–683.15. Ha HC, Snyder SH. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is a mediator of necrotic cell death by ATP depletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:13978–13982.16. Martin DR, Lewington AJ, Hammerman MR, Padanilam BJ. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase attenuates ischemic renal injury in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000; 279:R1834–R1840.17. Shevalye H, Stavniichuk R, Xu W, Zhang J, Lupachyk S, Maksimchyk Y, Drel VR, Floyd EZ, Slusher B, Obrosova IG. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibition counteracts multiple manifestations of kidney disease in long-term streptozotocin-diabetic rat model. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010; 79:1007–1014.18. Kim J, Padanilam BJ. Loss of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation during unilateral ureteral obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011; 301:F450–F459.19. Kim J, Long KE, Tang K, Padanilam BJ. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 activation is required for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 2012; 82:193–203.20. Haverty TP, Kelly CJ, Hines WH, Amenta PS, Watanabe M, Harper RA, Kefalides NA, Neilson EG. Characterization of a renal tubular epithelial cell line which secretes the autologous target antigen of autoimmune experimental interstitial nephritis. J Cell Biol. 1988; 107:1359–1368.21. Kim J, Padanilam BJ. Renal nerves drive interstitial fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013; 24:229–242.22. Rovere-Querini P, Capobianco A, Scaffidi P, Valentinis B, Catalanotti F, Giazzon M, Dumitriu IE, Müller S, Iannacone M, Traversari C, Bianchi ME, Manfredi AA. HMGB1 is an endogenous immune adjuvant released by necrotic cells. EMBO Rep. 2004; 5:825–830.23. Fleury C, Mignotte B, Vayssière JL. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochimie. 2002; 84:131–141.24. Zhou HZ, Swanson RA, Simonis U, Ma X, Cecchini G, Gray MO. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 hyperactivation and impairment of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I function in reperfused mouse hearts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006; 291:H714–H723.25. Kim N, Choi WS. Proapoptotic role of nuclear clusterin in brain. Anat Cell Biol. 2011; 44:169–175.26. Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci. 2007; 334:115–124.27. Shino Y, Itoh Y, Kubota T, Yano T, Sendo T, Oishi R. Role of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in cisplatin-induced injury in LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003; 35:966–977.28. Simbulan-Rosenthal CM, Rosenthal DS, Iyer S, Boulares H, Smulson ME. Involvement of PARP and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in the early stages of apoptosis and DNA replication. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999; 193:137–148.29. Oliver FJ, de la Rubia G, Rolli V, Ruiz-Ruiz MC, de Murcia G, Murcia JM. Importance of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and its cleavage in apoptosis. Lesson from an uncleavable mutant. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:33533–33539.30. Filipovic DM, Meng X, Reeves WB. Inhibition of PARP prevents oxidant-induced necrosis but not apoptosis in LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1999; 277:F428–F436.31. Goligorsky MS. TLR4 and HMGB1: partners in crime? Kidney Int. 2011; 80:450–452.32. Javaherian K, Liu JF, Wang JC. Nonhistone proteins HMG1 and HMG2 change the DNA helical structure. Science. 1978; 199:1345–1346.33. Yang H, Wang H, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ. The cytokine activity of HMGB1. J Leukoc Biol. 2005; 78:1–8.34. Wei M, Burenkova O, Lippard SJ. Cisplatin sensitivity in Hmbg1-/- and Hmbg1+/+ mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:1769–1773.35. Zhang B, Ramesh G, Uematsu S, Akira S, Reeves WB. TLR4 signaling mediates inflammation and tissue injury in nephrotoxicity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 19:923–932.36. Kim J, Kim JI, Na YK, Park KM. Intra-renal slow cell-cycle cells contribute to the restoration of kidney tubules injured by ischemia/reperfusion. Anat Cell Biol. 2011; 44:186–193.37. Wu H, Ma J, Wang P, Corpuz TM, Panchapakesan U, Wyburn KR, Chadban SJ. HMGB1 contributes to kidney ischemia reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 21:1878–1890.38. Ditsworth D, Zong WX, Thompson CB. Activation of poly (ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP-1) induces release of the pro-inflammatory mediator HMGB1 from the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:17845–17854.39. Lai Y, Chen Y, Watkins SC, Nathaniel PD, Guo F, Kochanek PM, Jenkins LW, Szabó C, Clark RS. Identification of poly-ADP-ribosylated mitochondrial proteins after traumatic brain injury. J Neurochem. 2008; 104:1700–1711.40. Pankotai E, Lacza Z, Murányi M, Szabó C. Intra-mitochondrial poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation: potential role for alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. Mitochondrion. 2009; 9:159–164.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Exogenous spermidine ameliorates tubular necrosis during cisplatin nephrotoxicity
- Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 contributes to oxidative stress through downregulation of sirtuin 3 during cisplatin nephrotoxicity
- Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase regulates glycolytic activity in kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells
- Spermidine is protective against kidney ischemia and reperfusion injury through inhibiting DNA nitration and PARP1 activation
- Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis by Cisplatin in Human Glioblastoma Cell Line