Anat Cell Biol.
2015 Mar;48(1):36-43. 10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.36.
Innervation of submandibular and sublingual glands in elderly donated cadavers: a preliminary histological study of differences in nerve morphology between mucous and serous acini
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Tokyo Dental College, Tokyo, Japan. yamamotomasahito @tdc.ac.jp
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan.
- 3Division of Internal Medicine, Iwamizawa Asuka Hospital, Iwamizawa, Japan.
- KMID: 2046073
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.36
Abstract
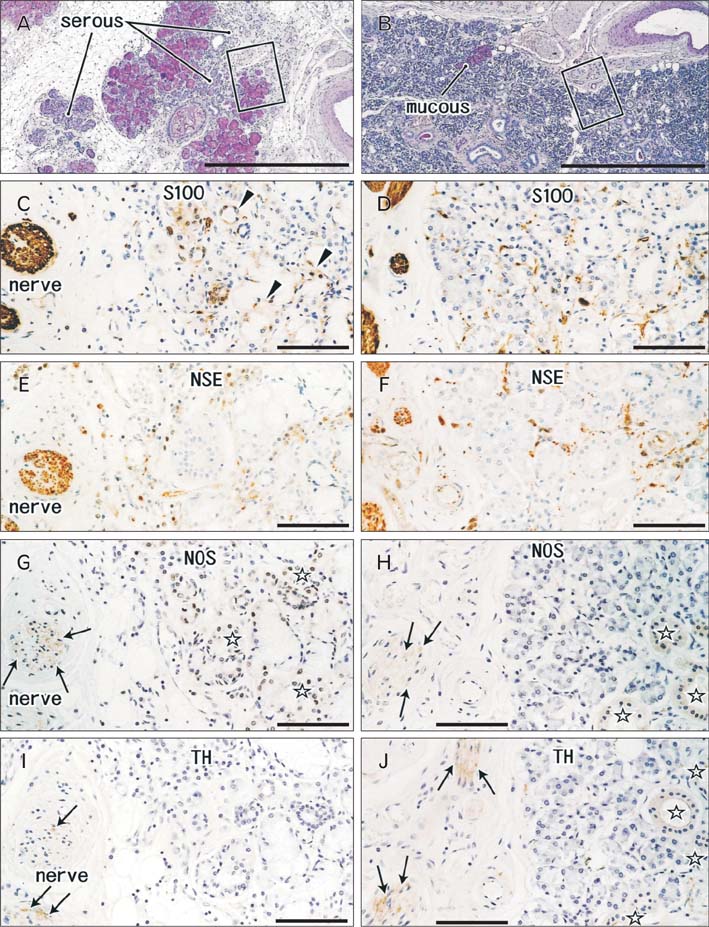
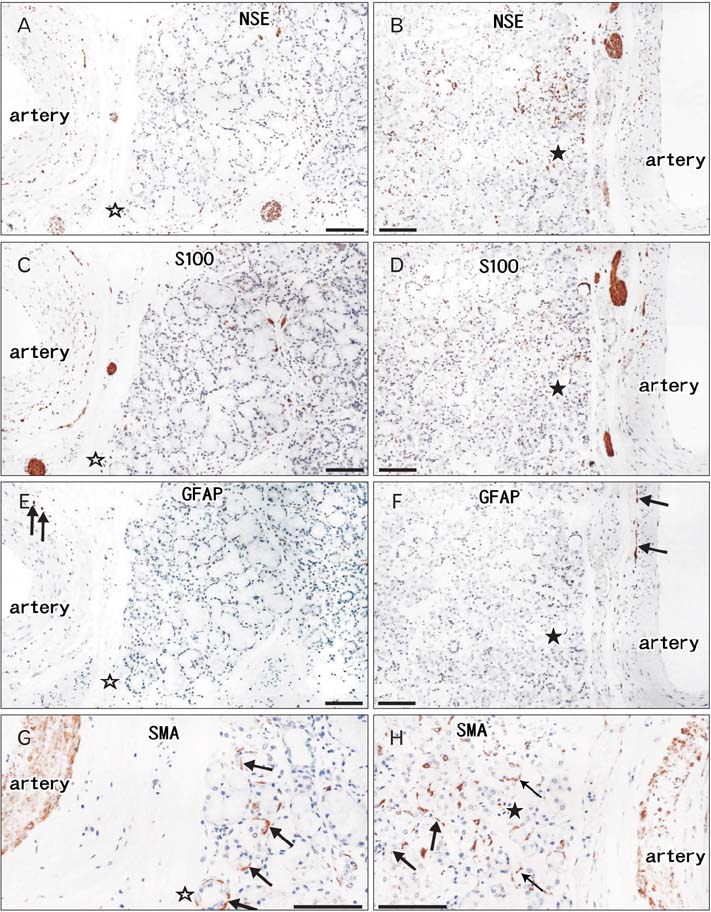
- We examined morphological differences between the sublingual and submandibular glands with special reference to their innervation. The sublingual gland contained abundant periodic acid Schiff-positive mucous acini: some lobules were composed of purely mucous acini, while others were purely serous or mixed. However, in the submandibular gland, the area of mucous acini was very limited. Notably, in the sublingual gland, immunohistochemistry for neuron-specific enolase demonstrated that the serous acini carried a higher density of nerve elements than the mucous acini. However, no such difference was evident in the submandibular gland, possibly due to the small areas of the mucous acini. In both types of gland, neuronal nitric oxide synthase-positive parasympathetic nerves as well as tyrosine hydroxylase-positive sympathetic nerves were observed in the interlobular tissue, but we were unable to trace these thin fibers to the acini. Myoepithelial cells expressed smooth muscle actin, but were negative for S100B protein, glial fibrillary acidic protein and neuron-specific enolase. However, antibody against S100A stained some of the myoepithelial cells and ductal cells in the sublingual gland. Cells positive for peripheral myelin protein 22 were seen in some of the ductal cells in the submandibular gland, but not in the sublingual gland. Therefore, with regard to the neurogenic features of the gland cells, S100B reactivity might disappear first in postnatal life, whereas S100A reactivity is likely to remain as aging progresses. The sublingual gland in elderly individuals seems to provide a good model for comparison of the nerve supply between mucous and serous acini.
MeSH Terms
-
Actins
Aged*
Aging
Cadaver*
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Muscle, Smooth
Myelin Sheath
Neurons
Nitric Oxide
Periodic Acid
Phosphopyruvate Hydratase
Sublingual Gland*
Submandibular Gland
Tyrosine
Actins
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Nitric Oxide
Periodic Acid
Phosphopyruvate Hydratase
Tyrosine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakazato Y, Ishida Y, Takahashi K, Suzuki K. Immunohistochemical distribution of S-100 protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein in normal and neoplastic salivary glands. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1985; 405:299–310.2. Gustafsson H, Virtanen I, Thornell LE. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and desmin in salivary neoplasms. Expression of four different types of intermediate filament proteins within the same cell type. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989; 57:303–313.3. Lee SK, Kim EC, Chi JG, Hashimura K, Mori M. Immunohistochemical detection of S-100, S-100 alpha, S-100 beta proteins, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and neuron specific enolase in the prenatal and adult human salivary glands. Pathol Res Pract. 1993; 189:1036–1043.4. Okura M, Hiranuma T, Tominaga G, Yoshioka H, Aikawa T, Shirasuna K, Matsuya T. Expression of S-100 protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein in cultured submandibular gland epithelial cells and salivary gland tissues. Histogenetic implication for salivary gland tumors. Am J Pathol. 1996; 148:1709–1716.5. Ogawa I, Nishida T, Miyauchi M, Sato S, Takata T. Dedifferentiated malignant myoepithelioma of the parotid gland. Pathol Int. 2003; 53:704–709.6. Angiero F, Sozzi D, Seramondi R, Valente MG. Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of the minor salivary glands: immunohistochemical and morphological features. Anticancer Res. 2009; 29:4703–4709.7. Santos EP, Cavalcante DR, Melo AU, Pereira JC, Gomes MZ, Albuquerque RL Jr. Plasmacytoid myoepithelioma of minor salivary glands: report of case with emphasis in the immunohistochemical findings. Head Face Med. 2011; 7:24.8. Katori Y, Hayashi S, Takanashi Y, Kim JH, Abe S, Murakami G, Kawase T. Heterogeneity of glandular cells in the human salivary glands: an immunohistochemical study using elderly adult and fetal specimens. Anat Cell Biol. 2013; 46:101–112.9. Ekstrom J, Ekman R, Håkanson R, Sjögren S, Sundler F. Calcitonin gene-related peptide in rat salivary glands: neuronal localization, depletion upon nerve stimulation, and effects on salivation in relation to substance P. Neuroscience. 1988; 26:933–949.10. Mirfendereski S, Tobin G, Håkanson R, Ekström J. Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating peptide (PACAP) in salivary glands of the rat: origin, and secretory and vascular effects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1997; 160:15–22.11. Takai N, Uchihashi K, Higuchi K, Yoshida Y, Yamaguchi M. Localization of neuronal-constitutive nitric oxide synthase and secretory regulation by nitric oxide in the rat submandibular and sublingual glands. Arch Oral Biol. 1999; 44:745–750.12. Tobin G, Giglio D, Gotrick B. Studies of muscarinic receptor subtypes in salivary gland function in anaesthetized rats. Auton Neurosci. 2002; 100:1–9.13. Gregson NA, Zhang G, Pritchard J, Wang A, Sanvito L, Hayday AC, Hughes RA. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for human peripheral myelin protein 22 and its use in immunohistochemical studies of the fetal and adult nervous system. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2007; 12:2–10.14. Rosso G, Negreira C, Sotelo JR, Kun A. Myelinating and demyelinating phenotype of Trembler-J mouse (a model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth human disease) analyzed by atomic force microscopy and confocal microscopy. J Mol Recognit. 2012; 25:247–255.15. Hayashi S, Murakami G, Ohtsuka A, Itoh M, Nakano T, Fukuzawa Y. Connective tissue configuration in the human liver hilar region with special reference to the liver capsule and vascular sheath. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2008; 15:640–647.16. Martínez-Madrigal F, Bosq J, Casiraghi O. Major salivary glands. In : Sternberg SS, editor. Histology for Pathologists. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1997. p. 405–429.17. Chi JG. Prenatal development of human major salivary glands. Histological and immunohistochemical characteristics with reference to adult and neoplastic salivary glands. J Korean Med Sci. 1996; 11:203–216.18. Mori M, Murase N, Hosaka M, Orito T. Immunohistochemical expression of S-100 protein in reactive and neoplastic myoepithelial cells of variant salivary pleomorphic adenomas. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 1986; 19:231–240.19. Dardick I, Stratis M, Parks WR, DeNardi FG, Kahn HJ. S-100 protein antibodies do not label normal salivary gland myoepithelium. Histogenetic implications for salivary gland tumors. Am J Pathol. 1991; 138:619–628.20. Kusakabe T, Matsuda H, Kawakami T, Syoui N, Kurihara K, Tsukuda M, Takenaka T. Distribution of neuropeptide-containing nerve fibers in the human submandibular gland, with special reference to the difference between serous and mucous acini. Cell Tissue Res. 1997; 288:25–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunohistochemical Localizaion of Carbonic Anhydrase Isozymes IV and IX in Rat Salivary Gland
- The changes of salivary gland after the ligation of the excretory duct in submandibular glands
- A Case of Multiple Sialoliths in Sublingual Gland Misdiagnosed as Sialoliths in Submandibular Gland
- Lectin Histochemistry for Studying Glycoconjugates in Rat Lingual Salivary Glands during the Postnatal Development
- Effect of propofol on salivary secretion from the submandibular, sublingual, and labial glands during intravenous sedation