Restor Dent Endod.
2012 Mar;37(1):50-53. 10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.50.
Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Wonkwang University School of Dentistry, Iksan, Korea. mksdd@wku.ac.kr
- 2Gangnam Luden Dental Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Conservative Dentistry, Gangnam Severance Dental Hospital, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1995684
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.50
Abstract
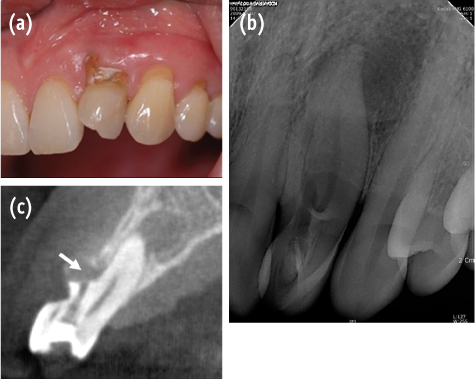
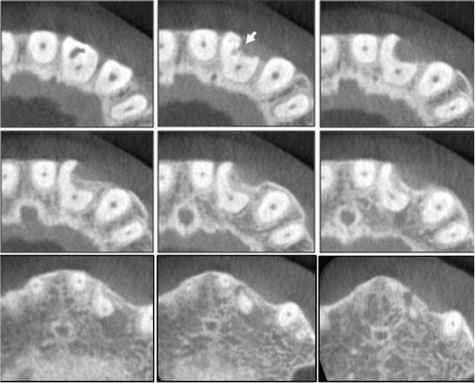
- Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is a useful diagnostic tool for identification of both internal and external root configurations. This case report describes the endodontic management of a lateral incisor with both dens invaginatus and external root irregularity by using CBCT. Nonsurgical endodontic retreatment was performed on the lateral incisor with dens invaginatus. A perforation through the dens invaginatus and external concavity was repaired using mineral trioxide aggregate. After 18 mon of follow-up, there were no clinical symptoms. Recall radiographs appeared normal and showed healing of the periapical pathosis. The understanding of both internal root canal configuration and external root irregularity using CBCT can ensure predictable and successful results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
Moon-Hwan Lee, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung-Kyo Kim
Restor Dent Endod. 2013;38(4):253-257. doi: 10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.253.Management of root canal perforation by using cone-beam computed tomography
Kyung-San Min
Restor Dent Endod. 2013;38(1):55-56. doi: 10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.55.Dilemmas pertaining to three canals in the mesiobuccal root of a maxillary second molar: a case report
Ankit Arora, Shashi Rashmi Acharya, Muliya Vidya Saraswathi, Padmaja Sharma, Amber Ather
Restor Dent Endod. 2013;38(3):172-177. doi: 10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.172.
Reference
-
1. Hülsmann M. Dens invaginatus: aetiology, classification, prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment considerations. Int Endod J. 1997. 30:79–90.
Article2. Hovland EJ, Block RM. Nonrecognition and subsequent endodontic treatment of dens invaginatus. J Endod. 1977. 3:360–362.
Article3. Conklin WW. Bilateral dens invaginatus in the mandibular incisor region. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1978. 45:905–908.
Article4. Lee AM, Bedi R, O'Donnell D. Bilateral double dens invaginatus of maxillary incisors in a young Chinese girl. Aust Dent J. 1988. 33:310–312.
Article5. Arai Y, Tammisalo E, Iwai K, Hashimoto K, Shinoda K. Development of a compact computed tomographic apparatus for dental use. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1999. 28:245–248.
Article6. Mozzo P, Procacci C, Taccoci A, Martini PT, Andreis IA. A new volumetric CT machine for dental imaging based on the cone-beam technique: preliminary results. Eur Radiol. 1998. 8:1558–1564.
Article7. La SH, Jung DH, Kim EC, Min KS. Identification of independent middle mesial canal in mandibular first molar using cone-beam computed tomography imaging. J Endod. 2010. 36:542–545.
Article8. Song CK, Chang HS, Min KS. Endodontic management of supernumerary tooth fused with maxillary first molar by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2010. 36:1901–1904.
Article9. Patel S. The use of cone beam computed tomography in the conservative management of dens invaginatus: a case report. Int Endod J. 2010. 43:707–713.
Article10. Durack C, Patel S. The use of cone beam computed tomography in the management of dens invaginatus affecting a strategic tooth in a patient affected by hypodontia: a case report. Int Endod J. 2011. 44:474–483.
Article11. Pai SF, Yang SF, Lin LM. Nonsurgical endodontic treatment of dens invaginatus with large periradicular lesion: a case report. J Endod. 2004. 30:597–600.
Article12. Kamburoğlu K, Kurşun S, Yüksel S, Oztaş B. Observer ability to detect ex vivo simulated internal or external cervical root resorption. J Endod. 2011. 37:168–175.
Article13. Shemesh H, Cristescu RC, Wesselink PR, Wu MK. The use of cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiographs to diagnose root perforation. J Endod. 2011. 37:513–516.
Article14. Main C, Mirzayan N, Shabahang S, Torabinejad M. Repair of root perforations using mineral trioxide aggregate: a long-term study. J Endod. 2004. 30:80–83.
Article15. Oh MJ, Jeong YN, Bae IH, Yang SY, Park BJ, Koh JT, Hwang YC, Hwang IN, Oh WM. Biocompatibility of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010. 35:359–367.
Article16. Cho YB. Mineral trioxide aggregate and its substitutes. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010. 35:149–151.17. Jeong YN, Yang SY, Park BJ, Park YJ, Hwang YC, Hwang IN, Oh WM. Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trixoxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010. 35:344–352.
Article18. Asgary S, Parirokh M, Eghbal MJ, Brink F. Chemical differences between white and gray mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod. 2005. 31:101–103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A rare case of dilated invaginated odontome with talon cusp in a permanent maxillary central incisor diagnosed by cone beam computed tomography
- Endodontic treatment of maxillary lateral incisors with anatomical variations
- Successful nonsurgical treatment of type II dens invaginatus with 5 root canals using a self-adjusting file: a case report
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report
- Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report