Korean J Urol.
2012 Dec;53(12):870-874. 10.4111/kju.2012.53.12.870.
Change in Penile Length in Children: Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. scpark@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Andong Medical Center, Andong, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Joen Hyundai Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Jinju Medical Center, Jinju, Korea.
- 7School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1988734
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.12.870
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Studies of penile length in children have been rarely conducted. In Korea, great improvements in height and weight have been observed because of economic development over the past 25 years. We investigated the current status of penile length in Korean children and compared the results with those of a previous Korean study conducted in 1987.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
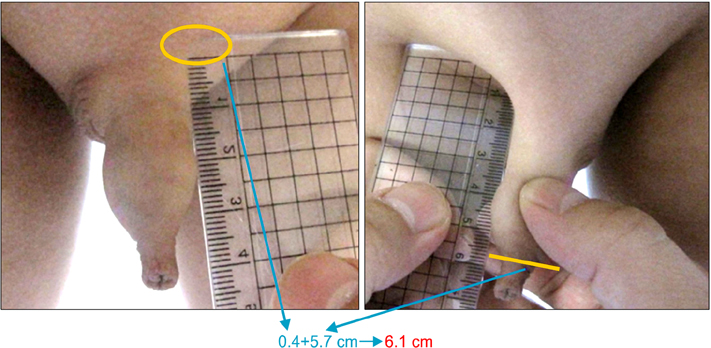
The subjects in this study were 233 boys aged 1 to 158 months, each of whom had been brought to outpatient clinics between April and October 2011. Penile length was measured according to the stretched penile length (SPL) technique; testicular size was measured (in ml) by using orchidometry. A comparison of penile lengths between the current study and the 1987 study was made by using Student's t-test.
RESULTS
SPL increased significantly by 0.7 to 1.1 cm in most age groups (p<0.05). Current anthropometric measures of Korean children such as height, body weight, and testicular size have increased compared with those from 1987.
CONCLUSIONS
Penile length has increased significantly over the last quarter century. Therefore, it is suggested that novel reference values for penile length in prepubertal Korean children be determined in studies with a larger community-based population in order to diagnose and treat size-related penile disorders.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim KS, Han J. Reconstructive surgery for intersex and micropenis. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2009. 14:1–10.2. Phillip M, De Boer C, Pilpel D, Karplus M, Sofer S. Clitoral and penile sizes of full term newborns in two different ethnic groups. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1996. 9:175–179.3. Chung KH, Choi H, Kim SW. Penile and testicular sizes of Korean children. Korean J Urol. 1987. 28:255–258.4. Reilly JM, Woodhouse CR. Small penis and the male sexual role. J Urol. 1989. 142(2 Pt 2):569–571.5. Wiygul J, Palmer LS. Micropenis. ScientificWorldJournal. 2011. 11:1462–1469.6. Tsang S. When size matters: a clinical review of pathological micropenis. J Pediatr Health Care. 2010. 24:231–240.7. Tuladhar R, Davis PG, Batch J, Doyle LW. Establishment of a normal range of penile length in preterm infants. J Paediatr Child Health. 1998. 34:471–473.8. Camurdan AD, Oz MO, Ilhan MN, Camurdan OM, Sahin F, Beyazova U. Current stretched penile length: cross-sectional study of 1040 healthy Turkish children aged 0 to 5 years. Urology. 2007. 70:572–575.9. Cinaz P, Yesilkaya E, Onganlar YH, Boyraz M, Bideci A, Camurdan O, et al. Penile anthropometry of normal prepubertal boys in Turkey. Acta Paediatr. 2012. 101:e33–e36.10. Schonfeld WA, Beebe GW. Normal growth and variation in the male genitalia from birth to maturity. J Urol. 1942. 48:759–777.11. Lee PA, Danish RK, Mazur T, Migeon CJ. Micropenis. III. Primary hypogonadism, partial androgen insensitivity syndrome, and idiopathic disorders. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1980. 147:175–181.12. Ozbey H, Temiz A, Salman T. A simple method for measuring penile length in newborns and infants. BJU Int. 1999. 84:1093–1094.13. Kim SY, Jun JS, Lee SG. Normative data of penile length in Korean newborns. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:944–949.14. Feldman KW, Smith DW. Fetal phallic growth and penile standards for newborn male infants. J Pediatr. 1975. 86:395–398.15. Flatau E, Josefsberg Z, Reisner SH, Bialik O, Iaron Z. Letter: Penile size in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1975. 87:663–664.16. Al-Herbish AS. Standard penile size for normal full term newborns in the Saudi population. Saudi Med J. 2002. 23:314–316.17. Lian WB, Lee WR, Ho LY. Penile length of newborns in Singapore. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 13:55–62.18. Vasudevan G, Manivarmane , Bhat BV, Bhatia BD, Kumar S. Genital standards for south Indian male newborns. Indian J Pediatr. 1995. 62:593–596.19. Sutan-Assin M, Rukman J, Dahlan A. Penile dimensions of newborn infants. Paediatr Indones. 1989. 29:146–150.20. Fujieda K, Matsuura N. Growth and maturation in the male genitalia from birth to adolescence. II. Change of penile length. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1987. 29:220–223.21. Fok TF, Hon KL, So HK, Wong E, Ng PC, Chang A, et al. Normative data of penile length for term Chinese newborns. Biol Neonate. 2005. 87:242–245.22. Boas M, Boisen KA, Virtanen HE, Kaleva M, Suomi AM, Schmidt IM, et al. Postnatal penile length and growth rate correlate to serum testosterone levels: a longitudinal study of 1962 normal boys. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006. 154:125–129.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Penile circumference and stretched penile length in prepubertal children: A retrospective, single-center pilot study
- Penile and Testicular Sizes of Korean Children
- The Relationship between Height and Body Weight and Penile Size in University Students
- Study on Penile Length of Korean Young Adults with or without Circumcision
- Scrotal septum detachment during penile plication to compensate for loss of penile length compared with conventional surgical technique