Korean J Urol.
2014 Mar;55(3):172-177. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.3.172.
Clinical Outcomes of CyberKnife Radiotherapy in Prostate Cancer Patients: Short-term, Single-Center Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. hjkim@kyuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 1988420
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.3.172
Abstract
- PURPOSE
In this retrospective study, we analyzed the outcomes of prostate cancer patients treated with the CyberKnife radiotherapy system (Accuray).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between 2007 and 2010, 31 patients were treated for prostate cancer by use of the CyberKnife radiotherapy system. After excluding six patients who were lost to follow-up, data for the remaining 25 patients were analyzed. Patients were divided into the CyberKnife monotherapy group and a postexternal beam radiotherapy boost group. Clinicopathologic features and treatment outcomes were compared between the groups. The primary endpoint was biochemical recurrence-free survival period based on the Phoenix definition. Toxicities were evaluated by using the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group scoring criteria.
RESULTS
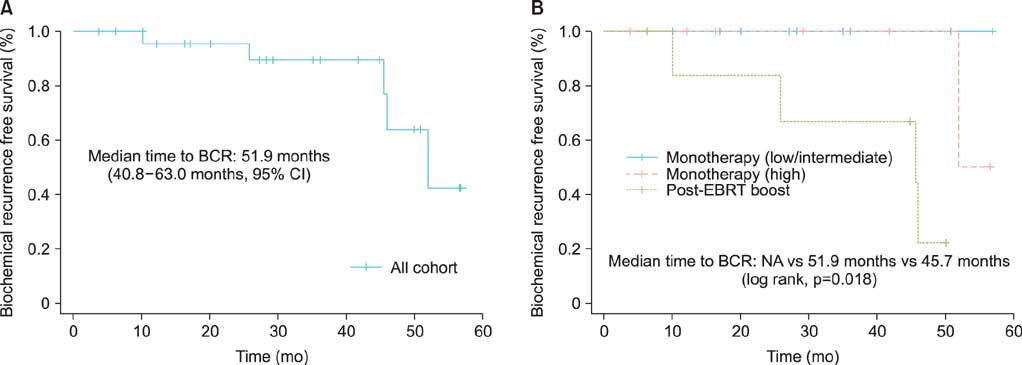
Of 25 patients, 17 (68%) and 8 (32%) were classified in the monotherapy and boost groups, respectively. With a median follow-up of 29.3 months, most of the toxicities were grade 1 or 2 except for one patient in the boost group who experienced late grade 3 gastrointestinal toxicity. The overall biochemical recurrence rate was 20% (5/25) and the median time to biochemical recurrence was 51.9 months. None of the patients with low or intermediate risk had experienced biochemical recurrence during follow-up. Among D'Amico high-risk populations, 16.7% (1/6) in the monotherapy group and 50.0% (4/8) in the boost group experienced biochemical recurrence.
CONCLUSIONS
Our data support that prostate cancer treatment by use of the CyberKnife radiotherapy system is feasible. The procedure can be a viable option for managing prostate cancer either in a monotherapy setting or as a boost after conventional radiotherapy regardless of the patient's risk stratification.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in 2010. Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 45:1–14.2. Oermann EK, Slack RS, Hanscom HN, Lei S, Suy S, Park HU, et al. A pilot study of intensity modulated radiation therapy with hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) boost in the treatment of intermediate- to high-risk prostate cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 9:453–462.3. Smart RF. Radical radiotherapy for carcinoma of the prostate. N Z Med J. 1979; 90:285–287.4. Kim BK, Park SW, Ha SW. Pattern of decrease of prostate specific antigen after radical radiotherapy for the prostate cancer. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 1999; 17:136–140.5. Chin OH, Kim SI, Hong SJ. Early experience of localized prostate cancer treated with neoadjuvant androgen ablation therapy and radiotherapy. Korean J Urol. 2001; 42:702–706.6. Kuban DA, Levy LB, Cheung MR, Lee AK, Choi S, Frank S, et al. Long-term failure patterns and survival in a randomized dose-escalation trial for prostate cancer. Who dies of disease? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011; 79:1310–1317.7. Fowler JF. The radiobiology of prostate cancer including new aspects of fractionated radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2005; 44:265–276.8. Kim GH, Park K, Jo MK, Lee CW, Yang KM, Cho CG. CyberKnife for the treatment of nonmetastatic prostate cancer: preliminary results. Korean J Urol. 2006; 47:1172–1177.9. Freeman DE, King CR. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for low-risk prostate cancer: five-year outcomes. Radiat Oncol. 2011; 6:3.10. Friedland JL, Freeman DE, Masterson-McGary ME, Spellberg DM. Stereotactic body radiotherapy: an emerging treatment approach for localized prostate cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 8:387–392.11. Ju AW, Wang H, Oermann EK, Sherer BA, Uhm S, Chen VJ, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy as monotherapy for intermediate-risk prostate cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2013; 8:30.12. Hyun JH, Park BH, Koo DY, Kim KS, Song KH, Jeong WK, et al. Early experience of prostate cancer treated with cyberknife radiotherapy. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:1066–1072.13. Lawton CA, Won M, Pilepich MV, Asbell SO, Shipley WU, Hanks GE, et al. Long-term treatment sequelae following external beam irradiation for adenocarcinoma of the prostate: analysis of RTOG studies 7506 and 7706. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991; 21:935–939.14. Coste-Maniere E, Olender D, Kilby W, Schulz RA. Robotic whole body stereotactic radiosurgery: clinical advantages of the Cyberknife integrated system. Int J Med Robot. 2005; 1:28–39.15. King CR, Lehmann J, Adler JR, Hai J. CyberKnife radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: rationale and technical feasibility. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 2:25–30.16. King CR, Brooks JD, Gill H, Pawlicki T, Cotrutz C, Presti JC Jr. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer: interim results of a prospective phase II clinical trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009; 73:1043–1048.17. Kal HB, Van Gellekom MP. How low is the alpha/beta ratio for prostate cancer? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 57:1116–1121.18. Wang JZ, Li XA, Yu CX, DiBiase SJ. The low alpha/beta ratio for prostate cancer: what does the clinical outcome of HDR brachytherapy tell us? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003; 57:1101–1108.19. Duchesne GM, Peters LJ. What is the alpha/beta ratio for prostate cancer? Rationale for hypofractionated high-dose-rate brachytherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 44:747–748.20. Hoskin PJ, Motohashi K, Bownes P, Bryant L, Ostler P. High dose rate brachytherapy in combination with external beam radiotherapy in the radical treatment of prostate cancer: initial results of a randomised phase three trial. Radiother Oncol. 2007; 84:114–120.21. Pieters BR, de Back DZ, Koning CC, Zwinderman AH. Comparison of three radiotherapy modalities on biochemical control and overall survival for the treatment of prostate cancer: a systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 2009; 93:168–173.22. Fuller DB, Naitoh J, Lee C, Hardy S, Jin H. Virtual HDR CyberKnife treatment for localized prostatic carcinoma: dosimetry comparison with HDR brachytherapy and preliminary clinical observations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008; 70:1588–1597.23. Katz AJ, Santoro M, Ashley R, Diblasio F. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for low- and low-intermediate-risk prostate cancer: Is there a dose effect? Front Oncol. 2011; 1:49.24. Kang JK, Cho CK, Choi CW, Yoo S, Kim MS, Yang K, et al. Image-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer. Tumori. 2011; 97:43–48.25. Jabbari S, Weinberg VK, Kaprealian T, Hsu IC, Ma L, Chuang C, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy as monotherapy or post-external beam radiotherapy boost for prostate cancer: technique, early toxicity, and PSA response. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 82:228–234.26. Aluwini S, van Rooij P, Hoogeman M, Bangma C, Kirkels WJ, Incrocci L, et al. CyberKnife stereotactic radiotherapy as monotherapy for low- to intermediate-stage prostate cancer: early experience, feasibility, and tolerance. J Endourol. 2010; 24:865–869.27. McBride SM, Wong DS, Dombrowski JJ, Harkins B, Tapella P, Hanscom HN, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy in low-risk prostate adenocarcinoma: preliminary results of a multi-institutional phase 1 feasibility trial. Cancer. 2012; 118:3681–3690.28. Townsend NC, Huth BJ, Ding W, Garber B, Mooreville M, Arrigo S, et al. Acute toxicity after cyberknife-delivered hypofractionated radiotherapy for treatment of prostate cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2011; 34:6–10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy in low- and intermediate-risk prostate carcinoma
- CyberKnife for the Treatment of Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer: Preliminary Results
- Early Experience of Prostate Cancer Treated with CyberKnife(TM) Radiotherapy
- Multimodal therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer: the roles of radiotherapy, androgen deprivation therapy, and their combination
- CyberKnife(TM) for the Treatment of Non-Metastatic Prostate Cancer