J Adv Prosthodont.
2010 Mar;2(1):18-24. 10.4047/jap.2010.2.1.18.
Effect of etched microgrooves on hydrophilicity of titanium and osteoblast responses: A pilot study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Graduate School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Biomaterials & Prosthodontics, East-West Neo Medical Center, Institute of Oral Biology, School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. ysprosth@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1975173
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2010.2.1.18
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this pilot study was to investigate the effect of etched microgrooves on the hydrophilicity of Ti and osteoblast responses. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Microgrooves were applied on Ti to have 15 and 60 micrometer width, and 3.5 and 10 micrometer depth by photolithography, respectively. Further acid etching was applied to create Ti surfaces with etched microgrooves. Both smooth- and acid-etched Ti were used as the controls. The hydrophilicity of Ti was analyzed by determining contact angles. Cell proliferation and osteogenic activity of MC3T3 mouse preosteoblasts were analyzed by bromodeoxyuridine assay and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity test, respectively. One-way ANOVA, Pearson's correlation analysis and multiple regression analysis were used for statistics.
RESULTS
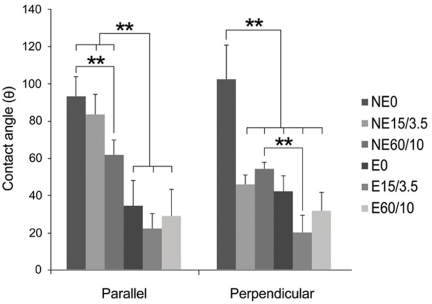
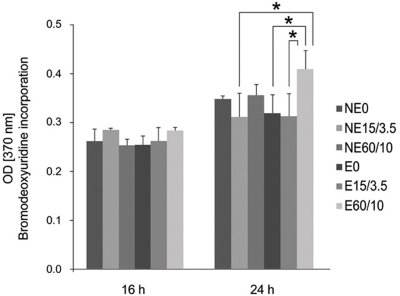
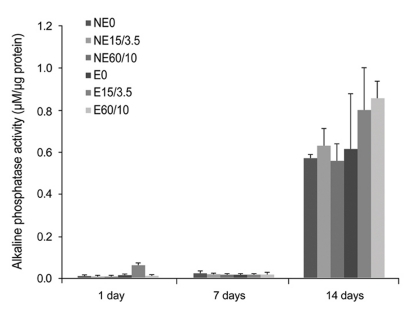
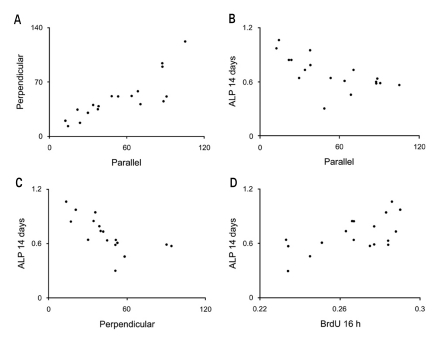
Etched microgrooves significantly increased the hydrophilicity of Ti compared to the smooth Ti. 60 micrometer-wide etched microgrooves significantly enhanced cell proliferation, whereas the osteogenic activity showed statistically non-significant differences between groups. Result of the osteogenic activity significantly correlated with those of hydrophilicity and cell proliferation. Hydrophilicity was determined to be an influential factor on osteogenic activity.
CONCLUSION
This study indicates that increase in hydrophilicity of Ti caused by etched microgrooves acts as an influential factor on osteogenic activity. However, statistically non-significant increase in the ALP activity suggests further investigation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. den Braber ET, de Ruijter JE, Ginsel LA, von Recum AF, Jansen JA. Quantitative analysis of fibroblast morphology on microgrooved surfaces with various groove and ridge dimensions. Biomaterials. 1996; 17:2037–2044. PMID: 8902235.
Article2. Walboomers XF, Ginsel LA, Jansen JA. Early spreading events of fibroblasts on microgrooved substrates. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 51:529–534. PMID: 10880098.
Article3. Chou L, Firth JD, Uitto VJ, Brunette DM. Substratum surface topography alters cell shape and regulates fibronectin mRNA level, mRNA stability, secretion and assembly in human fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1995; 108:1563–1573. PMID: 7615675.
Article4. Hamilton DW, Wong KS, Brunette DM. Microfabricated discontinuous-edge surface topographies influence osteoblast adhesion, migration, cytoskeletal organization, and proliferation and enhance matrix and mineral deposition in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int. 2006; 78:314–325. PMID: 16604286.5. Hamilton DW, Brunette DM. The effect of substratum topography on osteoblast adhesion mediated signal transduction and phosphorylation. Biomaterials. 2007; 28:1806–1819. PMID: 17215038.
Article6. Matsuzaka K, Walboomers XF, de Ruijter JE, Jansen JA. The effect of poly-L-lactic acid with parallel surface micro groove on osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Biomaterials. 1999; 20:1293–1301. PMID: 10403047.7. Kenar H, Köse GT, Hasirci V. Tissue engineering of bone on micropatterned biodegradable polyester films. Biomaterials. 2006; 27:885–895. PMID: 16143391.
Article8. Chehroudi B, Ratkay J, Brunette DM. The role of implant surface geometry on mineralization in vivo and in vitro; a transmission and scanning electron microscopic study. Cells and Materials. 1992; 2:89–104.9. Qu J, Chehroudi B, Brunette DM. The use of micromachined surfaces to investigate the cell behavioural factors essential to osseointegration. Oral Dis. 1996; 2:102–115. PMID: 8957944.
Article10. Perizzolo D, Lacefield WR, Brunette DM. Interaction between topography and coating in the formation of bone nodules in culture for hydroxyapatite- and titanium-coated micromachined surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001; 56:494–503. PMID: 11400127.
Article11. Lamolle SF, Monjo M, Rubert M, Haugen HJ, Lyngstadaas SP, Ellingsen JE. The effect of hydrofluoric acid treatment of titanium surface on nanostructural and chemical changes and the growth of MC3T3-E1 cells. Biomaterials. 2009; 30:736–742. PMID: 19022499.
Article12. Schwarz F, Ferrari D, Herten M, Mihatovic I, Wieland M, Sager M, Becker J. Effects of surface hydrophilicity and microtopography on early stages of soft and hard tissue integration at non-submerged titanium implants: an immunohistochemical study in dogs. J Periodontol. 2007; 78:2171–2184. PMID: 17970685.
Article13. Schwarz F, Wieland M, Schwartz Z, Zhao G, Rupp F, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Schedle A, Broggini N, Bornstein MM, Buser D, Ferguson SJ, Becker J, Boyan BD, Cochran DL. Potential of chemically modified hydrophilic surface characteristics to support tissue integration of titanium dental implants. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009; 88:544–557. PMID: 18837448.
Article14. Lee SW, Kim SY, Lee MH, Lee KW, Leesungbok R, Oh N. Influence of etched microgrooves of uniform dimension on in vitro responses of human gingival fibroblasts. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:458–466. PMID: 19250242.15. Lee SW, Kim SY, Rhyu IC, Chung WY, Leesungbok R, Lee KW. Influence of microgroove dimension on cell behavior of human gingival fibroblasts cultured on titanium substrata. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:56–66. PMID: 19133333.
Article16. Kim SY, Oh N, Lee MH, Kim SE, Leesungbok R, Lee SW. Surface microgrooves and acid etching on titanium substrata alter various cell behaviors of cultured human gingival fibroblasts. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:262–272. PMID: 19397638.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of titanium surface microgrooves and thermal oxidation on in vitro osteoblast responses
- Effect of microgrooves and fibronectin conjugation on the osteoblast marker gene expression and differentiation
- Micropatterned grooves and acid-etching on titanium substrata alter viability and gene expression of adhered human gingival fibroblasts: A pilot study
- On the effect of saline immersion to the removal torque for resorbable blasting media and acid treated implants
- Regulation of human gingival fibroblast gene expression on microgrooves: A DNA microarray study