Tuberc Respir Dis.
2006 Sep;61(3):285-288. 10.4046/trd.2006.61.3.285.
Exacerbation of Sarcoidosis Following Interferon-alpha Therapy for Chronic Active Hepatitis C
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Women University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jinhwalee@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Ewha Women University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Ewha Women University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1970269
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2006.61.3.285
Abstract
- Interferon alpha is an immunomodulator that is used as an antiviral agent to treat chronic active viral hepatitis C. However, interferon can induce or exacerbate sarcoidosis. We report a case of 42-year-old man with an exacerbation of pulmonary sarcoidosis after the cessation of interferon and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. The patient's sarcoidosis improved spontaneously and he continues to be monitored regularly without steroid therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
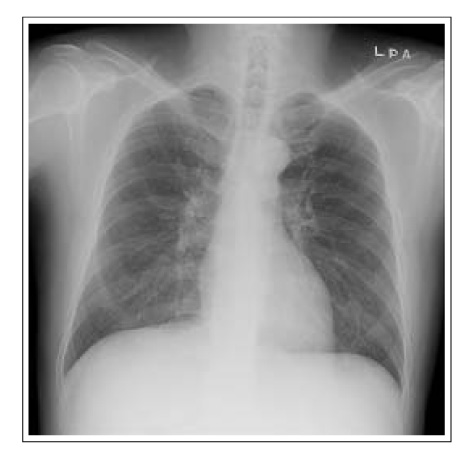
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sleijfer S, Bannink M, van Gool AR, Kruit WH, Stoter G. Side effects of interferon-alpha therapy. Pharm World Sci. 2005. 27:423–431.2. Dusheiko G. Side effects of alpha interferon in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1997. 26:112S–121S.3. Blum L, Serfaty L, Wattiaux MJ, Picard O, Cabane J, Imbert JC. Nodules hypodermiques sarcoïdosiques au cours d'une hépatite virale C traitée par interféron alpha 2 b. Rev Med Interne. 1993. 14:Suppl 462. 1161.4. Hoffmann RM, Jung MC, Motz R, Gossl C, Emslander HP, Zachoval R, et al. Sarcoidosis associated with interferon-alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 1998. 28:1058–1063.5. Gitlin N. Manifestation of sarcoidosis during interferon and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C: a report of two cases. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. 14:883–885.6. Ramos-Casals M, Mana J, Nardi N, Brito-Zeron P, Xaubet A, Sanchez-Tapias JM, et al. Sarcoidosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection: analysis of 68 cases. Medicine. 2005. 84:69–80.7. Leclerc S, Myers RP, Moussalli J, Herson S, Poynard T, Benveniste O. Sarcoidosis and interferon therapy: report of five cases and review of the literature. Eur J Intern Med. 2003. 14:237–243.8. Yoon JG, Ahn JH, Ko SH, Lee HS, Kwon SS, Kim YK, et al. A case of interstitial pneumonitis developed by interferon alpha treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Tuberc Respir Dis. 1996. 43:637–644.9. Abdi EA, Nguyen GK, Ludwig RN, Dickout WJ. Pulmonary sarcoidosis following interferon therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1987. 59:896–900.10. Pietropaoli A, Modrak J, Utell M. Interferon-alpha therapy associated with the development of sarcoidosis. Chest. 1999. 116:569–572.11. Raanani P, Ben-Bassat I. Immune-mediated complications during interferon therapy in hematological patients. Acta Haematol. 2002. 107:133–144.12. Parronchi P, Mohapatra S, Sampognaro S, Giannarini L, Wahn U, Chong P, et al. Effects of interferon-alpha on cytokine profile, T cell receptor repertoire and peptide reactivity of human allergen-specific T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1996. 26:697–703.13. Baumer I, Zissel G, Schlaak M, Muller-Quernheim J. Th1/Th2 cell distributionin pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997. 16:171–177.14. Tam RC, Pai B, Bard J, Lim C, Averett DR, Phan UT, et al. Ribavirin polarizes human T cell responses towards a Type 1 cytokine profile. J Hepatol. 1999. 30:376–382.15. Menon Y, Cucurull E, Reisin E, Espinoza LR. Interferon-alpha-associated sarcoidosis responsive to infliximab therapy. Am J Med Sci. 2004. 328:173–175.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Associated with Pegylated Interferon Alpha-2a and Ribavirin Therapy
- A Case of Hypothyroidism Induced by Alpha-Interferon Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis B
- The Effect of Low-Dosage Alpha-Interferon Therapy in Children with Chronic Active Hepatitis B
- Effect of alpha-interferon treatment on serum ALT levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C
- Effect of alpha-Interferon 2b on Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with High Serum ALT