Korean J Hematol.
2012 Dec;47(4):281-285. 10.5045/kjh.2012.47.4.281.
Surgery in patients with congenital factor VII deficiency: A single center experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea. pysmd@khnmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedics, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1832107
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2012.47.4.281
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Congenital factor VII (FVII) deficiency is a rare hemorrhagic disorder that can cause excessive bleeding during and after surgery in affected patients. The recombinant form of activated factor VII (rFVIIa, NovoSeven(R) from Novo Nordisk, Bagsvaerd, Denmark), which was developed as a second-generation bypassing agent, has recently been used in the management of bleeding for patients with congenital FVII deficiency.
METHODS
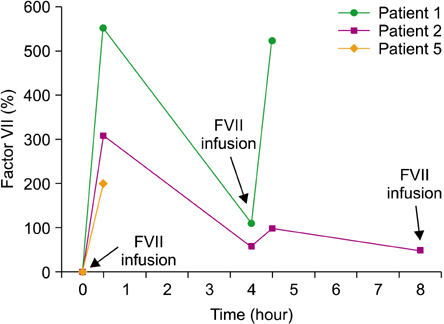
We reviewed the results of 8 surgical procedures in 5 patients with congenital FVII deficiency at the Kyung Hee University Hospital, Gangdong, Seoul, Korea, between January 2008 and June 2010. We administrated rFVIIa preoperatively in six patients and postoperatively in five patients.
RESULTS
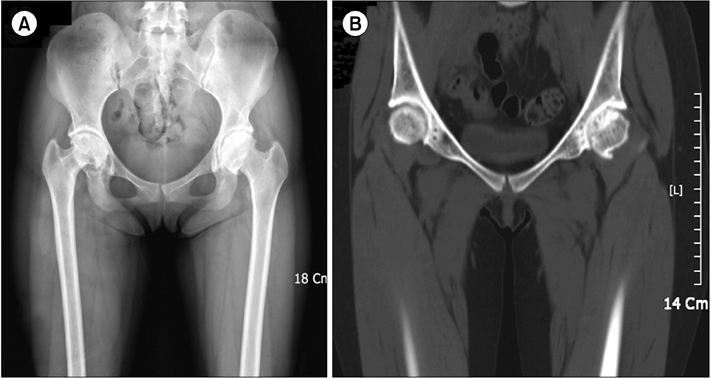
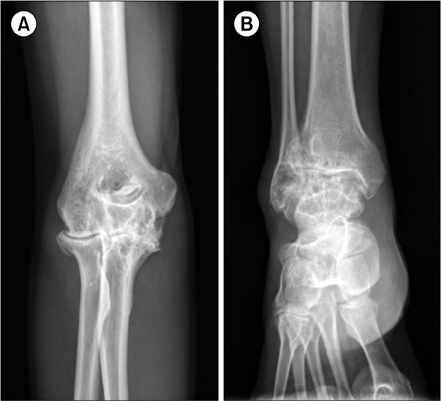
Between January 2008 and June 2010 at our center, 8 operations were performed successfully and no complications were observed in the 5 patients with congenital FVII deficiency. The median level of FVII activity was 2% (range, 0.6-7%). Four orthopedic procedures, 1 tonsillectomy, and 3 dental extractions were performed. The median duration of hospitalization was 8.5 days (range, 0-15 days). rFVIIa was administered at all procedures, except the dental extraction that was performed using only antifibrinolytic agents without any replacement. No bleeding or thrombogenic complications were observed in any case.
CONCLUSION
Patients with congenital FVII deficiency who require surgery can be treated efficiently and safely with rFVIIa or antifibrinolytic agents. rFVIIa was well tolerated and maintained effective hemostasis and showed good clinical outcome after the major surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mannucci PM, Duga S, Peyvandi F. Recessively inherited coagulation disorders. Blood. 2004. 104:1243–1252.
Article2. Herrmann FH, Wulff K, Auerswald G, et al. Factor VII deficiency: clinical manifestation of 717 subjects from Europe and Latin America with mutations in the factor 7 gene. Haemophilia. 2009. 15:267–280.
Article3. Korea Hemophilia Foundation. Annual report 2011. 2011. Seoul, Korea: Korea Hemophilia Foundation;28.4. Perry DJ. Factor VII deficiency. Br J Haematol. 2002. 118:689–700.
Article5. Mariani G, Herrmann FH, Dolce A, et al. Clinical phenotypes and factor VII genotype in congenital factor VII deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 2005. 93:481–487.
Article6. Mariani G, Bernardi F. Factor VII deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2009. 35:400–406.
Article7. Triplett DA, Brandt JT, Batard MA, Dixon JL, Fair DS. Hereditary factor VII deficiency: heterogeneity defined by combined functional and immunochemical analysis. Blood. 1985. 66:1284–1287.
Article8. Ingerslev J, Kristensen HL. Clinical picture and treatment strategies in factor VII deficiency. Haemophilia. 1998. 4:689–696.
Article9. Mariani G, Herrmann FH, Schulman S, et al. Thrombosis in inherited factor VII deficiency. J Thromb Haemost. 2003. 1:2153–2158.
Article10. Giansily-Blaizot M, Biron-Andreani C, Aguilar-Martinez P, et al. Inherited factor VII deficiency and surgery: clinical data are the best criteria to predict the risk of bleeding. Br J Haematol. 2002. 117:172–175.
Article11. Benlakhal F, Mura T, Schved JF, Giansily-Blaizot M. A retrospective analysis of 157 surgical procedures performed without replacement therapy in 83 unrelated factor VII-deficient patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2011. 9:1149–1156.
Article12. Lapecorella M, Mariani G. Factor VII deficiency: defining the clinical picture and optimizing therapeutic options. Haemophilia. 2008. 14:1170–1175.
Article13. Srivastava A, Brewer AK, Mauser-Bunschoten EP, et al. Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia. 2012. [Epub ahead of print].
Article14. Brummel Ziedins K, Rivard GE, Pouliot RL, et al. Factor VIIa replacement therapy in factor VII deficiency. J Thromb Haemost. 2004. 2:1735–1744.
Article15. Mariani G, Dolce A. Lee CA, Berntorp EE, Hoots KW, editors. Congenital factor VII deficiency. Textbook of hemophilia. 2010. 2nd ed. Cambridge, UK: Wiley-Blackwell;341–347.
Article16. Mariani G, Dolce A, Batorova A, et al. Recombinant, activated factor VII for surgery in factor VII deficiency: a prospective evaluation - the surgical STER. Br J Haematol. 2011. 152:340–346.
Article17. Tran HT, Tjønnfjord GE, Paus A, Holme PA. rFVIIa administered by continuous infusion during surgery in patients with severe congenital FVII deficiency. Haemophilia. 2011. 17:764–770.
Article18. Cid AR, Lorenzo JI, Haya S, Montoro JM, Casaña P, Aznar JA. A comparison of FVII:C and FVIIa assays for the monitoring of recombinant factor VIIa treatment. Haemophilia. 2001. 7:39–41.
Article19. Tiede A, Friedrich U, Stenmo C, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of subcutaneously administered recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa). J Thromb Haemost. 2011. 9:1191–1199.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Orthognathic Surgery in a Patient with Factor VII Deficiency
- A case of intracranial hemorrhage in a neonate with congenital factor VII deficiency
- Four cases report of congenital factor VII deficiency
- A Case of Intractable Gastrointestinal Bleeding during Chemotherapy in Hereditary Coagulation Factor Deficiency
- A Case of Congenital Factor VII Deficiency Presented with Subacute Subdural Hematoma