J Clin Neurol.
2007 Dec;3(4):181-186. 10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.181.
Oral Administration of Memantine Prolongs Survival in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. isjoo@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Brain Disease Research Center, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada.
- KMID: 1808551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2007.3.4.181
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-mediated neurotoxicity and oxidative stress have been implicated in the etiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Memantine is a low-affinity, noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist that may protect against motor neuron degeneration.
METHODS
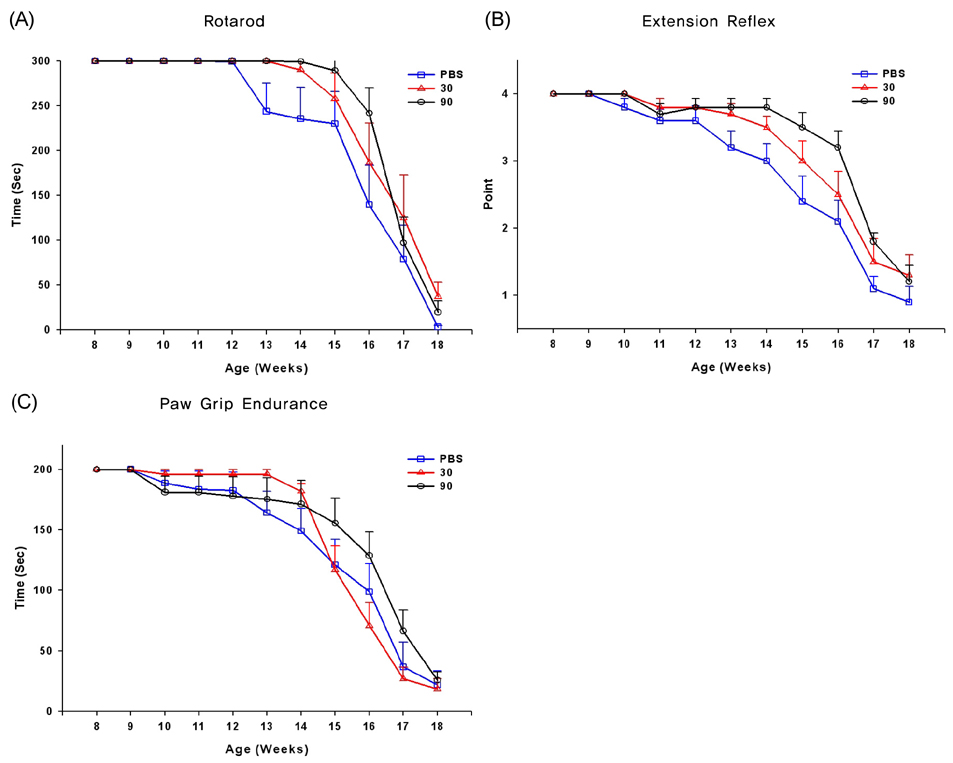
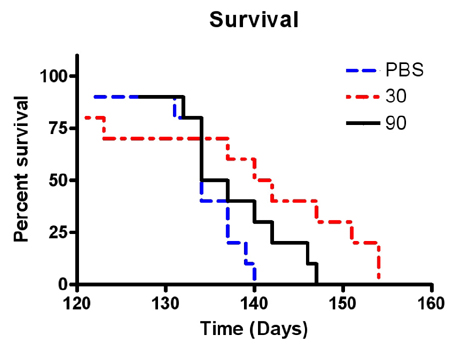
Thirty transgenic mice expressing the G93A SOD1 mutation were randomly divided into control, low-dose memantine (30 mg/kg/day), and high-dose memantine (90 mg/kg/day) groups, with memantine supplied daily with drinking water beginning at 75 days of age. Body weight, survival, and behavioral performances including a rotarod test, paw grip endurance, and hindlimb extension reflex were assessed in the control and memantine-diet groups.
RESULTS
Clinical symptoms were evident in the G93A transgenic mice by 11 weeks of age. Memantine was tolerated well. Compared to control, mice treated with memantine performed better in the rotarod test and hindlimb extension reflex. Moreover, low-dose memantine treatment significantly prolonged the survival of the transgenic mice relative to control mice (141 vs 134 days, p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
These findings suggest that memantine, even when administered at the time of symptom onset, has beneficial effects on patients with ALS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shaw PJ, Ince PG. Glutamate, excitotoxicity and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol. 1997. 244:S3–S14.
Article2. Rothstein JD. Excitotoxic mechanisms in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Adv Neurol. 1995. 68:7–20.3. Van Den Bosch L, Van Damme P, Bogaert E, Robberecht W. The role of excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. 1762:1068–1082.
Article4. Choi DW. Glutamate neurotoxicity and diseases of the nervous system. Neuron. 1988. 1:623–634.
Article5. Prehn JH, Lippert K, Krieglstein J. Are NMDA or AMPA/kainate receptor antagonists more efficacious in the delayed treatment of excitotoxic neuronal injury? Eur J Pharmacol. 1995. 292:179–189.
Article6. Traynor BJ, Bruijn L, Conwit R, Beal F, O'Neill G, Fagan SC, et al. Neuroprotective agents for clinical trials in ALS: a systemic assessment. Neurology. 2006. 67:20–27.
Article7. Bensimon G, Lacomblez L, Meininger V. A controlled trial of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1994. 330:585–591.
Article8. Lacomblez L, Bensimon G, Leigh PN, Guillet P, Meininger V; Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Riluzole Study Group II. Dose-ranging study of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 1996. 347:1425–1431.
Article9. Doble A. The pharmacology and mechanism of action of riluzole. Neurology. 1996. 47:S233–S241.
Article10. Collingridge GL, Singer W. Excitatory amino acid receptors and synaptic plasticity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990. 11:290–296.
Article11. Danysz W, Zajaczkowski W, Parsons CG. Modulation of learning processes by ionotropic glutamate receptor ligands. Behav Pharmacol. 1995. 6:455–474.
Article12. Chen HS, Pellegrini JW, Aggarwal SK, Lei SZ, Warach S, Jensen FE, et al. Open-channel block of N-methyl-Daspartate (NMDA) responses by memantine: therapeutic advantage against NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1992. 12:4427–4436.
Article13. Chen HS, Lipton SA. The chemical biology of clinically tolerated NMDA receptor antagonists. J Neurochem. 2006. 97:1611–1626.
Article14. Volbracht C, van Beek J, Zhu C, Blomgren K, Leist M. Neuroprotective properties of memantine in different in vitro and in vivo models of excitotoxicity. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. 23:2611–2622.
Article15. Lee ST, Chu K, Park JE, Kang L, Ko SY, Jung KW, et al. Memantine reduces striatal cell death with decreasing calpain level in 3-nitropropionic model of Huntington's disease. Brain Res. 2006. 1118:199–207.
Article16. Fleischhacker WW, Buchgeher A, Schubert H. Memantine in the treatment of senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1986. 10:87–93.
Article17. Reisberg G, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Mobius HJ. Memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:1333–1341.
Article18. Wang R, Zhang D. Memantine prolongs survival in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. 22:2376–2380.
Article19. Chu CP, Kunitake T, Kato K, Watanabe S, Qiu DL, Tanoue A, et al. The alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor modulates cardiovascular and drinking responses to central salt loading in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2004. 356:33–36.
Article20. Gurney ME, Cutting FB, Zhai P, Doble A, Taylor CP, Andrus PK, et al. Benefit of vitamin E, riluzole, and gabapentin in a transgenic model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1996. 39:147–157.
Article21. Martin D, Thompson MA, Nadler JV. The neuroprotective agent riluzole inhibits release of glutamate and aspartate from slices of hippocampal area of CA1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993. 250:473–476.
Article22. Debono MW, Le Guern J, Canton T, Doble A, Pradier L. Inhibition by riluzole of electrophysiological responses mediated by rat kainateand NMDA receptors in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993. 235:283–289.
Article23. Albo F, Pieri M, Zona C. Modulation of AMPA receptors in spinal motor neurons by the neuroprotective agent riluzole. J Neurosci Res. 2004. 78:200–207.
Article24. Mantz J, Laudenbach V, Lecharny J-B, Henzel D, Desmonts J-M. Riluzole, a novel antiglutamate, blocks GABA uptake by striatal synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994. 257:R7–R8.
Article25. Lipton SA. Paradigm shift in neuroprotection by NMDA receptor blockade: memantine and beyond. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006. 5:160–170.
Article26. Reisberg B, Doody R, Stoffler A, Schmitt F, Ferris S, Mobius HJ. A 24-week open-label extension of memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2006. 63:49–54.
Article27. Bowser R, Cudkowicz M, Kaddurah-Daouk R. Biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2006. 6:387–398.
Article28. Barneoud P, Lolivier J, Sanger DJ, Scatton B, Moser P. Quantitative motor assessment in FALS mice: a longitudinal study. Neuroreport. 1997. 8:2861–2865.29. Van Den Bosch L, Vandenberghe W, Klassen H, Van Houtte E, Robberecht W. Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors and selective vulnerability of motor neurons. J Neurol Sci. 2000. 180:29–34.
Article30. Sen I, Nalini A, Joshi NB, Joshi PG. Cerebrospinal fluid from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients preferentially elevates intracellular calcium and toxicity in motor neurons via AMPA/kainate receptor. J Neurol Sci. 2005. 235:45–54.
Article31. Tortarolo M, Grignaschi G, Calvaresi N, Zennaro E, Spaltro G, Colovic M, et al. Glutamate AMPA receptors change in motor neurons of SOD1G93A transgenic mice and their inhibition by a noncompetitive antagonist ameliorates the progression of amytrophic lateral sclerosis-like disease. J Neurosci Res. 2006. 83:134–146.
Article32. Kornhuber J, Quack G. Cerebrospinal fluid and serum concentrations of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist memantine in man. Neurosci Lett. 1995. 195:137–139.
Article33. Minkeviciene R, Banerjee P, Tanila H. Memantine improves spatial learning in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. 311:677–682.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuroprotective Effect of Rapamycin (Autophagy Enhancer) in Transgenic SOD1-G93A Mice of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Rosmarinic Acid Alleviates Neurological Symptoms in the G93A-SOD1 Transgenic Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Melittin Ameliorates the Inflammation of Organs in an Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Animal Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Associated With CADASIL
- Syndrome of Progressive Bulbar Palsy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Case Report