The Limitations of Thrombectomy with Solitaire(TM) AB as First-line Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single Center Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Sungnam, Korea. pedineur@dmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1808456
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.3.203
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
A self-expanding retrievable intracranial stent, such as Solitaire AB, is useful for mechanical thrombectomy, producing novel results in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. On the other hand, difficult situations can arise after a thrombectomy when using as in first-line treatment.
METHODS
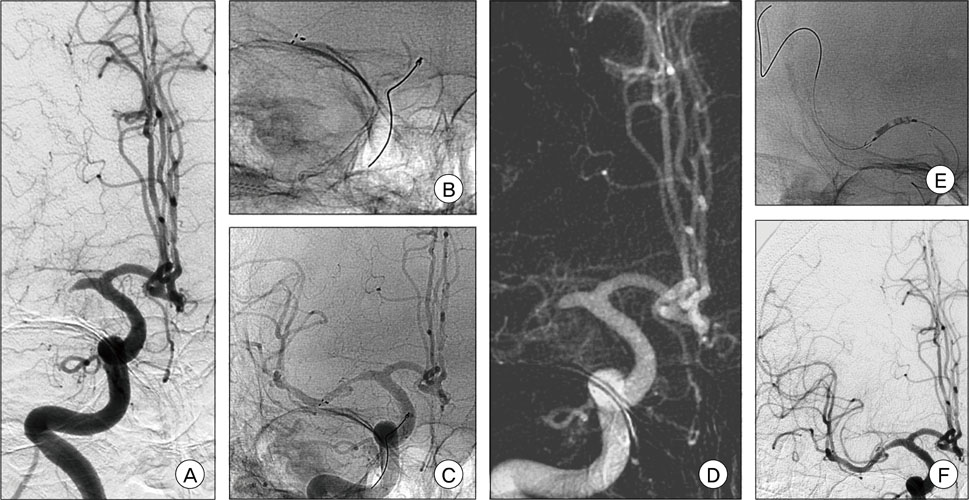
This was a retrospective, single-center study of 23 patients with an acute ischemic stroke attributable to a large artery occlusion within the first eight hours from symptom onset. The occlusion sites were the T segment in five patients, proximal middle cerebral artery in six patients, distal middle cerebral artery in three patients, vertebral and/or basilar artery in five patients, proximal internal cerebral artery in one patient and tandem in three patients. All patients underwent a mechanical thrombectomy using the Solitaire(TM) stent system as the first-line treatment but required additional procedures due to the unsatisfactory results of a thrombectomy.
RESULTS
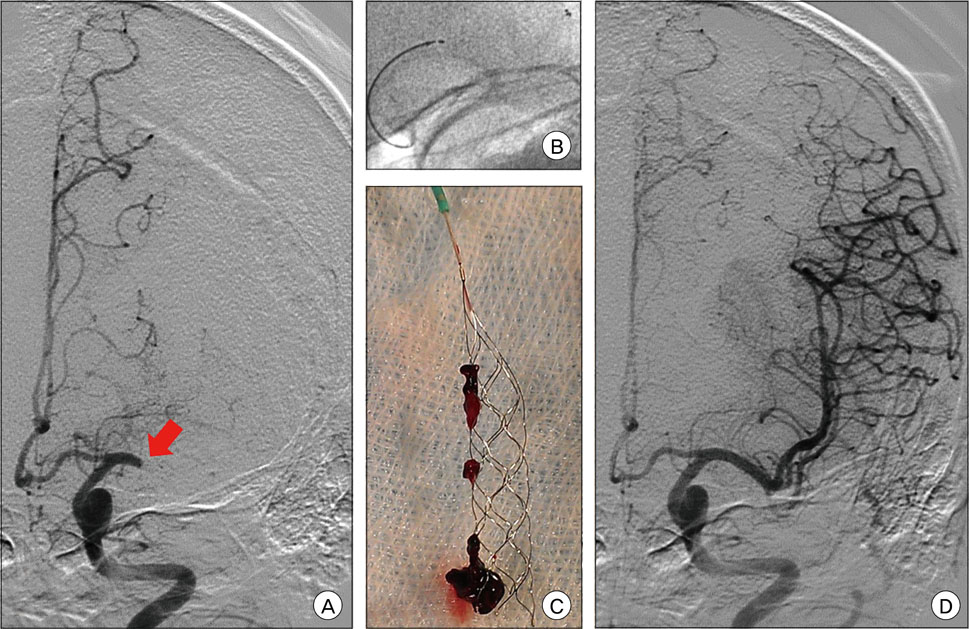
Only six patients achieved complete recanalization by a thrombectomy using the Solitaire. Permanent stent deployment after the thrombectomy was performed in ten patients. Stent and balloon angioplasty was performed after a stent-based thrombectomy in six patients. Balloon angioplasty after thrombectomy was performed in one patient.
CONCLUSION
Mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire(TM) stent as a first-line treatment can produce unfortunate results that will require additional procedures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Dual Mechanical Thrombectomy for Recanalization of a Resistant Acute Posterior Circulation Stroke
Ahmet Peker, Ayça Akgoz, Ethem Murat Arsava, Mehmet Akif Topçuoglu, Anil Arat
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2017;19(2):96-100. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2017.19.2.96.Single Centre Experience on Decision Making for Mechanical Thrombectomy Based on Single-Phase CT Angiography by Including NCCT and Maximum Intensity Projection Images – A Comparison with Magnetic Resonance Imaging after Non-Contrast CT
Myeong Soo Kim, Gi Sung Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(2):188-201. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2019.0131.Angiographic and Clinical Factors Related with Good Functional Outcome after Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Cerebral Artery Occlusion
Jong Hyuk Park, Young Min Han, Kyeong Sool Jang, Wan Soo Yoon, Dong Kyu Jang, Sang Kyu Park
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(3):192-196. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.192.Mechanical Thrombectomy with Solitaire Stent Retrieval for Acute Cardioembolic Stroke
Hokyun Han, Hyunho Choi, Keun-Tae Cho, Byong-Cheol Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(6):627-634. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.003.
Reference
-
1. Ansari S, McConnell DJ, Azari H, Levy EI, Hoh BL, Waters MF, et al. Impact of intracranial self-expanding stents in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: efficacy and limitations. J Neurointerv Surg. 2011. 12. 3(4):364–368.
Article2. Brekenfeld C, Schroth G, Mordasini P, Fischer U, Mono ML, Weck A, et al. Impact of retrievable stents on acute ischemic stroke treatment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. 08. 32(7):1269–1273.
Article3. Castaño C, Dorado L, Guerrero C, Millán M, Gomis M, Perez de la Ossa N, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with the solitaire AB device in large artery occlusions of the anterior circulation: a pilot study. Stroke. 2010. 08. 41(8):1836–1840.4. Gralla J, Brekenfeld C, Mordasini P, Schroth G. Mechanical thrombolysis and stenting in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2012. 01. 43(1):280–285.
Article5. Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, et al. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2003. 08. 34(8):e109–e137.
Article6. Koh JS, Lee SJ, Ryu CW, Kim HS. Safety and efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy with solitaire stent retrieval for acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Neurointervention. 2012. 02. 7(1):1–9.
Article7. Levy EI, Ecker RD, Horowitz MB, Gupta R, Hanel RA, Sauvageau E, et al. Stent-assisted intracranial recanalization for acute stroke; early results. Neurosurgery. 2006. 03. 58(3):458–463. discussion 458-63.
Article8. Machi P, Costalat V, Lobotesis K, Maldonado IL, Vendrell JF, Riquelme C, et al. Solitaire FR thrombectomy system: immediate results in 56 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012. 01. 4(1):62–66.
Article9. Miteff F, Faulder KC, Goh AC, Steinfort BS, Sue C, Harrington TJ. Mechanical thrombectomy with a self-expanding retrievable intracranial stent (Solitaire AB): experience in 26 patients with acute cerebral artery occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. Jun-Jul. 32(6):1078–1081.10. Nogueira RG, Smith WS. MERCI and Multi MERCI Writing Committee. Safety and efficacy of endovascular thrombectomy in patients with abnormal hemostasis: pooled analysis of the MERCI and multi MERCI trials. Stroke. 2009. 02. 40(2):516–522.11. Papanagiotou P, Roth C, Walter S, Behnke S, Politi M, Fassbender K, et al. Treatment of acute cerebral artery occlusion with a fully recoverable intracranial stent: a new technique. Circulation. 2010. 06. 121(23):2605–2606.12. Rha JH, Saver JL. The impact of recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome; a meta-analysis. stroke. 2007. 03. 38(3):967–973.13. Stampfl S, Hartmann M, Ringleb PA, Haehnel S, Bendszus M, Rohde S. Stent Placement for flow restoration in acute ischemic stroke : a single-center experience with the Solitaire stent system. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. 08. 32(7):1245–1248.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mechanical Thrombectomy Using a Solitaire Stent in Acute Ischemic Stroke; Initial Experience in 40 Patients
- Mechanical Thrombectomy Using a Solitaire Stent in Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Relationship between the Visible Antegrade Flow on First Device Deployment and Final Success in Revascularization
- Safety and Efficacy of Mechanical Thrombectomy with Solitaire Stent Retrieval for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review
- Refinement of a Thrombectomy Technique to Treat Acute Ischemic Stroke: Technical Note on Microcatheter Advance during Retrieving Self-Expandable Stent
- Adjuvant Tirofiban Injection Through Deployed Solitaire Stent As a Rescue Technique After failed Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Stroke