J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2014 Jun;21(2):84-89. 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.2.84.
Generation of Proinflammatory Mediator of Intervertebral Disc Cells by Nicotine Stimulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. doyoun@gmail.com
- KMID: 1800403
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2014.21.2.84
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: Experimental investigation in vitro.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the relationship between the degeneration of intervertebral disc cells, and low back pain induced by degeneration of intervertebral disc cells and increases in use of proinflammatory mediators via nicotine stimulation. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Smoking is a leading cause of degeneration of intervertebral disc cells and low back pain. According to the existing literature, nicotine, one of the main ingredients in cigarettes, causes the degeneration of intervertebral disk cells including decrease of glycoprotein through generation of carboxy-hemoglobin, vasoconstriction, and disability of fibrinolysis and changes of metabolism of nucleus pulposus cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
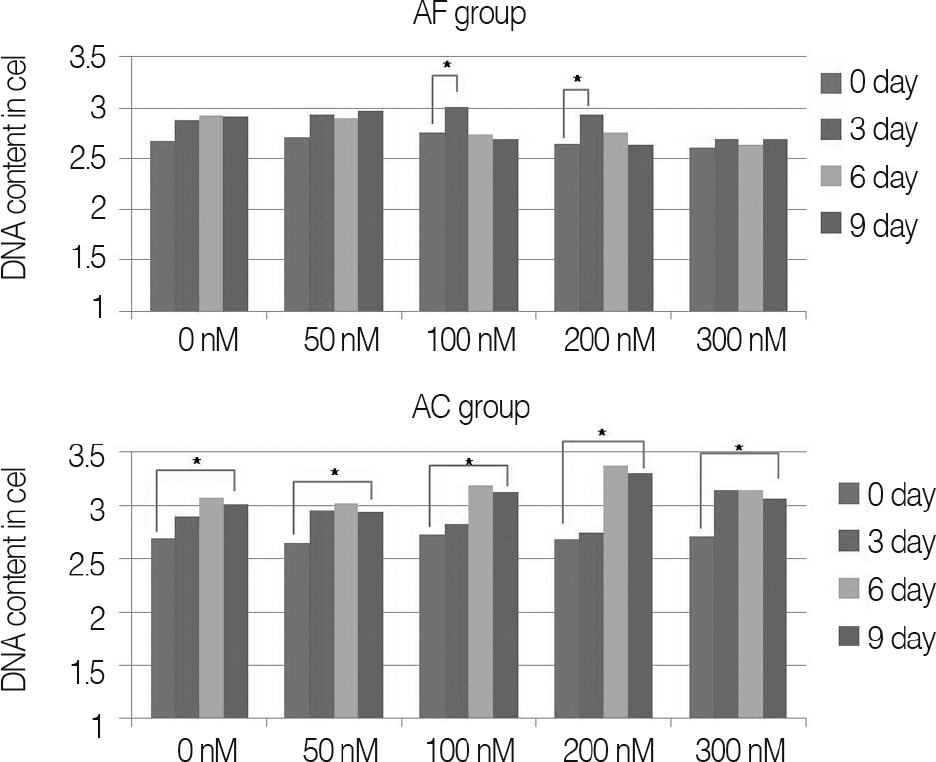
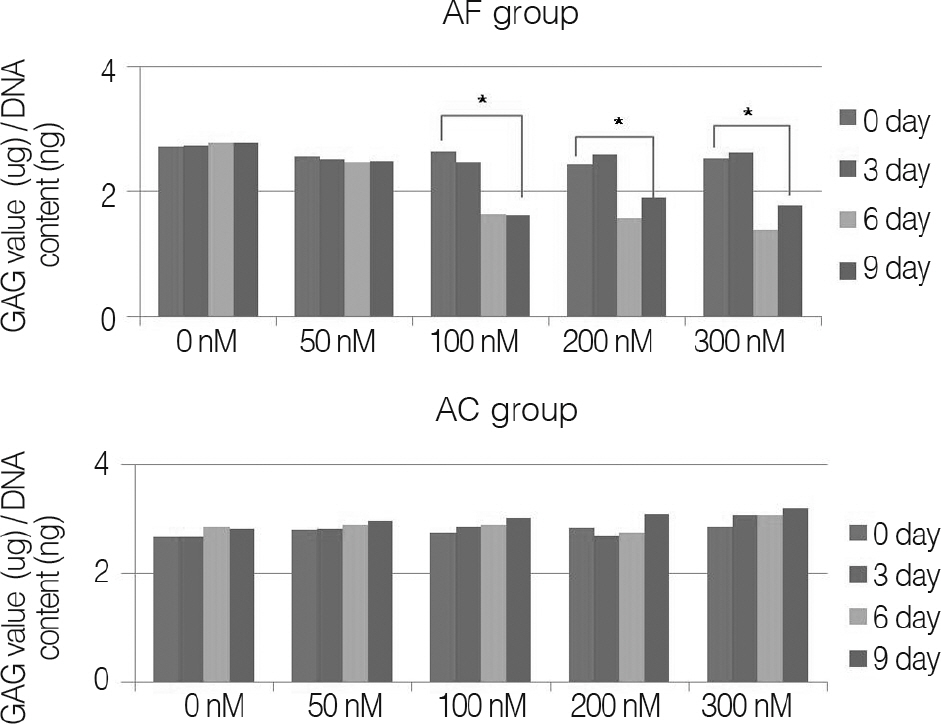
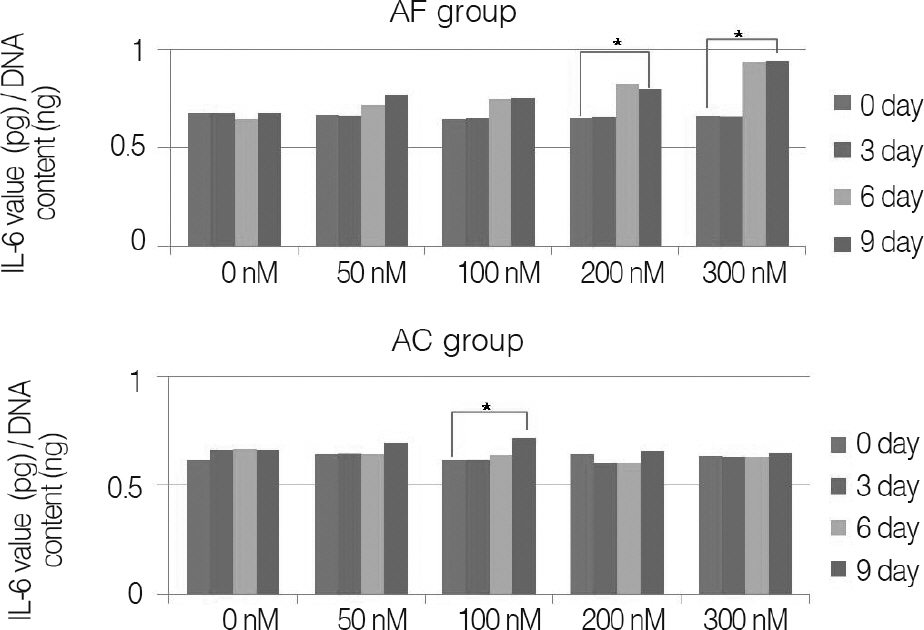
Annulus fibrosus of intervertebral disc and knee joint cartilage were collected from pigs; these cells were acquired by gradual enzyme decomposition. Using Trypan blue, concentration and survival rate of cells were examined; cells were inserted on alginate beads for tertiary cultivation. Nicotine was then applied at 0, 50, 100, 200 and 300 nM, respectively, and the samples were cultivated for three, six and nine days, respectively. After collecting culture fluid, it was measured for interleukin(IL)-1beta, IL-6 and IL-8 with the ELISA Test. DNA of cells used for cultivation was quantitated and the amount of the resulting proinflammatory mediator was normalized. The results were then compared with the result of same study on cartilage of porcine knee joints.
RESULTS
For changes of the inflammatory mediator based on the concentration of nicotine, in nicotine stimulation with low concentration of 50 nM and the control group, there was no significant change, while transient increases of inflammatory mediator showed in nicotine stimulation with concentrations of 100, 200 nM, respectively. There was not a significant increase of IL-1beta observed in all nicotine stimulation groups; these were the same results in porcine cartilage study. The level of IL-6 in 200, 300 nM nicotine concentration showed significant increases, respectively. The level of IL-8 in high dose nicotine stimulation groups also showed significant increases of DNA on the sixth day. And in porcine cartilage study group, significant changes were observed in 200, 300 nM, but the absolute value was lower than that of annulus fibrous cells group.
CONCLUSION
Inflammatory mediators such as IL-6 and IL-8 increased as the result of tertiary cultivation of annulus fibrosus cells of porcine intervertebral disk and nicotine stimulation. It is believed that the cells of the disc annulus are more sensitive than articular chondrocytes to nicotine stimulation. This may be the focus of future long-term studies effects of nicotine other inflammatory cytokines.
MeSH Terms
-
Cartilage
Chondrocytes
Cytokines
DNA
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fibrinolysis
Glycoproteins
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Intervertebral Disc*
Knee Joint
Low Back Pain
Metabolism
Nicotine*
Smoke
Smoking
Survival Rate
Swine
Tobacco Products
Trypan Blue
Vasoconstriction
Cytokines
DNA
Glycoproteins
Interleukin-6
Interleukin-8
Nicotine
Smoke
Trypan Blue
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mooney V. Presidential Address International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine, Dallas, 1986: Where is the pain coming from? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12:754–9.2. Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1307–14.
Article3. Kepler CK, Markova DZ, Dibra F, et al. Expression and relationship of proinflammatory chemokine RANTES/CCL5 and cytokine IL-1β in painful human intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38:873–80.
Article4. He B, Wang YH, Yang J, Peng FL, Li F. Normal and de-generated rabbit nucleus pulposus cells in in vitro cultures: A biological comparison. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013; 33:228–33.
Article5. Chan SC, Bü rki A, Boné l HM, Benneker LM, Gantenbein-Ritter B. Papain-induced in vitro disc degeneration model for the study of injectable nucleus pulposus therapy. Spine J. 2013; 13:273–83.6. Benowitz NL. Drug therapy. Pharmacologic aspects of cigarette smoking and nicotine addition. N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:1318–30.7. Nemoto Y, Matsuzaki H, Tokuhasi Y, et al. Histological changes in intervertebral discs after smoking and cessation: experimental study using a rat passive smoking model. J Orthop Sci. 2006; 11:191–7.8. Oda H, Matsuzaki H, Tokuhashi Y, Wakabayashi K, Uematsu Y, Iwahashi M. Degeneration of intervertebral discs due to smoking: experimental assessment in a rat-smoking model. J Orthop Sci. 2004; 9:135–41.
Article9. Akmal M, Kesani A, Anand B, Singh A, Wiseman M, Goodship A. Effect of nicotine on spinal disc cells: a cellular mechanism for disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:568–75.
Article10. Iwahashi M, Matsuzaki H, Tokuhashi Y, Wakabayashi K, Uematsu Y. Mechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration caused by nicotine in rabbits to explicate intervertebral disc disorders caused by smoking. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:1396–401.
Article11. Uematsu Y, Matuzaki H, Iwahashi M. Effects of nicotine on the intervertebral disc: an experimental study in rabbits. J Orthop Sci. 2001; 6:177–82.
Article12. Shimia M, Babaei-Ghazani A, Sadat BE, Habibi B, Habibzadeh A. Risk factors of recurrent lumbar disk herniation. Asian J Neurosurg. 2013; 8:93–6.
Article13. Haugen AJ, Brox JI, Grøvle L, et al. Prognostic factors for non-success in patients with sciatica and disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012; 13:183.
Article14. Russell MA, Jarvis M, Iyer R, Feyerabend C. Relation of nicotine yield of cigarettes to blood nicotine concentrations in smokers. Br Med J. 1980; 5:972–6.
Article15. Herning RI, Jones RT, Benowitz NL, Mines AH. How a cigarette is smoked determines blood nicotine levels. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983; 33:84–90.
Article16. Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y, Motegi M, Okada Y, Kakiuchi T. Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:218–24.
Article17. Joos H, Wildner A, Hogrefe C, Reichel H, Brenner RE. Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit migration activity of chondrogenic progenitor cells from non-fibrillated osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15:R119.
Article18. Rand N, Reichert F, Floman Y, Rotshenker S. Murine nucleus pulposus-derived cells secrete interleukins-1-beta, -6, and -10 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in cell culture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2598–601.19. Burke JG, G Watson RW, Conhyea D, et al. Human nucleus pulposis can respond to a proinflammatory stimulus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2685–93.
Article20. Sachs D, Cunha FQ, Poole S, Ferreira SH. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta and interleukin-8 induce persistent mechanical nociceptor hypersensitivity. Pain. 2002; 96:89–97.21. Cui GB, An JZ, Zhang N, Zhao MG, Liu SB, Yi J. El-evated interleukin-8 enhances prefrontal synaptic transmission in mice with persistent inflammatory pain. Mol Pain. 2012; 8:11.
Article22. Takada T, Nishida K, Maeno K, et al. Intervertebral disc and macrophage interaction induces mechanical hyperal-gesia and cytokine production in a herniated disc model in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:2601–10.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Biochemical Factors of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Implications for Disc Regeneration
- Spontaneous Total Resolution of Severe Lumbar Disc Herniation
- The Production of Phospholipase A2 in Different Types of Cultured Human Intervertebral Disc Cells
- The Production of Interleukin - 1 and Stromelysin in the Cultured Intervertebral Disc Cells of Rabbit
- Notochordal Cells Influence Gene Expression of Inflammatory Mediators of Annulus Fibrosus Cells in Proinflammatory Cytokines Stimulation