Korean J Gastroenterol.
2009 Jul;54(1):28-35. 10.4166/kjg.2009.54.1.28.
Usefulness and Safety of Extracorporeal Liver Support Therapy Using MARS(R) for Patients with Liver Failure: A Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Cirrhosis Clinical Research Center, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dyk1025@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1792763
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2009.54.1.28
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
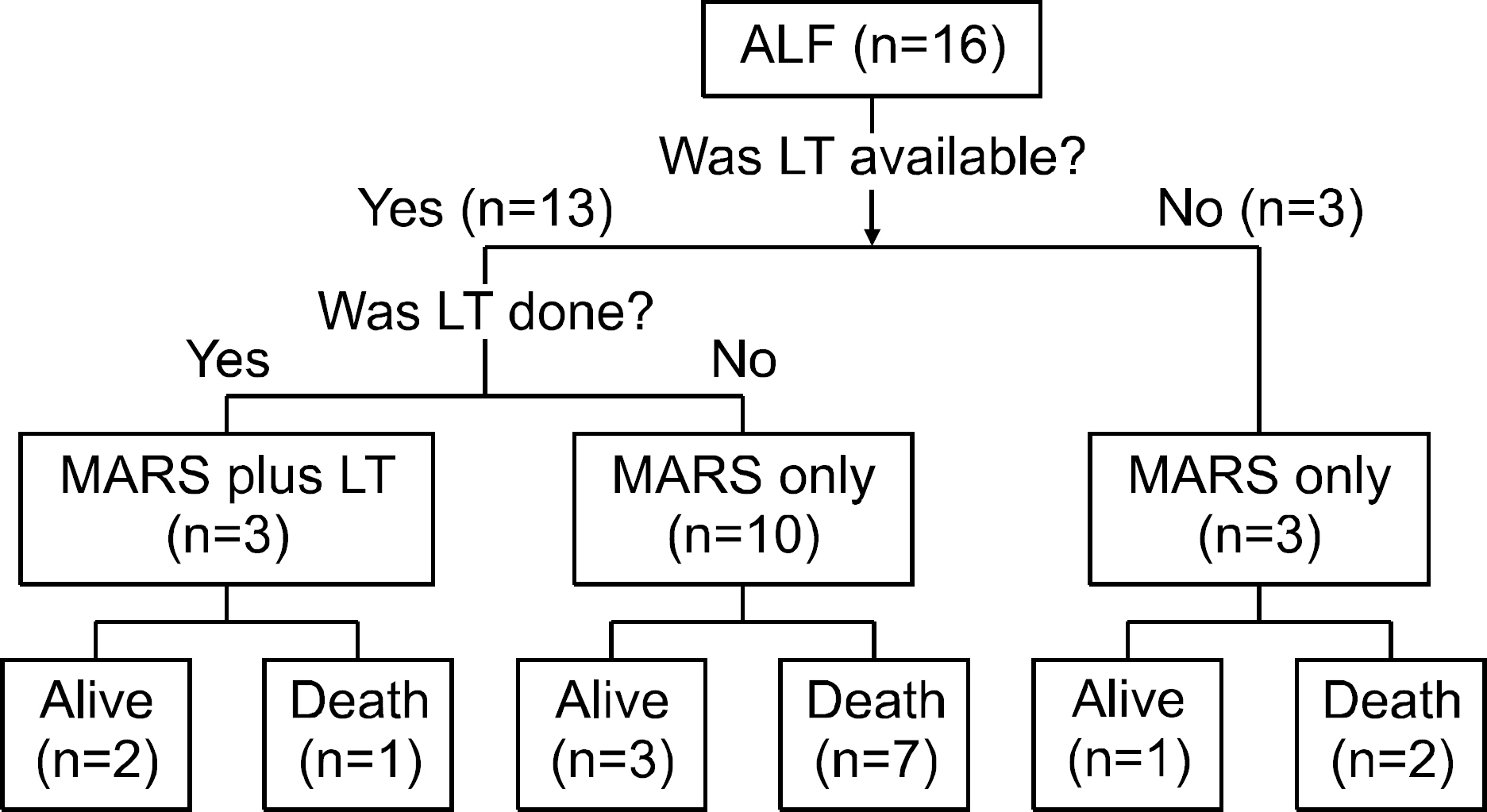
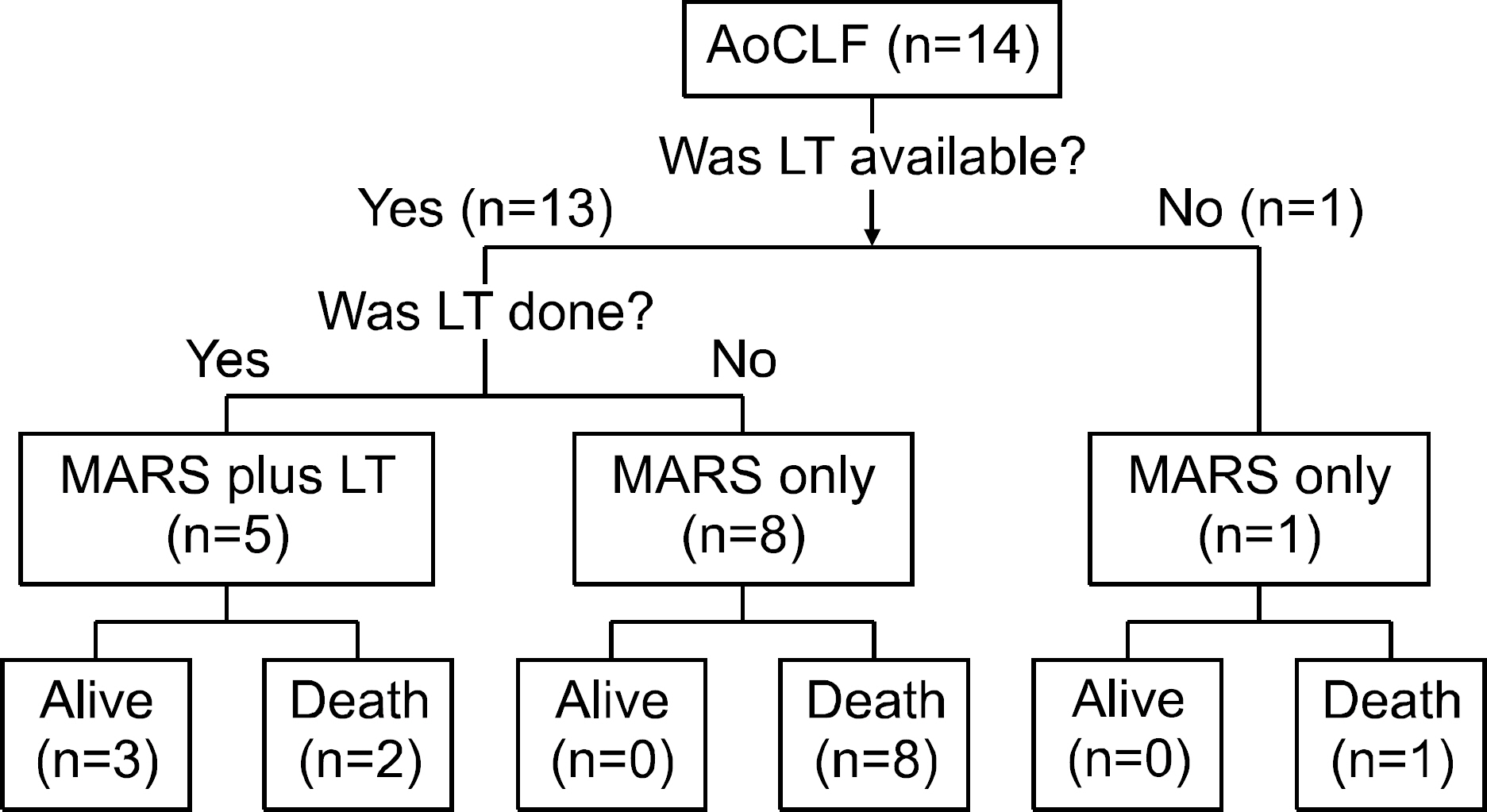
The molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS(R)) is a form of artificial extracorporeal liver support and can be used for a bridge to spontaneous recovery of hepatic function or liver transplantation in patients with liver failure. This study evaluated the usefulness of MARS(R) in patients with liver failure. METHODS: Between January 2004 and July 2007, 30 patients (21 males and 7 females; age 48.9+/-12.9 years) with acute or acute-on-chronic liver failure were managed using MARS(R). We assessed laboratory data, the grade of hepatic encephalopathy, Child-Turcotte-Pugh class, and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score. RESULTS: The number of patients with acute liver failure and acute-on-chronic liver failure was 16 and 14, respectively. The mean cycle of MARS(R) in patients with liver failure was 2.2 sessions. After MARS(R) had been performed, serum total bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), BUN, creatinine, ammonia level, daily urine output, and MELD score were improved (p<0.05). In contrast, MARS(R) failed to improve Child-Turcotte-Pugh score and the grade of hepatic encephalopathy. Liver transplantation was performed in 8 patients. Among them, 5 (62.5%) patients survived and 3 (37.5%) patients died. Twenty two patients underwent MARS(R) without liver transplantation and 4 (18.2%) of them survived. CONCLUSIONS: In patients with liver failure, MARS(R) improved the laboratory data and hepatic and renal function associated clinical characteristics. However, MARS(R) without liver transplantation did not improve survival. MARS(R) may be useful as a bridge therapy to liver transplantation in patients with liver failure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bernal W, Wendon J. Liver transplantation in adults with acute liver failure. J Hepatol. 2004; 40:192–197.
Article2. Allen JW, Hassanein T, Bhatia SN. Advances in bioartificial liver devices. Hepatology. 2001; 34:447–455.
Article3. Sussman NL, Chong MG, Koussayer T, et al. Reversal of fulminant hepatic failure using an extracorporeal liver assist device. Hepatology. 1992; 16:60–65.
Article4. Sosef MN, Abrahamse LS, van de Kerkhove MP, Hartman R, Chamuleau RA, van Gulik TM. Assessment of the AMC-bio-artificial liver in the anhepatic pig. Transplantation. 2002; 73:204–209.5. Stange J, Mitzner S. A carrier-mediated transport of toxins in a hybrid membrane. Safety barrier between a patients blood and a bioartificial liver. Int J Artif Organs. 1996; 19:677–691.
Article6. Schmidt LE, Wang LP, Hansen BA, Larsen FS. Systemic hemodynamic effects of treatment with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with hyperacute liver failure: a prospective controlled trial. Liver Transpl. 2003; 9:290–297.
Article7. Schmidt LE, Sorensen VR, Svendsen LB, Hansen BA, Larsen FS. Hemodynamic changes during a single treatment with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver Transpl. 2001; 7:1034–1039.
Article8. Sen S, Davies NA, Mookerjee RP, et al. Pathophysiological effects of albumin dialysis in acute-on-chronic liver failure: a randomized controlled study. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:1109–1119.
Article9. Heemann U, Treichel U, Loock J, et al. Albumin dialysis in cirrhosis with superimposed acute liver injury: a prospective, controlled study. Hepatology. 2002; 36:949–958.
Article10. Khuroo MS, Farahat KL. Molecular adsorbent recirculating system for acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure: a meta analysis. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:1099–1106.11. Polson J, Lee WM. AASLD position paper: the management of acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2005; 41:1179–1197.
Article12. Sen S, Williams R, Jalan R. The pathophysiological basis of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Liver. 2002; 22(suppl 2):5S–13S.
Article13. Chae HB. Clinical features and diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury. Korean J Hepatol. 2004; 10(suppl 1):7S–18S.14. Atterbury CE, Maddrey WC, Conn HO. Neomycin-sorbitol and lactulose in the treatment of acute portal-systemic encephalopathy. a controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Am J Dig Dis. 1978; 23:398–406.15. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients under-going transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2000; 31:864–871.
Article16. Stange J, Mitzner SR, Risler T, et al. Molecular adsorbent re-cycling system (MARS): clinical results of a new mem-brane-based blood purification system for bioartificial liver support. Artif Organs. 1999; 23:319–330.
Article17. Stefoni S, Coli L, Bolondi L, et al. Molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS) application in liver failure: clinical and hemodepurative results in 22 patients. Int J Artif Organs. 2006; 29:207–218.
Article18. Sen S, Williams R, Jalan R. Emerging indications for albumin dialysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2005; 100:468–475.
Article19. Saliba F. The Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System (MARS) in the intensive care unit: a rescue therapy for patients with hepatic failure. Crit Care. 2006; 10:118.20. Wai CT, Lim SG, Aung MO, et al. MARS: a futile tool in centres without active liver transplant support. Liver Int. 2007; 27:69–75.
Article21. Novelli G, Rossi M, Pretagostini M, et al. One hundred six-teen cases of acute liver failure treated with MARS. Transplant Proc. 2005; 37:2557–2559.
Article22. Kurtovic J, Boyle M, Bihari D, Riordan SM. An Australian experience with the molecular adsorbents recirculating system (Mars). Ther Apher Dial. 2006; 10:2–6.23. Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiodt FV, et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 teriary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 137:947–954.24. Choi JY, Bae SH, Yoon SK, et al. Preconditioning by extracorporeal liver support (MARS) of patients with cirrhosis and severe liver failure evaluated for living donor liver transplantation - a pilot study. Liver Int. 2005; 25:740–745.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two adolescent cases of early use of Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System® for drug-induced fulminant hepatic failure
- Use of the Molecular Adsorbent Recirculating System in Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy: a Case Report
- A Case of Acute Hepatic Failure due to Acetaminophen Overdose Treated with Molecular Adsorbents Recirculating System(R)
- Bleeding complications associated with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system: a retrospective study
- Anesthetic management during the first combined heart-liver transplant performed in Korea: a case report