Korean J Gastroenterol.
2013 Oct;62(4):243-247. 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.4.243.
A Case of Crohn's Disease Accompanied by Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. ismkim@kyuh.co.kr
- KMID: 1792744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2013.62.4.243
Abstract
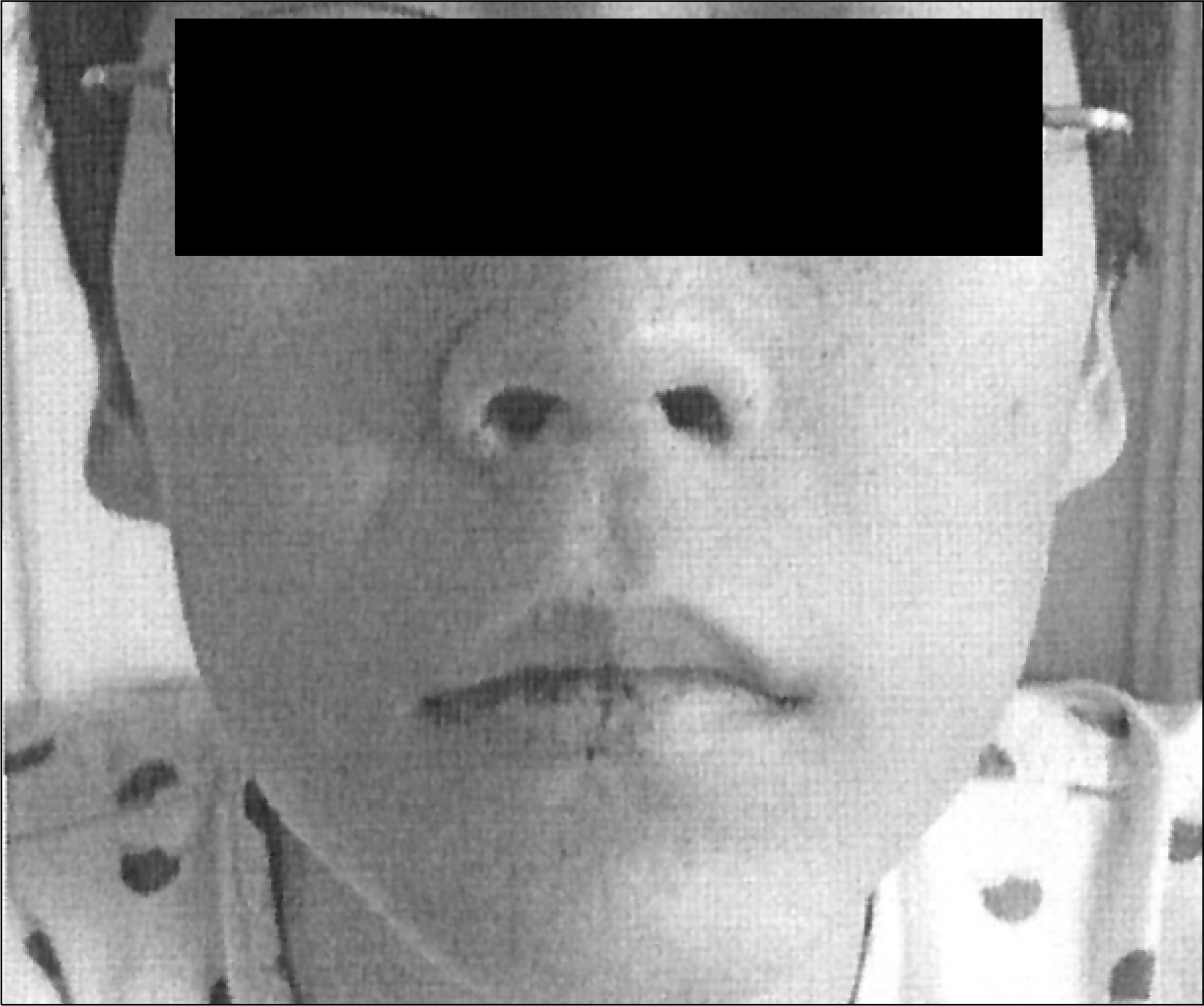
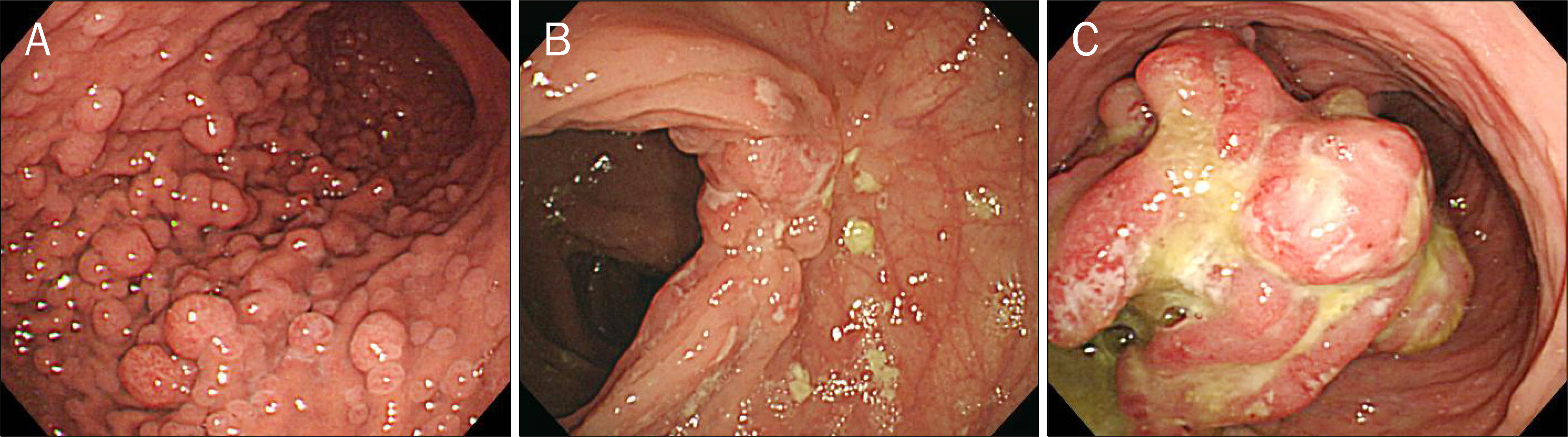
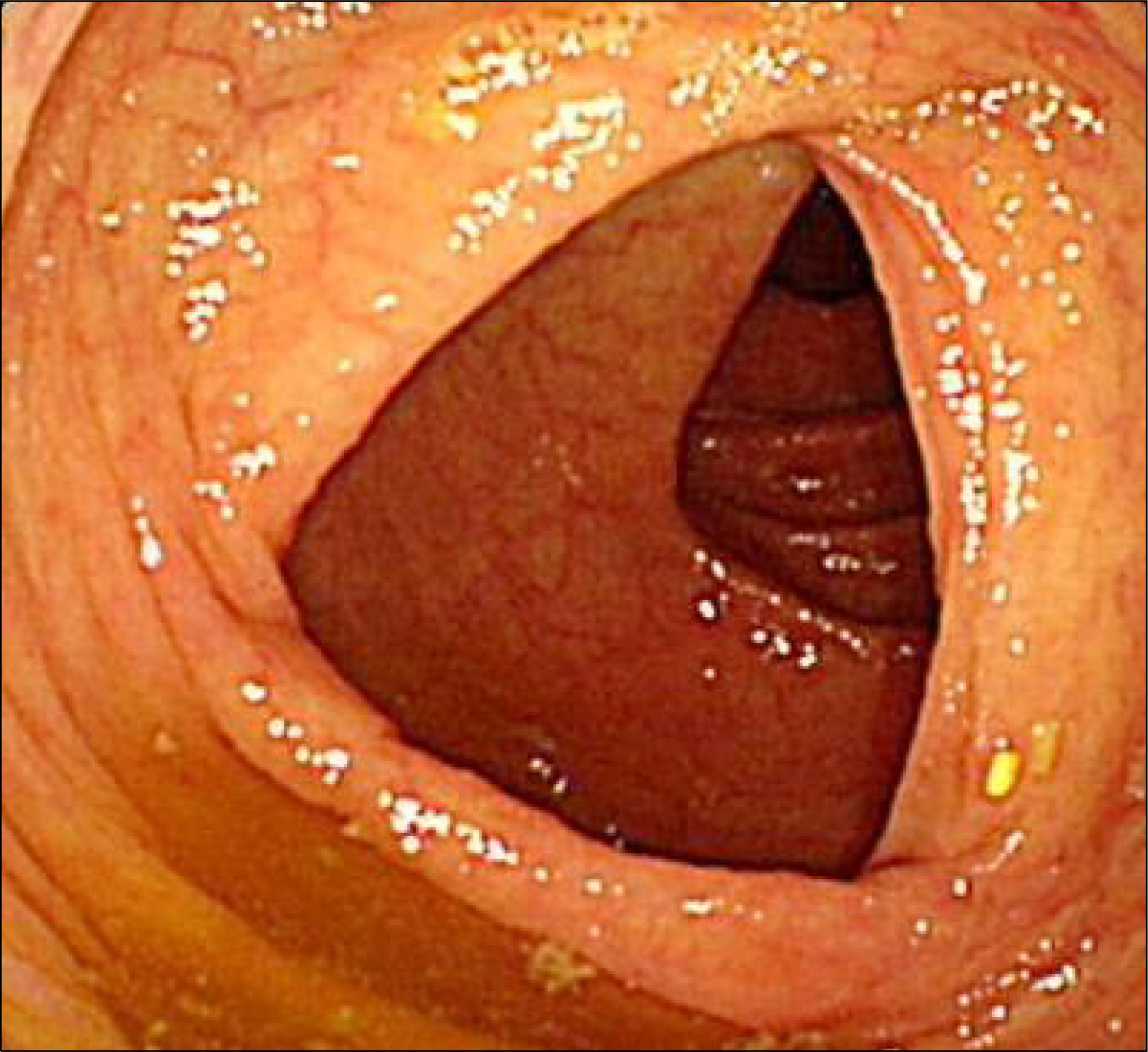
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is an autosomal dominant inherited disorder characterized by multiple gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyps and mucocutaneous pigmentation. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome has an incidence of approximately 1 in 25,000 to 300,000 births. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that typically manifests as regional enteritis with its incidence ranging from 3.1 to 14.6 cases per 100,000 person-years in North America. Herein, we report a case of a 30-year-old male patient who had both Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and Crohn's disease. We believe that this is the first case in Korea and the second report in the English literatures on Peutz-Jeghers syndrome coincidentally accompanied by Crohn's disease.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Crohn Disease/complications/*diagnosis/pathology
Endoscopy, Gastrointestinal
Humans
Intestinal Obstruction/etiology
Intestinal Perforation/etiology
Intestinal Polyps/pathology/surgery
Male
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome/complications/*diagnosis/genetics
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases/genetics
Protein-Serine-Threonine Kinases
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kopacova M, Tacheci I, Rejchrt S, Bures J. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome: diagnostic and therapeutic approach. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:5397–5408.2. Dormandy TL. Gastrointestinal polyposis with mucocutaneous-pigmentation (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome). N Engl J Med. 1957; 256:1093–1103.3. Chang MS, Kim H, Kim WH, et al. Korean Study Group for Pathology of Digestive Disease. Gastrointestinal polyposisin Koreans: a nationwide survey of clinicopathologic analysis of 112 surgically resected cases. Korean J Pathol. 1998; 32:404–412.4. Reid JD. Intestinal carcinoma in the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. JAMA. 1974; 229:833–834.
Article5. Park JB, Yang SK, Myung SJ, et al. Clinical characteristics atdiagnosis and course of Korean patients with Crohn's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 43:8–17.6. Yang SK. Current status and clinical characteristics of inflammatory bowel disease in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2002; 40:1–14.7. Abraham C, Cho JH. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:2066–2078.
Article8. Chung KM, Kim HS, Park SY, et al. The changes in incidence of Crohn's disease and intestinal tuberculosis in Korea. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008; 52:351–358.9. Posselt HG, Kohls C, Ball F, Bender SW. Familial occurrence of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and Crohn disease with manifestation of both diseases in the same patient. Z Gastroenterol. 1985; 23:670–675.