J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Feb;23(1):41-48. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.41.
Overexpression of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 in the Valvular Fibrosis of Chronic Rheumatic Heart Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. luciado@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Ehwa University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1786843
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.1.41
Abstract
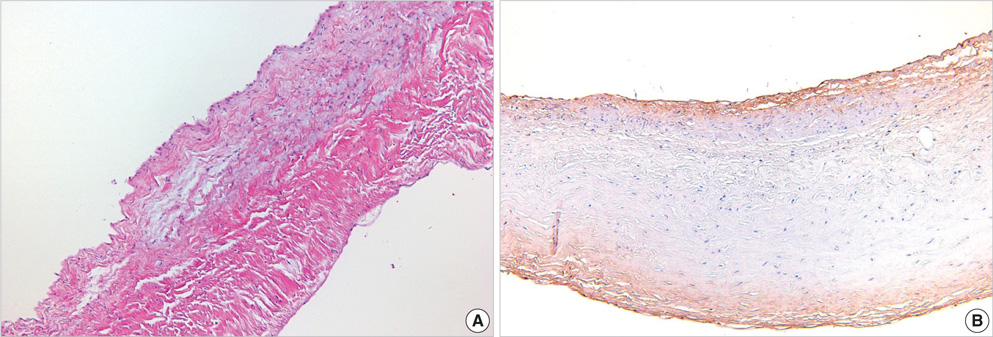
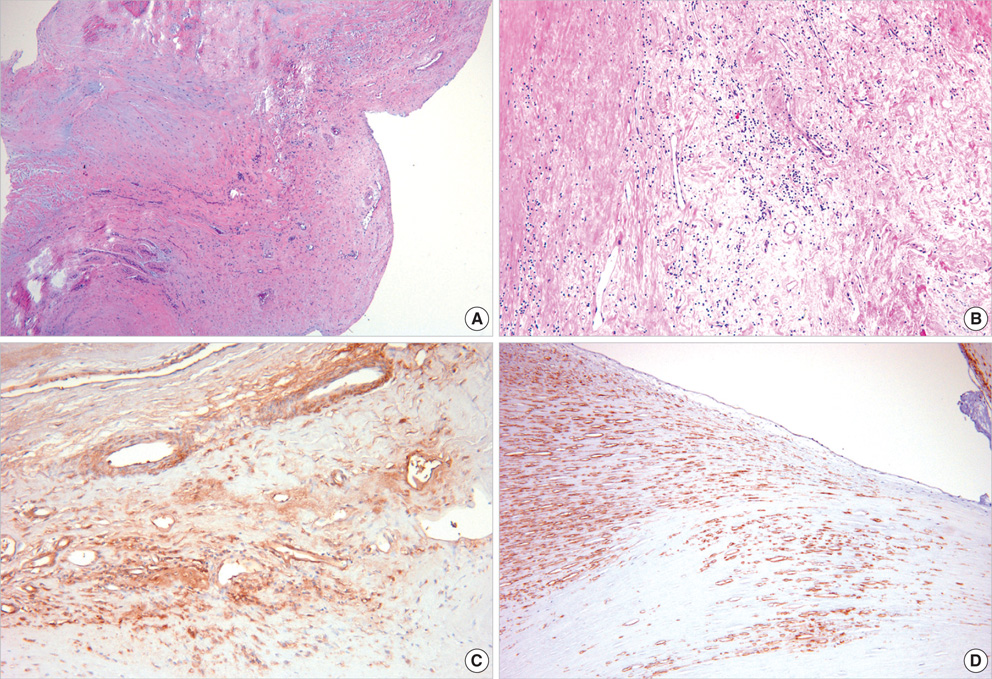
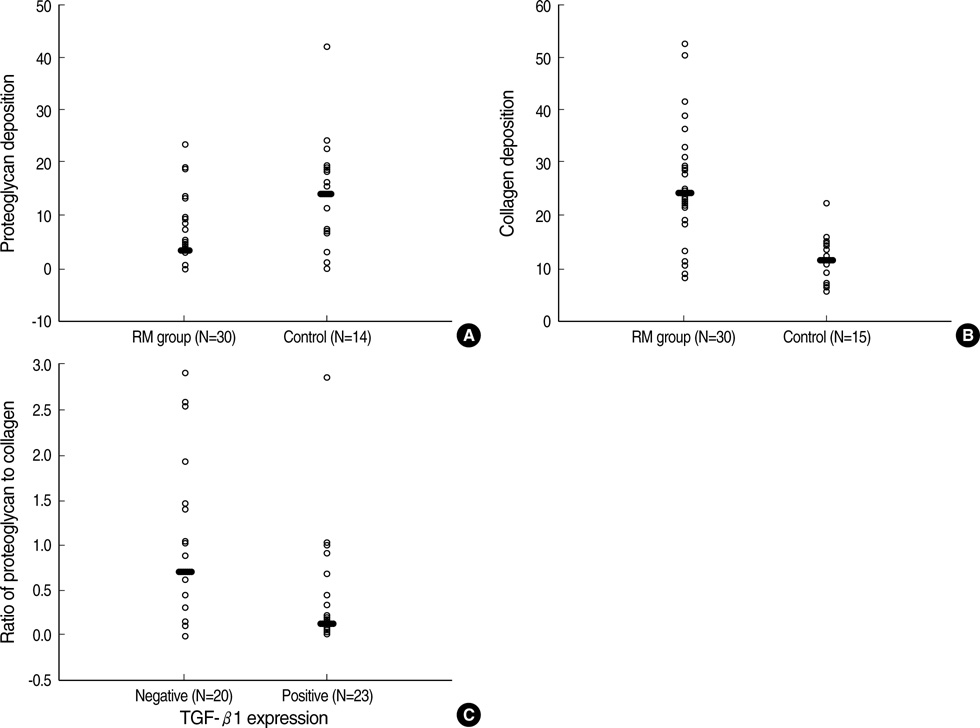
- For the purpose of determining the pathogenic role of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) in the mechanism of chronic rheumatic heart disease, we evaluated the expression of TGF-beta1, proliferation of myofibroblasts, and changes in extracellular matrix components including collagen and proteoglycan in 30 rheumatic mitral valves and in 15 control valves. High TGF-beta1 expression was identified in 21 cases (70%) of rheumatic mitral valves, whereas only 3 cases (20%) of the control group showed high TGF-beta1 expression (p<0.001). Additionally, increased proliferation of myofibroblasts was observed in the rheumatic valves. High TGF-beta1 expression positively correlated with the proliferation of myofibroblasts (p=0.004), valvular fibrosis (p< 0.001), inflammatory cell infiltration (p=0.004), neovascularization (p=0.007), and calcification (p<0.001) in the valvular leaflets. The ratio of proteoglycan to collagen deposition inversely correlated with TGF-beta1 expression in mitral valves (p=0.040). In conclusion, an ongoing inflammatory process, the expression of TGF-beta1, and proliferation of myofibroblasts within the valves have a potential role in the valvular fibrosis, calcification, and changes in the extracellular matrix that lead to the scarring sequelae of rheumatic heart disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schoen FJ. Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T, editors. The heart. Robbins pathologic basis of disease. 1999. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;543–599.
Article2. Rosai J. Rosai J, editor. Cardiovascular system. Ackerman's surgical pathology. 1996. 8th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;2173–2226.3. Veasy LG, Hill HR. Immunologic and clinical correlations in rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997. 16:400–407.
Article4. Kemeny E, Grieve T, Marcus R, Sareli P, Zabriskie JB. Identification of mononuclear cells and T cell subsets in rheumatic valvulitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989. 52:225–237.
Article5. Chen MC, Chang HW, Wu CJ, Yang CH, Yu TH, Chen CJ, Hung WC. Balance between plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 in rheumatic mitral stenosis. Cardiology. 2005. 104:171–175.6. Chiu-Braga YY, Hayashi SY, Schafranski M, Messias-Reason IJ. Further evidence of inflammation in chronic rheumatic valve disease (CRVD): high levels of advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) and high sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP). Int J Cardiol. 2006. 109:275–276.
Article7. Davutoglu V, Celik A, Aksoy M. Contribution of selected serum inflammatory mediators to the progression of chronic rheumatic valve disease, subsequent valve calcification and NYHA functional class. J Heart Valve Dis. 2005. 14:251–256.8. Bhatnagar A, grover A, ganguly NK. Superantigen-induced T cell responses in acute rheumatic fever and chronic rheumatic heart disease patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. 116:100–106.
Article9. Lakos G, Melichian D, Wu M, Varga J. Increased bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis in mice lacking the Th1-specific transcription factor T-bet. Pathobiology. 2006. 73:224–237.
Article10. Kimura T, Ishii Y, Yoh K, Morishima Y, Iizuka T, Kiwamoto T, Matsuno Y, Homma S, Nomura A, Sakamoto T, Takahashi S, Sekizawa K. Overexpression of the transcription factor GATA-3 enhances the development of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 2006. 169:96–104.
Article11. Wen FQ, Liu X, Kobayashi T, Abe S, Fang Q, Kohyama T, Ertl R, Terasaki Y, Manouilova L, Rennard SI. Interferon-gamma inhibits transforming growth factor-beta production in human airway epithelial cells by targeting Smads. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004. 30:816–822.12. Border WA, Noble NA. Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Eng J Med. 1994. 331:1286–1292.13. O'Kane S, Ferguson MW. Transforming growth factor betas and wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. 29:63–78.14. Mutsaers SE, Bishop JE, McGrouther G, Laurent GJ. Mechanisms of tissue repair: from wound healing to fibrosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. 29:5–17.
Article15. Jian B, Connolly J, Savani RC, Narula N, Liang B, Levy R. Serotonin mechanisms in heart valve disease I: Serotonin-induced up-regulation of transforming growth factor-beta1 via G-protein signal transduction in aortic valve interstitial cells. Am J Pathol. 2002. 161:2111–2121.16. Jian B, Narula N, Li QY, Mohler ER 3rd, Levy RJ. Progression of aortic valve stenosis: TGF-β1 is present in calcified aortic valve cusps and promotes aortic valve interstitial cell calcification via apoptosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003. 75:457–465.
Article17. Chou HT, Chen CH, Tsai CH, Tsai FJ. Association between transforming growth factor-beta1 gene C-509T and T869C polymorphisms and rheumatic heart disease. Am Heart J. 2004. 148:181–186.18. Robiolio PA, Rigolin VH, Wilson JS, Harrison JK, Sanders LL, Bashore TM, Feldman JM. Carcinoid heart disease: Correlation of high serotonin levels with valvular abnormalities detected by cardiac catheterization and echocardiography. Circulation. 1995. 92:790–795.19. Ng CM, Cheng A, Myers LA, Martinez-Murillo F, Jie C, Bedja D, Gabrielson KL, Hausladen JM, Mecham RP, Judge DP, Dietz HC. TGFbeta-dependent pathogenesis of mitral valve prolapse in a mouse model of Marfan syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2004. 114:1586–1592.20. Ayoub EM, Toranta A, Bartley TD. Effect of valvular surgery on antibody to the group A streptococcal carbohydrate. Circulation. 1974. 50:144–150.
Article21. Golbasi Z, Ucar O, Keles T, Sahin A, Cagli K, Camsari A, Diker E, Aydogdu S. Increased levels of high sensitive C-reactive protein in patients with chronic rheumatic valve disease: evidence of ongoing inflammation. Eur J Heart Fail. 2002. 4:593–595.22. Guilherme L, Cury P, Demarchi LM, Coelho V, Abel L, Lopez AP, Oshiro SE, Aliotti S, Cunha-Neto E, Pomerantzeff PM, Tanaka AC, Kalil J. Rheumatic heart disease: proinflammatory cytokines play a role in the progression and maintenance of valvular lesions. Am J Pathol. 2004. 165:1583–1591.23. Gorelik L, Flavell RA. Transforming growth factor-beta in T-cell biology. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002. 2:46–53.24. Walker GA, Masters KS, Shah DN, Anseth KS, Leinwand LA. Valvular myofibroblast activation by transforming growth factor-beta: implications for pathological extracellular matrix remodeling in heart valve disease. Circ Res. 2004. 95:253–260.25. Lijnen P, Petrov V. Transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced collagen production in cultures of cardiac fibroblasts is the result of the appearance of myofibroblasts. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2002. 24:333–344.
Article26. Khan R, Sheppard R. Fibrosis in heart disease: understanding the role of transforming growth factor-β1 in cardiomyopathy, valvular disease and arrhythmia. Immunology. 2006. 118:10–24.27. Lis Y, Burleigh MC, Parker DJ, Child AH, Hogg J, Davies MJ. Biochemical characterization of individual normal, floppy and rheumatic human mitral valves. Biochem J. 1987. 244:597–603.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significant fibrosis after radiation therapy in a patient with Marfan syndrome
- TGF-beta-activated kinase-1: New insights into the mechanism of TGF-beta signaling and kidney disease
- Smads as therapeutic targets for chronic kidney disease
- Effects of TGF-beta1 Ribbon Antisense on CCl4-induced Liver Fibrosis
- Expression of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 mRNA in Hepatocelluar Carcinoma and Surrounding Liver