J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Dec;22(6):1042-1047. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.1042.
Erythropoietin Attenuates Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury by Down-modulating Inflammation in Neonatal Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea. wspark@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 1785767
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.6.1042
Abstract
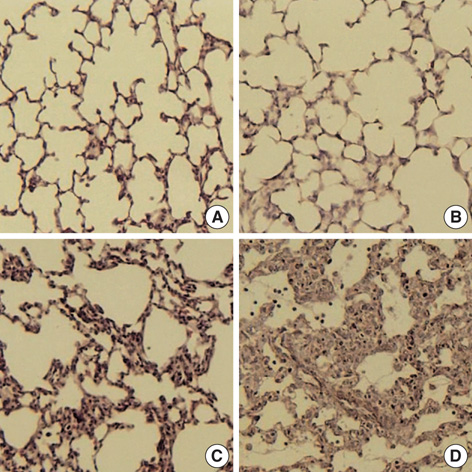
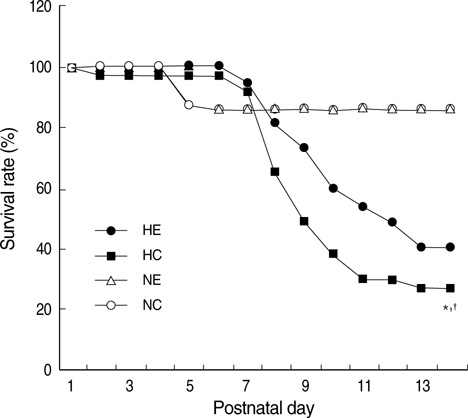
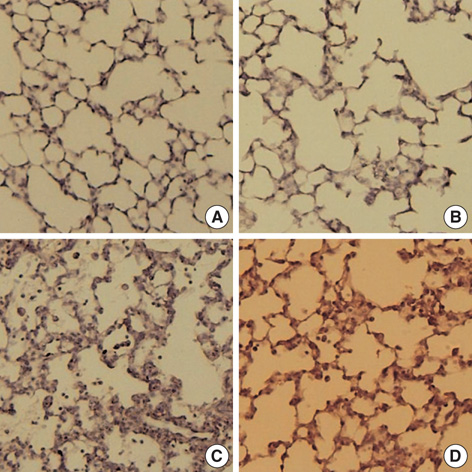
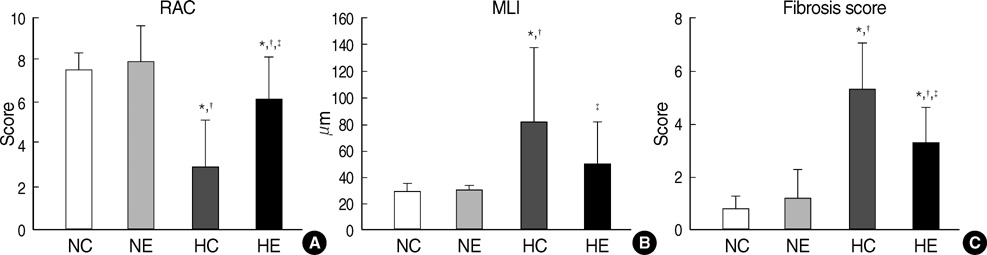
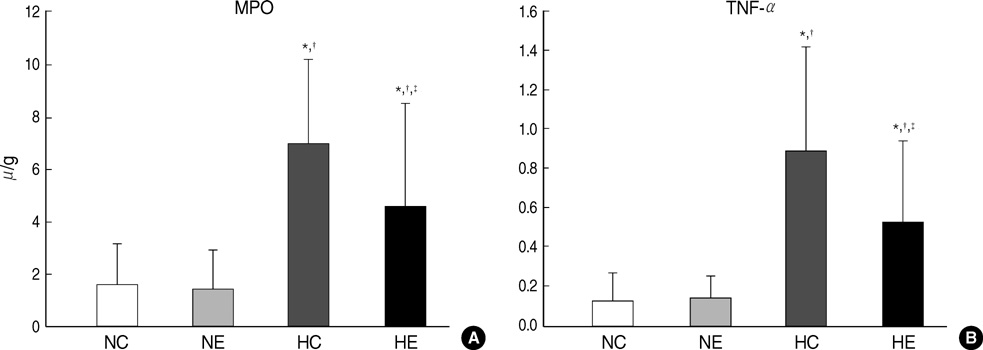
- This study was done to determine whether recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) treatment could attenuate hyperoxia-induced lung injury, and if so, whether this protective effect is mediated by the down-modulation of inflammation in neonatal rats. Newborn Sprague Dawley rat pups were subjected to 14 days of hyperoxia (>95% oxygen) within 10 hr after birth. Treatment with rhEPO significantly attenuated the mortality and reduced body weight gain caused by hyperoxia. With rhEPO treatment, given 3 unit/gm intraperitoneally at 4th, 5th, and 6th postnatal day, hyperoxia- induced alterations in lung pathology such as decreased radial alveolar count, increased mean linear intercept, and fibrosis were significantly improved, and the inflammatory changes such as myeloperoxidase activity and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression were also significantly attenuated. In summary, rhEPO treatment significantly attenuated hyperoxia-induced lung injury by down-modulating the inflammatory responses in neonatal rats.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jobe AH, Ikegami M. Prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2001. 13:124–129.
Article2. Northway WH Jr, Rosan RC, Porter DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967. 276:357–368.3. Kunig AM, Balasubramaniam V, Markham NE, Morgan D, Montgomery G, Grover TR, Abman SH. Recombinant human VEGF treatment enhances alveolarization after hyperoxic lung injury in neonatal rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005. 289:L529–L535.
Article4. Ozer EA, Kumral A, Ozer E, Duman N, Yilmaz O, Ozkal S, Ozkan H. Effect of retinoic acid on oxygen-induced lung injury in the newborn rat. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005. 39:35–40.
Article5. Jobe AH, Ikegami M. Mechanisms initiating lung injury in the preterm. Early Hum Dev. 1998. 53:81–94.
Article6. Merritt TA, Cochrane CG, Holcomb K, Bohl B, Hallman M, Strayer D, Edwards DK 3rd, Gluck L. Elastase and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor activity in tracheal aspirates during respiratory distress syndrome. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Clin Invest. 1983. 72:656–666.
Article7. Yi M, Jankov RP, Belcastro R, Humes D, Copland I, Shek S, Sweezey NB, Post M, Albertine KH, Auten RL, Tanswell AK. Opposing effects of 60% oxygen and neutrophil influx on alveologenesis in the neonatal rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 170:1188–1196.
Article8. Lindsay L, Oliver SJ, Freeman SL, Josien R, Krauss A, Kaplan G. Modulation of hyperoxia-induced TNF-alpha expression in the newborn rat lung by thalidomide and dexamethasone. Inflammation. 2000. 24:347–356.9. Wherry JC, Pennington JE, Wenzel RP. Tumor necrosis factor and the therapeutic potential of anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies. Crit Care Med. 1993. 21:Suppl 10. S436–S440.
Article10. Gibbs LS, Lai L, Malik AB. Tumor necrosis factor enhances the neutrophil-dependent increase in endothelial permeability. J Cell Physiol. 1990. 145:496–500.
Article11. Juul SE. Nonerythropoietic roles of erythropoietin in the fetus and neonate. Clin Perinatol. 2000. 27:527–541.
Article12. Ohls RK. The use of erythropoietin in neonates. Clin Perinatol. 2000. 27:681–696.
Article13. Ozer EA, Kumral A, Ozer E, Yilmaz O, Duman N, Ozkal S, Koroglu T, Ozkan H. Effects of erythropoietin on hyperoxic lung injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 2005. 58:38–41.
Article14. Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R, Mazzon E, Patel NS, Genovese T, Muia C, Crisafulli C, Caputi AP, Thiemermann C. Erythropoietin reduces the development of nonseptic shock induced by zymosan in mice. Crit Care Med. 2006. 34:1168–1177.
Article15. Villa P, Bigini P, Mennini T, Agnello D, Laragione T, Cagnotto A, Viviani B, Marinovich M, Cerami A, Coleman TR, Brines M, Ghezzi P. Erythropoietin selectively attenuates cytokine production and inflammation in cerebral ischemia by targeting neuronal apoptosis. J Exp Med. 2003. 198:971–975.
Article16. Agnello D, Bigini P, Villa P, Mennini T, Cerami A, Brines ML, Ghezzi P. Erythropoietin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on the CNS in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2002. 952:128–134.
Article17. Cooney TP, Thurlbeck WM. The radial alveolar count method of Emery and Mithal: a reappraisal 1--postnatal lung growth. Thorax. 1982. 37:572–579.
Article18. Cooney TP, Thurlbeck WM. The radial alveolar count method of Emery and Mithal: a reappraisal 2--intrauterine and early postnatal lung growth. Thorax. 1982. 37:580–583.
Article19. Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol. 1988. 41:467–470.
Article20. Gray KD, Simovic MO, Chapman WC, Blackwell TS, Christman JW, May AK, Parman KS, Stain SC. Endotoxin potentiates lung injury in cerulein-induced pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 2003. 186:526–530.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cell Division Cycle 2 Protects Neonatal Rats Against Hyperoxia-Induced Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Intratracheal Administration of Endotoxin Attenuates Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats
- Fetal Alveolar Type II Cell Injury Induced by Short-term Exposure to Hyperoxia
- Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor Attenuates Hyperoxia-Induced Lung Injury by Down-Modulating Inflammatory Responses in Neonatal Rats
- Development of Lung Injury and Change in Hyaluronan of Extracellular Matrix by the Effect of Hyperoxia in Neonatal Rat