J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Feb;19(1):15-20. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.1.15.
Epidemiology of Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhi Infections in Korea for Recent 9 Years: Trends of Antimicrobial Resistance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. paihj@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Division of Infectious Diseases, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Enteric Infections, Korean National Institute of Health, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1785687
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.1.15
Abstract
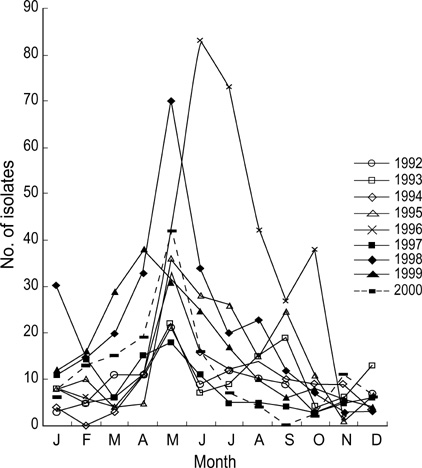
- The aim of this study is to characterize the epidemiological features of typhoid fever, categorized as class 1 notifiable disease in Korea and to analyze the recent change of antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi isolated nationwide. We retrospectively analyzed the 1,692 culture-proven cases from 1992 to 2000, using the data of the Korean National Institute of Health. The overall incidence of culture-proven typhoid fever was 0.41 per 100,000 population. It occurred all over the country, but the southeastern part of Korean peninsula had the higher incidence rate than other areas. There were several outbreaks suspected, of which two outbreaks were confirmed. The resistance rate against chloramphenicol showed mild increase, but the ampicillin, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, kanamycin, or nalidixic acid resistance remained at the similar levels for the past 9 yr. There were 21 (1.3%) multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains isolated since 1992, and the number of those has increased. Two strains resistant to ciprofloxacin were first identified in Korea.
MeSH Terms
-
Ampicillin/pharmacology
Anti-Bacterial Agents/pharmacology
Chloramphenicol/pharmacology
*Drug Resistance, Microbial
Drug Resistance, Multiple
Human
Kanamycin/pharmacology
Korea
Nalidixic Acid/pharmacology
Retrospective Studies
Salmonella Infections/*epidemiology
Salmonella enterica/*metabolism
Seasons
Serotyping
Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Time Factors
Trimethoprim/pharmacology
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Trends in Childhood Bacterial Infectious Diseases in the Republic of Korea
Young June Choe, Hoan Jong Lee
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(6):468-473. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.6.468.Guideline for the Antibiotic Use in Acute Gastroenteritis
Youn Jeong Kim, Ki-Ho Park, Dong-Ah Park, Joonhong Park, Byoung Wook Bang, Seung Soon Lee, Eun Jung Lee, Hyo-Jin Lee, Sung Kwan Hong, Yang Ree Kim
Infect Chemother. 2019;51(2):217-243. doi: 10.3947/ic.2019.51.2.217.
Reference
-
1. Hart CA, Kariuki S. Antimicrobial resistance in developing countries. Br Med J. 1998. 317:647–650.
Article2. Rowe B, Ward LR, Threlfall EJ. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhi: a worldwide epidemic. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. 24:Suppl 1. S106–S109.
Article3. Herikstad H, Hayes P, Mokhtar M, Fracaro ML, Threlfall EJ, Angulo FJ. Emerging quinolone-resistant Salmonella in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997. 3:371–372.
Article4. Threlfall EJ, Ward LR, Skinner JA, Smith HR, Lacey S. Ciprofloxacin-resistant Salmonella typhi and treatment failure. Lancet. 1999. 353:1590–1591.
Article5. Communicable Dieases Monthly Report. 1990. Seoul: The Korean National Institute of Health;28–29.6. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility test. Standards NCfCL. 1984. Vol. 4:369–406.7. Kim HH, Park MS, Kim SH, Yu JY, Chung BK, Lee BK. Epidemiological characteristics of Salmonella strains isolated in Korea in 1997. Korean J Vet Public Health. 1998. 22:253–260.8. Armitage P, Berry G. Statistical methods in medical research. 1994. Oxford; Boston: Blackwell Scientific Publications.9. Shin HR, Suh BS, Song JB, Lee DH, Lee MB, Park JH, Kim MS, Shin YH, Lee SW, Ohrr HC. An epidemiological investigation of typhoid fever outbreak in Pusan, 1996. Korean J Epidemiol. 1997. 19:122–130.10. Lee DS, Oh HT, Han DH, Ann BY, Kim SH, Kim KW, Kim YS, Park MS. A clinical and epidemiological analysis on an outbreak of typhoid fever during 1996 summer through autumn in Chunju area. Korean J Infect Dis. 1998. 30:54–60.11. Pai H, Byeon JH, Yu S, Lee BK, Kim S. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi strains isolated in Korea containing a multidrug resistance class 1 integron. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:2006–2008.
Article12. Kim J. Health and Diseases of Korean People. 2001. Seoul, Korea: SinGwang Publishing Co..13. Shin E. Estimation of reporting rate of notifiable acute communicable diseases and characteristics related to reporting in Korea. J Catholic Medical College. 1996. 49:1197–1209.14. Ackers ML, Puhr ND, Tauxe RV, Mintz ED. Laboratory-based surveillance of Salmonella serotype Typhi infections in the United States: antimicrobial resistance on the rise. JAMA. 2000. 283:2668–2673.15. Threlfall EJ, Ward LR. Decreased susceptibility to ciprofloxacin in Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, United Kingdom. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001. 7:448–450.16. Pillai PK, Prakash K. Current status of drug resistance & phage types of Salmonella typhi in India. Indian J Med Res. 1993. 97:154–158.17. Chitnis V, Chitnis D, Verma S, Hemvani N. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhi in India. Lancet. 1999. 354:514–515.
Article18. Hampton MD, Ward LR, Rowe B, Threlfall EJ. Molecular fingerprinting of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi. Emerg Infect Dis. 1998. 4:317–320.
Article19. Mirza S, Kariuki S, Mamun KZ, Beeching NJ, Hart CA. Analysis of plasmid and chromosomal DNA of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi from Asia. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:1449–1452.
Article20. Shanahan PM, Jesudason MV, Thomson CJ, Amyes SG. Molecular analysis of and identification of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical isolates of Salmonella typhi from India. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:1595–1600.
Article21. Connerton P, Wain J, Hien TT, Ali T, Parry C, Chinh NT, Vinh H, Ho VA, Diep TS, Day NP, White NJ, Dougan G, Farrar JJ. Epidemic typhoid in Vietnam: molecular typing of multiple-antibiotic-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi from four outbreaks. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. 38:895–897.22. Thong KL, Puthucheary S, Yassin RM, Sudarmono P, Padmidewi M, Soewandojo E, Handojo I, Sarasombath S, Pang T. Analysis of Salmonella typhi isolates from Southeast Asia by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. 33:1938–1941.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Salmonella Serovars from Foodborne and Waterborne Diseases in Korea, 1998-2007: Total Isolates Decreasing Versus Rare Serovars Emerging
- Prevalence of Salmonella enterica and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in zoo animals from Chile
- The Serogroup and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella spp. Isolated from the Clinical Specimens During 6 years in a Tertiary University Hospital
- A case of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi endocarditis with multiple splenic infarctions
- A Case of Typhoid Fever to Failed Ciprofloxacin, Infected in Korea