Infect Chemother.
2008 Jun;40(3):175-178. 10.3947/ic.2008.40.3.175.
A Case of Typhoid Fever to Failed Ciprofloxacin, Infected in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drjwchung@gmail.com
- KMID: 1782292
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2008.40.3.175
Abstract
- Typhoid fever caused by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. typhi) and usually ciprofloxacin is first used for treatment. However, the incidence of fluoroquinolone resistance or reduced susceptibility in S. typhi has been increased in Asia over the past decade and there have been reports of failed treatment with ciprofloxacin. Recently, if typhoid fever does not improved with ciprofloxacin treatment, S. typhi with reduced susceptibility to ciprofloxacin should be considered. We experienced a case of nalidixic acid-resistant S. typhi infection that was refractory to treatment with ciprofloxacin in Korea. A 47-year-old woman presented with fever and headache for 14 days. Blood culture revealed the presence of S. typhi that was susceptible to ciprofloxacin. However, she remained feverish and new symptoms of abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea developed after 5 days treatment with ciprofloxacin and subsequent testing showed that isolate was resistant to nalidixic acid.
MeSH Terms
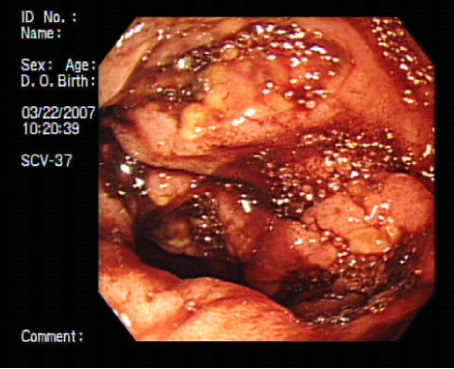
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Infections
Infect Chemother. 2010;42(6):323-361. doi: 10.3947/ic.2010.42.6.323.
Reference
-
1. Cao XT, Kneen R, Nguyen TA, Truong DL, White NJ, Parry CM. A comparative study of ofloxacin and cefixime for treatment of typhoid fever in children. The Dong Nai Pediatric Center Typhoid Study Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1999. 18:245–248.2. Smith MD, Duong NM, Hoa NT, Wain J, Ha HD, Diep TS, Day NP, Hien TT, White NJ. Comparison of ofloxacin and ceftriaxone for short-course treatment of enteric fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994. 38:1716–1720.
Article3. Hoa NT, Diep TS, Wain J, Parry CM, Hien TT, Smith MD, Walsh AL, White NJ. Community-acquired septicaemia in southern Viet Nam: the importance of multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhi. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1998. 92:503–508.
Article4. Lewis MD, Serichantalergs O, Pitarangsi C, Chuanak N, Mason CJ, Regmi LR, Pandey P, Laskar R, Shrestha CD, Malla S. Typhoid fever: a massive, single-point source, multidrug-resistant outbreak in Nepal. Clin Infect Dis. 2005. 40:554–561.
Article5. Parry CM. The treatment of multidrug-resistant and nalidixic acid-resistant typhoid fever in Viet Nam. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2004. 98:413–422.
Article6. Walia M, Gaind R, Mehta R, Paul P, Aggarwal P, Kalaivani M. Current perspectives of enteric fever: a hospital-based study from India. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2005. 25:161–174.
Article7. Park JE, Chung MH, Lee JS, Kim JJ. An imported case of typhoid fever refractory to ciprofloxacin treatment. Infect Chemother. 2007. 39:46–49.8. Wain J, Hoa NT, Chinh NT, Vinh H, Everett MJ, Diep TS, Day NP, Solomon T, White NJ, Piddock LJ, Parry CM. Quinolone-resistant Salmonella typhi in Viet Nam: molecular basis of resistance and clinical response to treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. 25:1404–1410.
Article9. Asna SM, Haq JA, Rahman MM. Nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi with decreased susceptibility to ciprofloxacin caused treatment failure: a report from Bangladesh. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2003. 56:32–33.10. Kadhiravan T, Wig N, Kapil A, Kabra SK, Renuka K, Misra A. Clinical outcomes in typhoid fever: adverse impact of infection with nalidixic acid-resistant Salmonella typhi. BMC Infect Dis. 2005. 5:37.
Article11. Slinger R, Desjardins M, McCarthy AE, Ramotar K, Jessamine P, Guibord C, Toye B. Suboptimal clinical response to ciprofloxacin in patients with enteric fever due to Salmonella spp. with reduced fluoroquinolone susceptibility: a case series. BMC Infect Dis. 2004. 4:36.
Article12. Crump JA, Barrett TJ, Nelson JT, Angulo FJ. Reevaluating fluoroquinolone breakpoints for Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi and for non-Typhi salmonellae. Clin Infect Dis. 2003. 37:75–81.
Article13. Rahman M, Siddique AK, Shoma S, Rashid H, Salam MA, Ahmed QS, Nair GB, Breiman RF. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi with decreased ciprofloxacin susceptibility in Bangladesh. Epidemiol Infect. 2006. 134:433–438.
Article14. Poutanen S, Low DE. Is it time to change fluoroquinolone MIC breakpoints for Salmonella spp. Clin Microbiol Newsl. 2003. 25:97–102.
Article15. Park SG, Park SK, Jung JH, Jin YH. Antibiotic susceptibility of Salmonella spp. isolated from diarrhea patients in Seoul from 1996 to 2001. J Fd Hyg Safety. 2002. 17:61–70.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three cases of ciprofloxacin treatment failure in imported typhoid fever
- A Case of Icteric Typhoid Hepatitis Complicated with Splenic Infarction
- A Case of Typhoid Fever Complicated by Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Acute Pancreatitis and Hepatitis
- A Case of Bronchitis and Bronchial Dysplasia Associated with Typhoid Fever
- A Case of Bronchitis and Bronchial Dysplasia Associated with Typhoid Fever