Computational Flow Dynamics of the Severe M1 Stenosis Before and After Stenting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. dcsuh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Mechanical Engreering, Dankook University, Yongin, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Molding & Forming Technology Team, KITECH, 7-47, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1783976
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2011.6.1.13
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Computational flow dynamic (CFD) study has not been widely applied in intracranial artery stenosis due to requirement of high resolution in identifying the small intracranial artery. We described a process in CFD study applied to symptomatic severe intracranial (M1) stenosis before and after stenting.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reconstructed 3D angiography in STL format was transferred to Magics (Materialise NV, Leuven, Belgium) for smoothing of vessel surface and trimming of branch vessels and to HyperMesh (Altair Engineering Inc., Auckland, New Zealand) for generating tetra volume mesh from triangular surface-meshed 3D angiogram. Computational analysis of blood flow in the blood vessels was performed using the commercial finite element software ADINA Ver 8.5 (ADINA R & D, Inc., Lebanon, MA). The distribution of wall shear stress (WSS), peak velocity and pressure in a patient was analyzed before and after intracranial stenting.
RESULTS
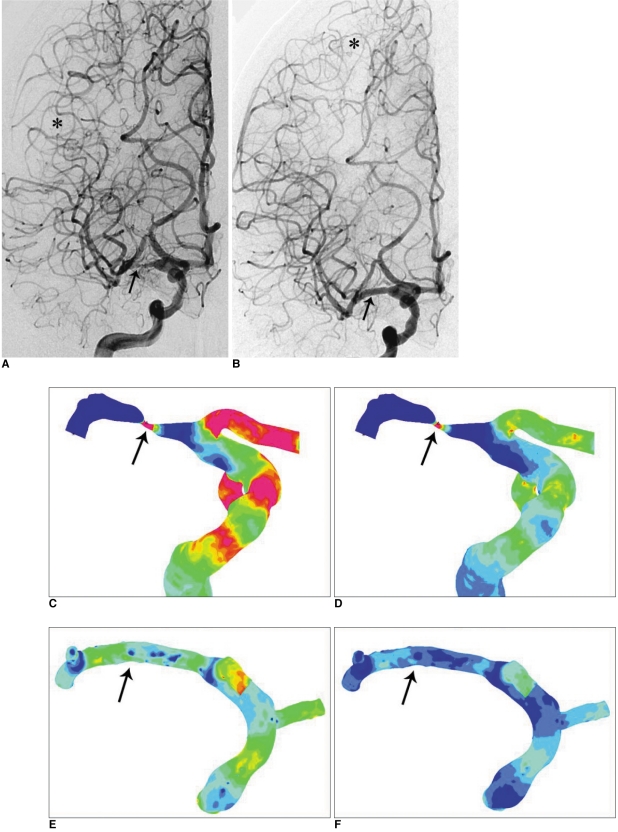
Computer simulation of wall shear stress, flow velocity and wall pressure before and after stenting could be demonstrated three dimensionally by video mode according to flow vs. time dimension. Such flow model was well correlated with angiographic finding related to maximum degree of stenosis. Change of WSS, peak velocity and pressure at the severe stenosis was demonstrated before and after stenting. There was no WSS after stenting in case without residual stenosis.
CONCLUSION
Our study revealed that CFD analysis before and after intracranial stenting was feasible despite of limited vessel wall dimension and could reveal change of WSS as well as flow velocity and wall pressure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
The Use of Protection Device in Landmark-wire Technique of Symptomatic Subclavian Artery Occlusion with Combined Approach via Trans-femoral vs. Trans-brachial Arteries: Technical note
Soonchan Park, Jae Hyuk Kwak, Hye Jin Baek, Jee Won Park, Jong Sung Kim, Dae Chul Suh
Neurointervention. 2011;6(2):89-94. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2011.6.2.89.Mechanism of Procedural Failure Related to Wingspan
Lin-Bo Zhao, Soonchan Park, Donggeun Lee, Deok Hee Lee, Dae Chul Suh
Neurointervention. 2012;7(2):102-108. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2012.7.2.102.Outpatient (Same-day care) Neuroangiography and Neurointervention
Yun-Gyeong Jeong, Eun Hye Kim, Sun Moon Hwang, Ga Young Lee, Jong Woo Kim, Yeong Jun Choi, Jae-Hyuk Kwak, Dae Chul Suh
Neurointervention. 2012;7(1):17-22. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2012.7.1.17.Computational Modeling with Fluid-Structure Interaction of the Severe M1 Stenosis Before and After Stenting
Soonchan Park, Sang-Wook Lee, Ok Kyun Lim, Inki Min, Minhtuan Nguyen, Young Bae Ko, Kyunghwan Yoon, Dae Chul Suh
Neurointervention. 2013;8(1):23-28. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2013.8.1.23.Long-term Outcomes of Drug-eluting Stents in Symptomatic Intracranial Stenosis
Soonchan Park, Dong-geun Lee, Won-Jung Chung, Deok Hee Lee, Dae Chul Suh
Neurointervention. 2013;8(1):9-14. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2013.8.1.9.Considerations of Blood Properties, Outlet Boundary Conditions and Energy Loss Approaches in Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling
Ji Young Moon, Dae Chul Suh, Yong Sang Lee, Young Woo Kim, Joon Sang Lee
Neurointervention. 2014;9(1):1-8. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2014.9.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Suh DC, Lee SH, Kim KR, Park ST, Lim SM, Kim SJ, et al. Pattern of atherosclerotic carotid stenosis in Korean patients with stroke: different involvement of intracranial versus extracranial vessels. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:239–244. PMID: 12591640.2. Gorelick PB, Caplan LR, Hier DB, Parker SL, Patel D. Racial differences in the distribution of anterior circulation occlusive disease. Neurology. 1984; 34:54–59. PMID: 6537853.
Article3. Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q, Zamanillo MC. Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. The northern manhattan stroke study. Stroke. 1995; 26:14–20. PMID: 7839388.4. Suh DC, Kim JK, Choi JW, Choi BS, Pyun HW, Choi YJ, et al. Intracranial stenting of severe symptomatic intracranial stenosis: results of 100 consecutive patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:781–785. PMID: 18310234.
Article5. Choi JW, Kim JK, Choi BS, Lim HK, Kim SJ, Kim JS, et al. Angiographic pattern of symptomatic severe M1 stenosis: comparison with presenting symptoms, infarct patterns, perfusion status, and outcome after recanalization. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010; 29:297–303. PMID: 20090322.
Article6. Suh DC, Sung KB, Cho YS, Choi CG, Lee HK, Lee JH, et al. Transluminal angioplasty for middle cerebral artery stenosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:553–558. PMID: 10319958.7. Groen HC, Gijsen FJ, van der Lugt A, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS, van der Steen AF, et al. Plaque rupture in the carotid artery is localized at the high shear stress region: a case report. Stroke. 2007; 38:2379–2381. PMID: 17615365.8. Malek AM, Alper SL, Izumo S. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. JAMA. 1999; 282:2035–2042. PMID: 10591386.
Article9. Choi JW, Kim JK, Choi BS, Kim JH, Hwang HJ, Kim JS, et al. Adjuvant revascularization of intracranial artery occlusion with angioplasty and/or stenting. Neuroradiology. 2009; 51:33–43. PMID: 18818910.
Article10. Oh TS, Ko YB, Park ST, Yoon KH, Lee SW, Park JW, et al. Computational flow dynamics study in severe carotid bulb stenosis with ulceration. Neurointervention. 2010; 5:97–102.
Article11. Suh DC, Park ST, Oh TS, Park SO, Lim OK, Park SC, et al. High shear stress in systolic phase at the surface of the enhancing plaque is related to symptom presentation of the severe M1 stenosis. Korean J Radiol. 2011; [In press].12. Garrett MC, Komotar RJ, Starke RM, Merkow MB, Otten ML, Sciacca RR, et al. The efficacy of direct extracranial-intracranial bypass in the treatment of symptomatic hemodynamic failure secondary to athero-occlusive disease: a systematic review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009; 111:319–326. PMID: 19201526.
Article13. He Y, Duraiswamy N, Frank AO, Moore JE. Blood flow in stented arteries: a parametric comparison of strut design patterns in three dimensions. J Biomech Eng. 2005; 127:637–647. PMID: 16121534.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Computational Modeling with Fluid-Structure Interaction of the Severe M1 Stenosis Before and After Stenting
- Wingspan Stenting for Symptomatic Severe In-Stent Stenosis of a Closed-Cell Stent after Stent-Assisted Coiling of a Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm
- Evaluation of Local Flow Conditions in Jailed Side Branch Lesions Using Computational Fluid Dynamics
- High Shear Stress at the Surface of Enhancing Plaque in the Systolic Phase is Related to the Symptom Presentation of Severe M1 Stenosis
- Considerations of Blood Properties, Outlet Boundary Conditions and Energy Loss Approaches in Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling