Korean J Hematol.
2011 Jun;46(2):80-87. 10.5045/kjh.2011.46.2.80.
The pathophysiology of chronic graft-versus-host disease: the unveiling of an enigma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ckmin@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1782771
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2011.46.2.80
Abstract
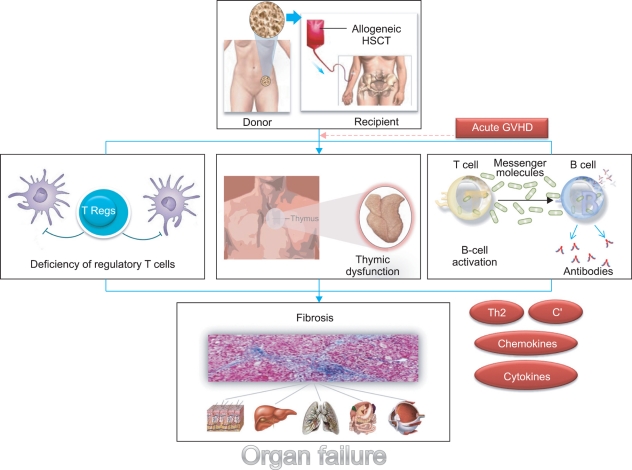
- Chronic graft-versus-host disease (CGVHD) is one of the most significant complications of long-term survivors after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). CGVHD may have protean manifestations and can pose unique diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. New recommendations that emphasize the importance of qualitative differences, as opposed to time of onset after HSCT, are now being used to standardize the diagnosis and clinical assessment of CGVHD, but they require validation. During the past 3 decades, experimental studies and clinical observations have elucidated the mechanisms of acute GVHD, but its biology is much less well-understood. Experimental studies have generated at least 4 theories to explain the pathophysiology of CGVHD: (1) thymic damage and the defective negative selection of T cells, (2) regulatory T cell deficiencies, (3) auto-antibody production by aberrant B cells, and (4) the formation of profibrotic lesions. Mouse models have provided important insights into the pathophysiology of CGVHD, and these have helped improve clinical outcomes following allo-HSCT, but no animal model fully replicates all of the features of CGVHD in humans. In this article, recent clinical changes, the pathogenesis of CGHVD, the cellular and cytokine networks implicated in its pathogenesis, and the animal models used to devise strategies to prevent and treat CGVHD are reviewed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Expression of
SOCS1 andSOCS3 genes in human graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Tae Hyang Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Sohye Park, Seung Hwan Shin, Seung-Ah Yahng, Jae-Ho Yoon, Sung-Eun Lee, Byung-Sik Cho, Yoo-Jin Kim, Seok Lee, Chang-Ki Min, Dong-Wook Kim, Jong-Wook Lee, Woo-Sung Min, Chong-Won Park, Hee-Je Kim
Blood Res. 2013;48(1):16-23. doi: 10.5045/br.2013.48.1.16.Development of Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen Autoantibodies With the Manifestation of Graft Versus Host Disease After Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation
Hyunhye Kang, Seok-Goo Cho, Eun-Jee Oh
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(1):117-119. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.117.
Reference
-
1. Lee SJ, Vogelsang G, Flowers ME. Chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2003; 9:215–233. PMID: 12720215.
Article2. Baird K, Pavletic SZ. Chronic graft versus host disease. Curr Opin Hematol. 2006; 13:426–435. PMID: 17053454.
Article3. Lee SJ, Klein JP, Barrett AJ, et al. Severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease: association with treatment-related mortality and relapse. Blood. 2002; 100:406–414. PMID: 12091329.
Article4. Socié G, Stone JV, Wingard JR, et al. Late Effects Working Committee of the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:14–21. PMID: 10387937.
Article5. Lee SJ, Kim HT, Ho VT, et al. Quality of life associated with acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006; 38:305–310. PMID: 16819438.
Article6. Fraser CJ, Bhatia S, Ness K, et al. Impact of chronic graft-versus-host disease on the health status of hematopoietic cell transplantation survivors: a report from the Bone Marrow Transplant Survivor Study. Blood. 2006; 108:2867–2873. PMID: 16788100.
Article7. Cutler C, Giri S, Jeyapalan S, Paniagua D, Viswanathan A, Antin JH. Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell and bone marrow transplantation: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:3685–3691. PMID: 11504750.
Article8. Schmitz N, Eapen M, Horowitz MM, et al. Long-term outcome of patients given transplants of mobilized blood or bone marrow: a report from the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2006; 108:4288–4290. PMID: 16946302.
Article9. Akpek G, Lee SM, Anders V, Vogelsang GB. A high-dose pulse steroid regimen for controlling active chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001; 7:495–502. PMID: 11669216.
Article10. Arora M, Wagner JE, Davies SM, et al. Randomized clinical trial of thalidomide, cyclosporine, and prednisone versus cyclosporine and prednisone as initial therapy for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2001; 7:265–273. PMID: 11400948.
Article11. Lopez F, Parker P, Nademanee A, et al. Efficacy of mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005; 11:307–313. PMID: 15812396.
Article12. Busca A, Locatelli F, Marmont F, Audisio E, Falda M. Response to mycophenolate mofetil therapy in refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. Haematologica. 2003; 88:837–839. PMID: 12857569.13. Goldberg JD, Jacobsohn DA, Margolis J, et al. Pentostatin for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2003; 25:584–588. PMID: 12847332.
Article14. Carnevale-Schianca F, Martin P, Sullivan K, et al. Changing from cyclosporine to tacrolimus as salvage therapy for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2000; 6:613–620. PMID: 11128811.
Article15. Couriel DR, Hosing C, Saliba R, et al. Extracorporeal photochemotherapy for the treatment of steroid-resistant chronic GVHD. Blood. 2006; 107:3074–3080. PMID: 16368882.
Article16. Couriel DR, Saliba R, Escalón MP, et al. Sirolimus in combination with tacrolimus and corticosteroids for the treatment of resistant chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2005; 130:409–417. PMID: 16042691.
Article17. Foss FM, DiVenuti GM, Chin K, et al. Prospective study of extracorporeal photopheresis in steroid-refractory or steroid-resistant extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease: analysis of response and survival incorporating prognostic factors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005; 35:1187–1193. PMID: 15852025.
Article18. Greinix HT, Volc-Platzer B, Rabitsch W, et al. Successful use of extracorporeal photochemotherapy in the treatment of severe acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 1998; 92:3098–3104. PMID: 9787144.
Article19. Johnston LJ, Brown J, Shizuru JA, et al. Rapamycin (sirolimus) for treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005; 11:47–55. PMID: 15625544.
Article20. Ferrara JL, Levy R, Chao NJ. Pathophysiologic mechanisms of acute graft-vs.-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999; 5:347–356. PMID: 10595812.
Article21. Sullivan KM, Shulman HM, Storb R, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease in 52 patients: adverse natural course and successful treatment with combination immunosuppression. Blood. 1981; 57:267–276. PMID: 7004534.
Article22. Imanguli MM, Alevizos I, Brown R, Pavletic SZ, Atkinson JC. Oral graft-versus-host disease. Oral Dis. 2008; 14:396–412. PMID: 18593456.
Article23. Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005; 11:945–956. PMID: 16338616.24. Arora M, Nagaraj S, Witte J, et al. New classification of chronic GVHD: added clarity from the consensus diagnoses. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009; 43:149–153. PMID: 18794869.
Article25. Cho BS, Min CK, Eom KS, et al. Feasibility of NIH consensus criteria for chronic graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia. 2009; 23:78–84. PMID: 18830253.
Article26. Vigorito AC, Campregher PV, Storer BE, et al. Evaluation of NIH consensus criteria for classification of late acute and chronic GVHD. Blood. 2009; 114:702–708. PMID: 19470693.
Article27. Choi SW, Levine JE, Ferrara JL. Pathogenesis and management of graft-versus-host disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2010; 30:75–101. PMID: 20113888.
Article28. Sprent J, Kishimoto H. The thymus and central tolerance. Transplantation. 2001; 72(8 Suppl):S25–S28. PMID: 11888152.29. Dutt S, Tseng D, Ermann J, et al. Naive and memory T cells induce different types of graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 2007; 179:6547–6554. PMID: 17982043.
Article30. Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Lacey DL, Vallera DA, Blazar BR. Keratinocyte growth factor administered before conditioning ameliorates graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mice. Blood. 1998; 92:3960–3967. PMID: 9808590.
Article31. Blazar BR, Weisdorf DJ, Defor T, et al. Phase 1/2 randomized, placebo-control trial of palifermin to prevent graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Blood. 2006; 108:3216–3222. PMID: 16835378.
Article32. Zhang C, Todorov I, Zhang Z, et al. Donor CD4+ T and B cells in transplants induce chronic graft-versus-host disease with autoimmune manifestations. Blood. 2006; 107:2993–3001. PMID: 16352808.
Article33. Imado T, Iwasaki T, Kataoka Y, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor preserves graft-versus-leukemia effect and T-cell reconstitution after marrow transplantation. Blood. 2004; 104:1542–1549. PMID: 15100150.
Article34. Rieger K, Loddenkemper C, Maul J, et al. Mucosal FOXP3+ regulatory T cells are numerically deficient in acute and chronic GvHD. Blood. 2006; 107:1717–1723. PMID: 16278306.
Article35. Anderson BE, McNiff JM, Matte C, Athanasiadis I, Shlomchik WD, Shlomchik MJ. Recipient CD4+ T cells that survive irradiation regulate chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2004; 104:1565–1573. PMID: 15150080.
Article36. Zorn E, Kim HT, Lee SJ, et al. Reduced frequency of FOXP3+CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2005; 106:2903–2911. PMID: 15972448.37. Clark FJ, Gregg R, Piper K, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host disease is associated with increased numbers of peripheral blood CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells. Blood. 2004; 103:2410–2416. PMID: 14604970.
Article38. Sharma MD, Baban B, Chandler P, et al. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells from mouse tumor-draining lymph nodes directly activate mature Tregs via indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J Clin Invest. 2007; 117:2570–2582. PMID: 17710230.
Article39. Nguyen VH, Zeiser R, Dasilva DL, et al. In vivo dynamics of regulatory T-cell trafficking and survival predict effective strategies to control graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic transplantation. Blood. 2007; 109:2649–2656. PMID: 17095616.
Article40. Di Biaso I, Di Maio L, Bugarin C, et al. Regulatory T cells and extracorporeal photochemotherapy: correlation with clinical response and decreased frequency of proinflammatory T cells. Transplantation. 2009; 87:1422–1425. PMID: 19424046.
Article41. Bastien JP, Krosl G, Therien C, et al. Photodepletion differentially affects CD4+ Tregs versus CD4+ effector T cells from patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2010; 116:4859–4869. PMID: 20798236.
Article42. Hoffmann P, Ermann J, Edinger M, Fathman CG, Strober S. Donor-type CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells suppress lethal acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med. 2002; 196:389–399. PMID: 12163567.
Article43. Giorgini A, Noble A. Blockade of chronic graft-versus-host disease by alloantigen-induced CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in nonlymphopenic hosts. J Leukoc Biol. 2007; 82:1053–1061. PMID: 17684039.44. Chen X, Vodanovic-Jankovic S, Johnson B, Keller M, Komorowski R, Drobyski WR. Absence of regulatory T-cell control of TH1 and TH17 cells is responsible for the autoimmune-mediated pathology in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2007; 110:3804–3813. PMID: 17693581.
Article45. Ratanatharathorn V, Carson E, Reynolds C, et al. Anti-CD20 chimeric monoclonal antibody treatment of refractory immune-mediated thrombocytopenia in a patient with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Ann Intern Med. 2000; 133:275–279. PMID: 10929168.
Article46. Patriarca F, Skert C, Sperotto A, et al. The development of autoantibodies after allogeneic stem cell transplantation is related with chronic graft-vs-host disease and immune recovery. Exp Hematol. 2006; 34:389–396. PMID: 16543073.
Article47. Svegliati S, Olivieri A, Campelli N, et al. Stimulatory autoantibodies to PDGF receptor in patients with extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2007; 110:237–241. PMID: 17363728.
Article48. Sarantopoulos S, Stevenson KE, Kim HT, et al. High levels of B-cell activating factor in patients with active chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:6107–6114. PMID: 17947475.
Article49. Miklos DB, Kim HT, Miller KH, et al. Antibody responses to H-Y minor histocompatibility antigens correlate with chronic graft-versus-host disease and disease remission. Blood. 2005; 105:2973–2978. PMID: 15613541.
Article50. Cutler C, Miklos D, Kim HT, et al. Rituximab for steroid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2006; 108:756–762. PMID: 16551963.
Article51. Kim SJ, Lee JW, Jung CW, et al. Weekly rituximab followed by monthly rituximab treatment for steroid-refractory chronic graft-versus-host disease: results from a prospective, multicenter, phase II study. Haematologica. 2010; 95:1935–1942. PMID: 20663943.
Article52. Alousi AM, Uberti J, Ratanatharathorn V. The role of B cell depleting therapy in graft versus host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010; 51:376–389. PMID: 20141428.
Article53. Puliaev R, Puliaeva I, Welniak LA, et al. CTL-promoting effects of CD40 stimulation outweigh B cell-stimulatory effects resulting in B cell elimination and disease improvement in a murine model of lupus. J Immunol. 2008; 181:47–61. PMID: 18566369.
Article54. Shulman HM, Kleiner D, Lee SJ, et al. Histopathologic diagnosis of chronic graft-versus-host disease: National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: II. Pathology Working Group Report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006; 12:31–47. PMID: 16399567.
Article55. Wynn TA. Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004; 4:583–594. PMID: 15286725.
Article56. Nikolic B, Lee S, Bronson RT, Grusby MJ, Sykes M. Th1 and Th2 mediate acute graft-versus-host disease, each with distinct end-organ targets. J Clin Invest. 2000; 105:1289–1298. PMID: 10792004.
Article57. Hillebrandt S, Wasmuth HE, Weiskirchen R, et al. Complement factor 5 is a quantitative trait gene that modifies liver fibrogenesis in mice and humans. Nat Genet. 2005; 37:835–843. PMID: 15995705.
Article58. Niculescu F, Niculescu T, Nguyen P, et al. Both apoptosis and complement membrane attack complex deposition are major features of murine acute graft-vs.-host disease. Exp Mol Pathol. 2005; 79:136–145. PMID: 15979610.
Article59. Tsoi MS, Storb R, Jones E, et al. Deposition of IgM and complement at the dermoepidermal junction in acute and chronic cutaneous graft-vs-host disease in man. J Immunol. 1978; 120:1485–1492. PMID: 26718.60. Liem LM, Fibbe WE, van Houwelingen HC, Goulmy E. Serum transforming growth factor-beta1 levels in bone marrow transplant recipients correlate with blood cell counts and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1999; 67:59–65. PMID: 9921796.61. Baron C, Somogyi R, Greller LD, et al. Prediction of graft-versus-host disease in humans by donor gene-expression profiling. PLoS Med. 2007; 4:e23. PMID: 17378698.
Article62. Jaffee BD, Claman HN. Chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) as a model for scleroderma. I. Description of model systems. Cell Immunol. 1983; 77:1–12. PMID: 6220812.63. Allen RD, Staley TA, Sidman CL. Differential cytokine expression in acute and chronic murine graft-versus-host-disease. Eur J Immunol. 1993; 23:333–337. PMID: 8436168.
Article64. De Wit D, Van Mechelen M, Zanin C, et al. Preferential activation of Th2 cells in chronic graft-versus-host reaction. J Immunol. 1993; 150:361–366. PMID: 8419469.65. Doutrelepont JM, Moser M, Leo O, et al. Hyper IgE in stimulatory graft-versus-host disease: role of interleukin-4. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991; 83:133–136. PMID: 1671004.66. Garlisi CG, Pennline KJ, Smith SR, Siegel MI, Umland SP. Cytokine gene expression in mice undergoing chronic graft-versus-host disease. Mol Immunol. 1993; 30:669–677. PMID: 8487782.
Article67. Tanaka J, Imamura M, Kasai M, et al. The important balance between cytokines derived from type 1 and type 2 helper T cells in the control of graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997; 19:571–576. PMID: 9085737.
Article68. Umland SP, Razac S, Nahrebne DK, Seymour BW. Effects of in vivo administration of interferon (IFN)-gamma, anti-IFN-gamma, or anti-interleukin-4 monoclonal antibodies in chronic autoimmune graft-versus-host disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992; 63:66–73. PMID: 1591885.69. Wynn TA, Cheever AW, Jankovic D, et al. An IL-12-based vaccination method for preventing fibrosis induced by schistosome infection. Nature. 1995; 376:594–596. PMID: 7637808.
Article70. Hoffmann KF, Cheever AW, Wynn TA. IL-10 and the dangers of immune polarization: excessive type 1 and type 2 cytokine responses induce distinct forms of lethal immunopathology in murine schistosomiasis. J Immunol. 2000; 164:6406–6416. PMID: 10843696.
Article71. Murata T, Husain SR, Mohri H, Puri RK. Two different IL-13 receptor chains are expressed in normal human skin fibroblasts, and IL-4 and IL-13 mediate signal transduction through a common pathway. Int Immunol. 1998; 10:1103–1110. PMID: 9723696.
Article72. Chiaramonte MG, Donaldson DD, Cheever AW, Wynn TA. An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response. J Clin Invest. 1999; 104:777–785. PMID: 10491413.
Article73. Oriente A, Fedarko NS, Pacocha SE, Huang SK, Lichtenstein LM, Essayan DM. Interleukin-13 modulates collagen homeostasis in human skin and keloid fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000; 292:988–994. PMID: 10688614.74. Saito A, Okazaki H, Sugawara I, Yamamoto K, Takizawa H. Potential action of IL-4 and IL-13 as fibrogenic factors on lung fibroblasts in vitro. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003; 132:168–176. PMID: 14600429.
Article75. Jacobsohn DA, Schechter T, Seshadri R, Thormann K, Duerst R, Kletzel M. Eosinophilia correlates with the presence or development of chronic graft-versus-host disease in children. Transplantation. 2004; 77:1096–1100. PMID: 15087778.
Article76. Atamas SP, White B. The role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003; 15:772–777. PMID: 14569209.
Article77. Zhou L, Askew D, Wu C, Gilliam AC. Cutaneous gene expression by DNA microarray in murine sclerodermatous graft-versus-host disease, a model for human scleroderma. J Invest Dermatol. 2007; 127:281–292. PMID: 16917493.
Article78. Yoon HK, Lim JY, Kim TJ, Cho CS, Min CK. Effects of pravastatin on murine chronic graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 2010; 90:853–860. PMID: 20808264.
Article79. Morris SC, Cheek RL, Cohen PL, Eisenberg RA. Allotype-specific immunoregulation of autoantibody production by host B cells in chronic graft-versus host disease. J Immunol. 1990; 144:916–922. PMID: 2295820.80. van der Veen FM, Rolink AG, Gleichmann E. Autoimmune disease strongly resembling systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in F1 mice undergoing graft-versus-host reaction (GVHR). Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982; 149:669–677. PMID: 6983233.
Article81. Sekiguchi DR, Eisenberg RA, Weigert M. Secondary heavy chain rearrangement: a mechanism for generating anti-double-stranded DNA B cells. J Exp Med. 2003; 197:27–39. PMID: 12515811.82. Sekiguchi DR, Jainandunsing SM, Fields ML, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host in Ig knockin transgenic mice abrogates B cell tolerance in anti-double-stranded DNA B cells. J Immunol. 2002; 168:4142–4153. PMID: 11937575.
Article83. Via CS, Shearer GM. T-cell interactions in autoimmunity: insights from a murine model of graft-versus-host disease. Immunol Today. 1988; 9:207–213. PMID: 3076417.84. Parkman R. Clonal analysis of murine graft-vs-host disease. I. Phenotypic and functional analysis of T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol. 1986; 136:3543–3548. PMID: 2871104.85. Claman HN, Jaffee BD, Huff JC, Clark RA. Chronic graft-versus-host disease as a model for scleroderma. II. Mast cell depletion with deposition of immunoglobulins in the skin and fibrosis. Cell Immunol. 1985; 94:73–84. PMID: 4016962.86. Ruzek MC, Jha S, Ledbetter S, Richards SM, Garman RD. A modified model of graft-versus-host-induced systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) exhibits all major aspects of the human disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50:1319–1331. PMID: 15077316.
Article87. Anderson BE, McNiff J, Yan J, et al. Memory CD4+ T cells do not induce graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. 2003; 112:101–108. PMID: 12840064.
Article88. McCormick LL, Zhang Y, Tootell E, Gilliam AC. Anti-TGF-beta treatment prevents skin and lung fibrosis in murine sclerodermatous graft-versus-host disease: a model for human scleroderma. J Immunol. 1999; 163:5693–5699. PMID: 10553100.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Chronic Graft Versus Host Disease
- Acute Cutaneous Graft-Versus-Host Reaction
- Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease after Liver Transplantation
- Two Cases of Chronic Cutaneous Graft-versus-host-reaction on the Site of Healed Herpes Zoster as an Isotopic Response
- A Histopathological Comparative Study between Erythema Multiforme and Acute Cutaneous Graft - versus - Host Reactions