J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Sep;27(9):1027-1036. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1027.
Clinicopathologic and Molecular Characteristics of Lung Adenocarcinoma Arising in Young Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. luciado@inha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Medicine, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1782135
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1027
Abstract
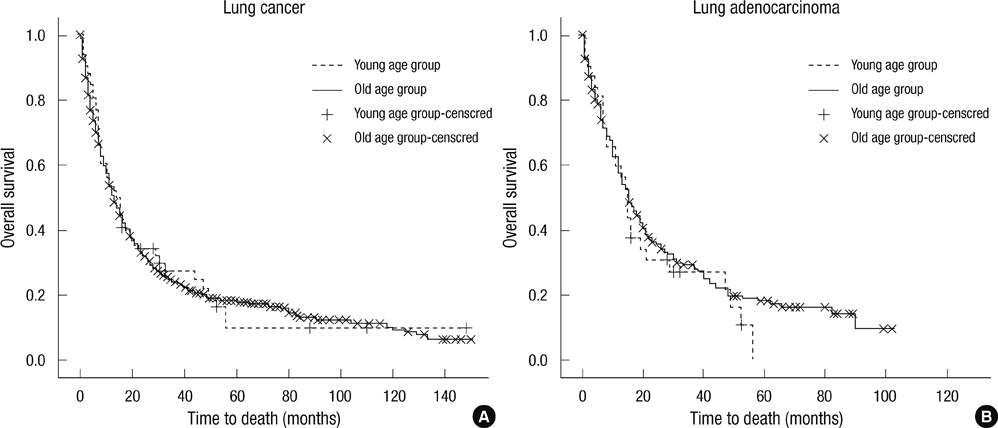
- Lung cancer rarely occurs in young patients. Recent studies have demonstrated that epidemiologic data are closely correlated to some molecular characteristics. We investigated the clinicopathologic characteristics of lung adenocarcinoma in young patients and evaluated immunohistochemically detected epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) positivity. Among lung adenocarcinoma patients, 31 cases were of the < or = 40 yr-old group and 261 cases of > 50 yr-old group. Young patients were more likely to be females (67.7% vs 40.2%), and nonsmokers (58.1% vs 45.2%) and more often had high TNM stage (stage IV was 80.6% vs 52.1%) and had a high rate of distant metastasis (51.6% vs 28.0%) compared with older patients. The signet ring cell feature was more common (25.8% vs 11.5%) and lepidic growth pattern was rarely present (3.2% vs 16.5%) in the adenocarcinoma of young patients. There was no significant survival difference between the two age groups. The rate of EGFR mutation status and ALK positivity did not show a statistical difference between two groups. In conclusion, lung adenocarcinoma of young patients demonstrates distinct pathologic features with frequent presence of a signet ring cell feature and rare occurrence of lepidic growth pattern. Further investigation for other genetic abnormalities would be needed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma/metabolism/mortality/*pathology
Adult
Age Factors
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Female
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Lung Neoplasms/metabolism/mortality/*pathology
Male
Middle Aged
Mutation
Neoplasm Staging
Receptor Protein-Tyrosine Kinases/metabolism
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor/metabolism
Smoking
Receptor Protein-Tyrosine Kinases
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, Won YJ, Boo YK, Shin HR, Park EC, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: Incidence, mortality and survival in 2006-2007. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1113–1121.2. Subramanian J, Morgensztern D, Goodgame B, Baggstrom MQ, Gao F, Piccirillo J, Govindan R. Distinctive characteristics of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in the young: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 2010. 5:23–28.3. Liu NS, Spitz MR, Kemp BL, Cooksley C, Fossella FV, Lee JS, Hong WK, Khuri FR. Adenocarcinoma of the lung in young patients. The M. D. Anderson experience. Cancer. 2000. 88:1837–1841.4. Green LS, Fortoul TI, Ponciano G, Robles C, Rivero O. Bronchogenic cancer in patients under 40 years old: the experience of a Latin American country. Chest. 1993. 104:1477–1481.5. Kuo C, Chen Y, Chao J, Tsai C, Perng R. Non-small cell lung cancer in very young and very old patients. Chest. 2000. 117:354–357.6. Blanco M, Garcia-Fontan E, Rivo JE, Repaaz JR, Obeso GA, Canizares MA. Bronchogenic carcinoma in patients under 50 years old. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009. 11:322–325.7. Skarin AT, Herbst RS, Leong TL, Bailey A, Sugarbaker D. Lung cancer in patients under age 40. Lung Cancer. 2001. 32:255–264.8. Tian DL, Liu HX, Zhang L, Yin HN, Hu YX, Zhao HR, Chen DY, Han LB, Li Y, Li HW. Surgery for young patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2003. 42:215–220.9. Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from "never smokers" and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. 101:13306–13311.10. Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004. 304:1497–1500.11. Zakowski MF, Hussain S, Pao W, Ladanyi M, Ginsberg MS, Heelan R, Miller VA, Rusch VW, Kris MG. Morphologic features of adenocarcinoma of the lung predictive of response to the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors Erlotinib and Gefitinib. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009. 133:470–477.12. Motoi N, Szoke J, Riely GJ, Seshan VE, Kris MG, Rusch VW, Gerald WL, Travis WD. Lung adenocarcinoma: Modification of the 2004 WHO mixed subtype to include the major histologic subtype suggests correlations between papillary and micropapillary adenocarcinoma subtypes, EGFR mutations and gene expression analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008. 32:810–827.13. Shaw AT, Yeap BY, Mino-Kenudson M, Digumarthy SR, Costa DB, Heist RS, Solomon B, Stubbs H, Admane S, McDermott U, et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK. J Clin Oncol. 2009. 27:4247–4253.14. Paik JH, Choe G, Kim H, Choe J, Lee HJ, Lee C, Lee JS, Jheon S, Chung J. Screening of anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement by immunohistochemistry in non-small cell lung cancer: Correlation with fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. 6:466–472.15. Raz DJ, Jablons DM. Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is not associated with younger age at diagnosis: an analysis of the SEER database. J Thorac Oncol. 2006. 1:339–343.16. Yu J, Kane S, Wu J, Benedettini E, Li D, Reeves C, Innocenti G, Wetzel R, Crosby K, Becker A, et al. Mutation-specific antibodies for the detection of EGFR mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. 15:3023–3028.17. Brevet M, Arcila M, Ladanyi M. Assessment of EGFR mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma by immunohistochemistry using antibodies specific to the two major forms of mutant EGFR. J Mol Diagn. 2010. 12:169–176.18. Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. Edge SB, editor. Lung. AJCC cancer staging manual. 2010. 7th ed. New York: Springer;253–266.19. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink HK, Harris CC. Kleihues P, Sobin LH, editors. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. World Health Organization classification of tumours. 2004. Lyon: IARCPress;35–44.20. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, Van Schil PE, et al. International Aassociation for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary Classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. 6:244–285.21. Noguchi M, Morikawa A, Kawasaki M, Matsuno Y, Yamada T, Hirohashi S, Kondo H, Shimosato Y. Small adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer. 1995. 75:2844–2852.22. Nakano H, Soda H, Takasu M, Tomonaga N, Yamaguchi H, Nakatomi K, Fujino S, Hayashi T, Nakamura Y, Tsukamoto K, et al. Heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations within a mixed adenocarcinoma lung nodule. Lung Cancer. 2008. 60:136–140.23. Kish JK, Ro JY, Ayala AG, McMurtrey MJ. Primary mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung with signet-ring cells: a histochemical comparison with signet-ring cell carcinomas of other sites. Hum Pathol. 1989. 20:1097–1102.24. Tsuta K, Ishii G, Yoh K, Nitadori J, Hasebe T, Nishiwaki Y, Endoh Y, Kodama T, Nagai K, Ochiai A. Primary lung carcinoma with signet-ring cell carcinoma components: clinicopathological analysis of 39 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004. 28:868–874.25. Iwasaki T, Ohta M, Lefor AT, Kawahara K. Signet-ring cell carcinoma component in primary lung adenocarcinoma: potential prognostic factor. Histopathology. 2008. 52:639–640.26. Lindstrom I, Nordling S, Nissen A, Tammilehto L, Mattson K, Knuutila S. DNA copy number changes in lung adenocarcinoma in younger patients. Mod Pathol. 2002. 15:372–378.27. Kondou M, Nagayasu T, Hidaka S, Tsuchiya T, Takeshita H, Yasutake T, Yano H, Minami H, Iwasaki K. Correlation between angiogenesis and p53 expression in lung adenocarcinoma of young patients. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009. 217:101–107.28. Shaw AT, Costa DB, Iafrate AJ, Dezube BJ, Shapiro GI, Bang YJ, Janne PA, Lynch TJ, Maki RG, Gamidge DR, et al. Clinical activity of the oral ALK and MET inhibitor PF-02341066 in non-small cell lung cancer (SNCLC) with EML4-ALK translocations. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. 4:S305–S306.29. Rodig SJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Dacic S, Yeap BY, Shaw A, Barletta JA, Stubbs H, Law K, Lindeman N, Mark E, et al. Unique clinicopathologic features characterize ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma in the western population. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. 15:5216–5223.30. Jakobsen JN, Sorensen JB. Intratumor heterogeneity and chemotherapy-induced changes in EGFR status in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. 69:289–299.31. Yatabe Y, Matsuo K, Mitsudomi T. Heterogeneous distribution of EGFR mutation is extremely rare in lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011. 29:2972–2977.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular Pathogenesis of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas
- The Clinical study of Lung Cancer in Patients Younger than 40 Years of Age
- Morphological Features of the Most Advanced Intra-Tumor Component in Multistep Progression
- Comparative Studies on Clinicopathologic Characteristics and surgical Results in Senile and Young Patients with Gastric Cancer
- Clinicopathologic Characteristics and the Prognosis of Gastric Cancer Patients at Both Extremes of Age