J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Apr;21(2):337-341. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.337.
Neuroprotective Effect of Cycloheximide on Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mhlee@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781846
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.2.337
Abstract
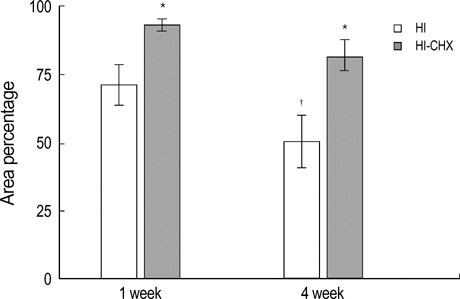
- This study was done to determine the neuroprotective effect of cycloheximide on neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Seven day-old newborn rat pups were subjected to 90 min of 8% oxygen following a unilateral carotid artery ligation. The extent of cerebral infarction was evaluated at 1 and 4 week of recovery. Apoptosis was identified by performing terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) staining and flow cytometry with a combination of fluoresceinated annexin V and propidium iodide. Brain infarction area was significantly increased at 4 week compared to 1 week after hypoxia-ischemia in the control group. With cycloheximide treatment, the number of TUNEL positive cells in the ipsilateral cerebral cortex at 48 hr and peri-infarct area at 1 and 4 week of recovery was significantly reduced, both apoptotic and necrotic cells by flow cytometry 48 hr after the injury were significantly reduced, and the extent of cerebral infarction at 1 and 4 week of recovery was also significantly attenuated compared to the hypoxia-ischemia control group. In summary, our data suggest that apoptosis plays an important role in the development of delayed infarction, and inhibition of apoptosis with cycloheximide significantly reduces the ensuing cerebral infarction in a newborn rat pup model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia.
MeSH Terms
-
Time Factors
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Rats
Propidium
Neuroprotective Agents/*pharmacology
In Situ Nick-End Labeling
Hypoxia-Ischemia, Brain/*drug therapy/metabolism/pathology
Cycloheximide/*pharmacology
Brain Infarction/pathology/prevention & control
Apoptosis/drug effects
Annexin A5/metabolism
Animals, Newborn
Animals
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Therapeutic Window for Cycloheximide Treatment after Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats
Won Soon Park, Dong Kyung Sung, Saem Kang, Soo Hyun Koo, Yu Jin Kim, Jang Hoon Lee, Yun Sil Chang, Munhyang Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2006;21(3):490-494. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.490.Erythropoietin Attenuates Brain Injury, Subventricular Zone Expansion, and Sensorimotor Deficits in Hypoxic-Ischemic Neonatal Rats
Sung Shin Kim, Kyung-Hoon Lee, Dong Kyung Sung, Jae Won Shim, Myo Jing Kim, Ga Won Jeon, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2008;23(3):484-491. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.484.
Reference
-
1. Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Mishra OP. Mechanisms of cerebral injury in perinatal asphyxia and strategies for prevention. J Pediatr. 1998. 132:S30–S34.2. Vannucci RC, Perlman JM. Interventions for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1997. 100:1004–1014.
Article3. Linnik MD, Zobrist RH, Hatfield MD. Evidence supporting a role for programmed cell death in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1993. 24:2002–2009.
Article4. Renvoize C, Biola A, Pallardy M, Breard J. Apoptosis: identification of dying cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1998. 14:111–120.5. Taylor DL, Edwards AD, Mehmet H. Oxidative metabolism, apoptosis and perinatal brain injury. Brain Pathol. 1999. 9:93–117.
Article6. Martin LJ, Al-Abdulla NA, Brambrink AM, Kirsch JR, Sieber FE, Portera-Cailliau C. Neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity, global cerebral ischemia, and target deprivation: a perspective on the contributions of apoptosis and necrosis. Brain Res Bull. 1998. 46:281–309.
Article7. Johnson EM Jr, Deckwerth TL. Molecular mechanisms of developmental neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993. 16:31–46.
Article8. Du C, Hu R, Csernansky CA, Hsu CY, Choi DW. Very delayed infarction after mild focal cerebral ischemia: a role for apoptosis? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996. 16:195–201.
Article9. Zhu C, Wang X, Xu F, Bahr BA, Shibata M, Uchiyama Y, Hagberg H, Blomgren K. The influence of age on apoptotic and other mechanisms of cell death after cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Cell Death Differ. 2005. 12:162–176.
Article10. Pulera MR, Adams LM, Liu H, Santos DG, Nishimura RN, Yang F, Cole GM, Wasterlain CG. Apoptosis in a neonatal rat model of cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. Stroke. 1998. 29:2622–2630.
Article11. Northington FJ, Ferriero DM, Flock DL, Martin LJ. Delayed neurodegeneration in neonatal rat thalamus after hypoxia-ischemia is apoptosis. J Neurosci. 2001. 21:1931–1938.
Article12. Nakajima W, Ishida A, Lange MS, Gabrielson KL, Wilson MA, Martin LJ, Blue ME, Johnston MV. Apoptosis has a prolonged role in the neurodegeneration after hypoxic ischemia in the newborn rat. J Neurosci. 2000. 20:7994–8004.
Article13. Yue X, Mehmet H, Squier MV, Hope PL, Azzopardi D, Edwards AD. Apoptosis and necrosis in the brains of infants dying after birth asphyxia. Pediatr Res. 1995. 37:387A.14. Rosenbaum DM, Michaelson M, Batter DK, Doshi P, Kessler JA. Evidence for hypoxia-induced, programmed cell death of cultured neurons. Ann Neurol. 1994. 36:864–870.
Article15. Pavlik A, Teisinger J. Effect of cycloheximide administered to rats in early postnatal life: prolonged of DNA synthesis in the developing brain. Brain Res. 1980. 192:531–541.16. Hwang JH, Sung DK, Choi CW, Kang S, Chang YS, Park WS, Lee M. Single cell dissociation methods for flow cytometric analysis of hypoxia-ischemia injured newborn rat pup brain. Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:545–550.17. Geddes R, Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ. Delayed cerebral atrophy following moderate hypoxia-ischemia in the immature rat. Dev Neurosci. 2001. 23:180–185.
Article18. Wijsman JH, Jonker RR, Keijzer R, van de Velde CJ, Cornelisse CJ, van Dierendonck JH. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labelling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993. 41:7–12.19. MacManus JP, Hill IE, Preston E, Rasquinha I, Walker T, Buchan AM. Differences in DNA fragmentation following transient cerebral or decapitation ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995. 15:728–737.
Article20. Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C. A novel assay for apoptosis: flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labeled annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 1995. 184:39–51.21. Honda O, Kuroda M, Joja I, Asaumi J, Takeda Y, Akaki S, Togami I, Kanazawa S, Kawasaki S, Hiraki Y. Assessment of secondary necrosis of Jurkat cells using a new microscopic system and double staining method with annexin V and propidium iodide. Int J Oncol. 2000. 16:283–288.
Article22. Darzynkiewicz Z, Bender E. Analysis of apoptotic cells by flow and laser scanning cytometry. Methods Enzymol. 2000. 322:18–39.
Article23. Walsh GM, Dewdson G, Wardlaw AJ, Levi-Schaffer F, Moqbel R. A comparative study of different methods for the assessment of apoptosis and necrosis in human eosinophils. J Immunol Methods. 1998. 217:153–163.
Article24. Schutte B, Nuydens R, Geerts H, Ramaekers F. Annexin V binding assay as a tool to measure apoptosis in differentiated neuronal cells. J Neurosci Methods. 1998. 86:63–69.
Article25. Darzynkiewicz Z, Juan G, Li X, Gorczyca W, Murakami T, Traganos F. Cytometry in cell necrobiology: analysis of apoptosis and accidental cell death (necrosis). Cytometry. 1997. 27:1–20.
Article26. Lobner D, Choi DW. Preincubation with protein synthesis inhibitors protects cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced death. Neuroscience. 1996. 72:335–341.
Article27. Formigli L, Papucci L, Tani A, Schiavone N, Tempestini A, Orlandini GE, Capaccioli S, Orlandini SZ. Aponecrosis: morphological and biochemical exploration of a syncretic process of cell death sharing apoptosis and necrosis. J Cell Physiol. 2000. 182:41–49.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neuroprotective Effect of Growth Hormone in Neonatal Rat with Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury
- Neuroprotective Effect of Lacosamide on Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats
- The effect of erythropoietin in neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
- Therapeutic Window for Cycloheximide Treatment after Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats
- Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol via anti-apoptosis on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats