Korean J Lab Med.
2010 Jun;30(3):295-300. 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.3.295.
Analysis of Acquired Resistance Genes in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. shkoo@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1781630
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.3.295
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a gram-negative bacillus and a nosocomial pathogen in immunocompromised patients. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX) is the drug of choice for treating S. maltophilia infection; however, resistance to TMP/SMX is increasing. In this study, we investigated the relationship between the incidence of TMP/SMX resistance and the presence of sul genes and mobile elements.
METHODS
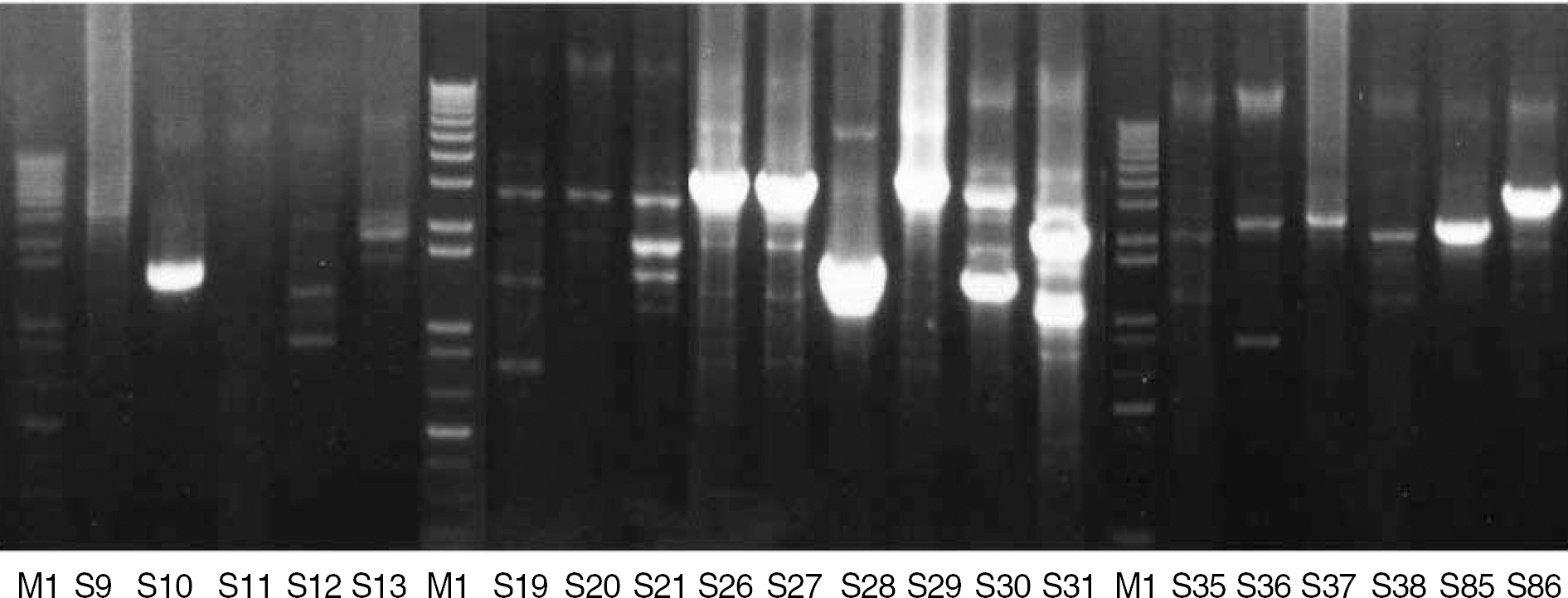
A total of 120 S. maltophilia isolates were collected from 3 university hospitals between April 2007 and April 2009. Antimicrobial susceptibilities were determined using the disk diffusion method. PCR and DNA sequencing were conducted for the detection of sul1, sul2, class 1 integron, and ISCR2 element. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequence-based PCR (REP-PCR) was carried out to evaluate the genetic relatedness.
RESULTS
The TMP/SMX-resistant (R) isolates harbored a significantly higher proportion of sul1 gene and class 1 integron than TMP/SMX-susceptible (S) isolates (P<0.001). Seventeen of 28 isolates with sul1 also had a class 1 integron, but none of the isolates without sul1 had a class 1 integron. The identified gene cassettes within class 1 integrons include aacA4, aadA1, aac6'-II, and qac. None of the 120 isolates carried sul2, glmM, or ISCR2 element. REP-PCR did not show any genetic relatedness among the isolates.
CONCLUSIONS
In Korea, the resistance of S. maltophilia isolates to TMP/SMX is due to sul1 within a class 1 integron rather than to sul2. The class 1 integron also harbors multiple antibiotic resistance genes in addition to sul1, and therefore it could mediate multidrug resistance in S. maltophilia.
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*pharmacology
Bacterial Proteins/genetics
Carrier Proteins/genetics
DNA, Bacterial/genetics
Disk Diffusion Antimicrobial Tests
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial/genetics
Humans
Integrons/genetics
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia/*drug effects/*genetics/isolation &purification
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Combination/*pharmacology
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from a Korean Tertiary Care Hospital
Hae-Sun Chung, Seong Geun Hong, Yangsoon Lee, Myungsook Kim, Dongeun Yong, Seok Hoon Jeong, Kyungwon Lee, Yunsop Chong
Yonsei Med J. 2012;53(2):439-441. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.439.Current Situation of Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Differences in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Complex Isolates by Multilocus Variable Number of Tandem Repeat Analysis
Ji-Young Rhee, Jae-Hoon Song, Kwan Soo Ko
Infect Chemother. 2016;48(4):285-293. doi: 10.3947/ic.2016.48.4.285.
Reference
-
1.Chang LL., Lin HH., Chang CY., Lu PL. Increased incidence of class 1 integrons in trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole-resistant clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. 59:1038–9.2.Valdezate S., Vindel A., Loza E., Baquero F., Canton R. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of unique Stenotrophomonas maltophilia clinical strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. 45:1581–4.3.Ahn GY., Yu FN., Jang SJ., Kim DM., Park G., Moon DS, et al. Pseudooutbreak of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia due to contamination of bronchoscope. Korean J Lab Med. 2007. 27:205–9. (안균열, 유봉남, 장숙진, 김동민, 박 건, 문대수 등. 기관지 내시경 오염에 기인한 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia 의 가유행 발생. 대한진단검사의학회지 2007;27:205-9.).4.Harlowe HD. Acute mastoiditis following pseudomonas maltophilia infection: case report. Laryngoscope. 1972. 82:882–3.5.Sutter VL. Identification of Pseudomonas species isolated from hospital environment and human sources. Appl Microbiol. 1968. 16:1532–8.6.Ben-Tovim T., Eylan E., Romano A., Stein R. Gram-negative bacteria isolated from external eye infections. Infection. 1974. 2:162–5.
Article7.Gardner P., Griffin WB., Swartz MN., Kunz LJ. Nonfermentative gramnegative bacilli of nosocomial interest. Am J Med. 1970. 48:735–49.
Article8.Seol SY., Jang KS., Jeong OG., Cho ER., Kim NH., Yu HS, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and molecular epidemiologic characteristics of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolated from clinical specimen. J Korean Soc Microbiol. 2000. 35:239–50. (설성용, 장경수, 정웅기, 조응래, 김능희, 유학선 등. 병원 재료에서 분리한 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia 의항균제내성및분자역학적특성. 대한미생물학회지 2000;35:239-50.).9.Chang LL., Chen HF., Chang CY., Lee TM., Wu WJ. Contribution of integrons, and SmeABC and SmeDEF efflux pumps to multidrug resistance in clinical isolates of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004. 53:518–21.10.Zhang L., Li XZ., Poole K. SmeDEF multidrug efflux pump contributes to intrinsic multidrug resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. 45:3497–503.11.Sader HS., Jones RN. Antimicrobial susceptibility of uncommonly isolated non-enteric Gram-negative bacilli. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2005. 25:95–109.
Article12.Perreten V., Boerlin P. A new sulfonamide resistance gene (sul3) in Escherichia coli is widespread in the pig population of Switzerland. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. 47:1169–72.13.Toleman MA., Bennett PM., Bennett DM., Jones RN., Walsh TR. Global emergence of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistance in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia mediated by acquisition of sul genes. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007. 13:559–65.14.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; sixteenth informational supplement. M100-S18 (M2). Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2008.15.Dillon B., Thomas L., Mohmand G., Zelynski A., Iredell J. Multiplex PCR for screening of integrons in bacterial lysates. J Microbiol Methods. 2005. 62:221–32.
Article16.Levesque C., Piche L., Larose C., Roy PH. PCR mapping of integrons reveals several novel combinations of resistance genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995. 39:185–91.
Article17.Lin CW., Chiou CS., Chang YC., Yang TC. Comparison of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and three rep-PCR methods for evaluating the genetic relatedness of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2008. 47:393–8.18.Garrison MW., Anderson DE., Campbell DM., Carroll KC., Malone CL., Anderson JD, et al. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: emergence of multidrug-resistant strains during therapy and in an in vitro pharmacodynamic chamber model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996. 40:2859–64.19.Fedler KA., Biedenbach DJ., Jones RN. Assessment of pathogen frequency and resistance patterns among pediatric patient isolates: report from the 2004 SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program on 3 continents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006. 56:427–36.
Article20.Barbolla R., Catalano M., Orman BE., Famiglietti A., Vay C., Smayevsky J, et al. Class 1 integrons increase trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole MICs against epidemiologically unrelated Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. 48:666–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Localized Cutaneous Infection due to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in Immunocompetent Patient
- A case of soft tissue infection by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia manifesting as subcutaneous nodules in a patient with leukemia
- Efflux Pump Inhibitor Carbonyl Cyanide-m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) Enhances Bacteriostatic Activity of Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Against Clinical Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates from Korea
- A Case of Corneal Ulcer Caused by Combined Infection of Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia and Aspergillus Fumigatus
- The sul1 Gene in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia With High-Level Resistance to Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole