Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Dec;28(6):483-492. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.6.483.
Molecular and Clinical Characteristics of Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 in Koreans
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine and Seoul National University Hospital, Korea. sparkle@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Seoul National University Hospital Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine and Seoul National University Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Seoul National University College of Medicine and Seoul National University Hospital, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine and Seoul National University Hospital, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1781584
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.6.483
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
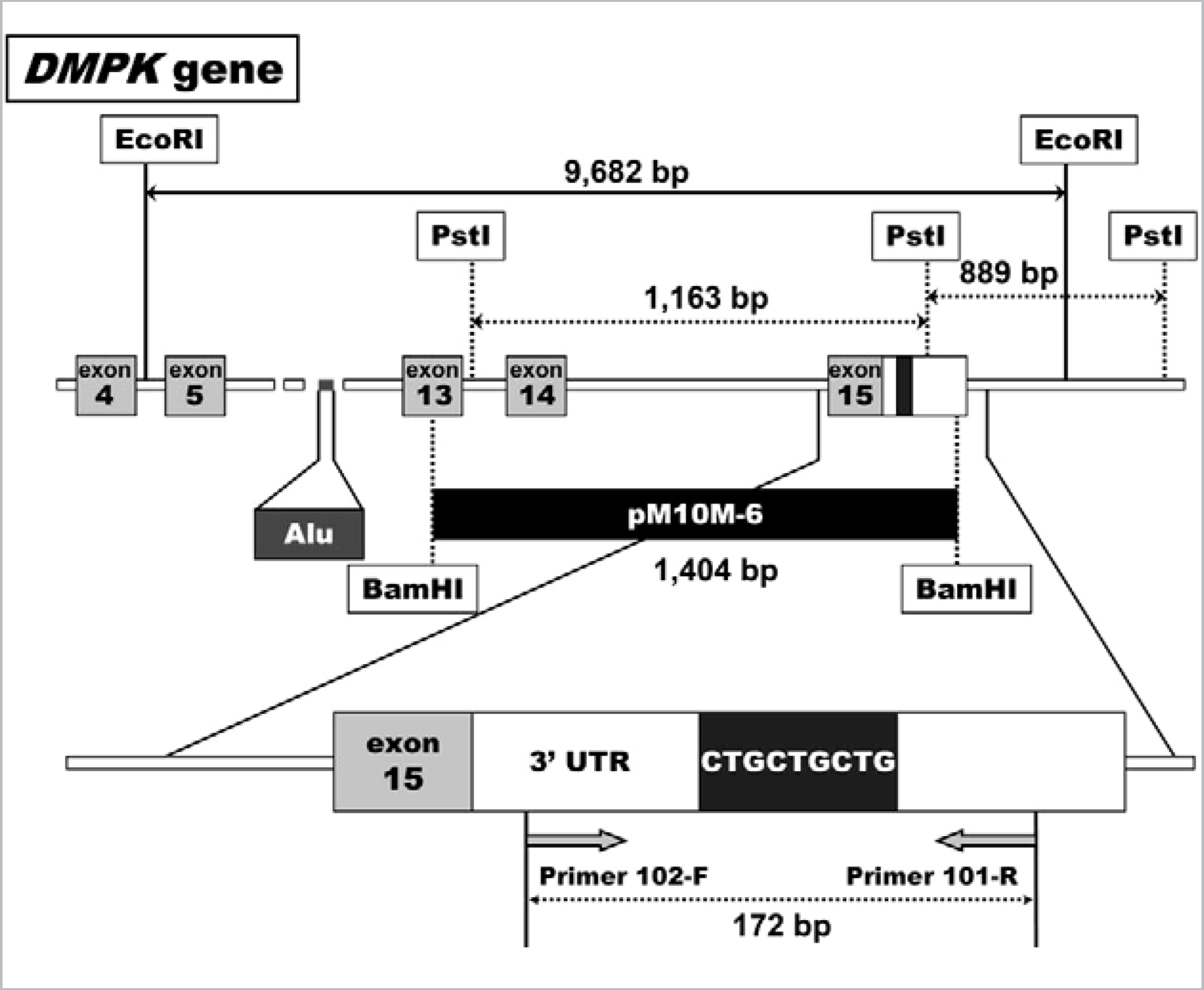
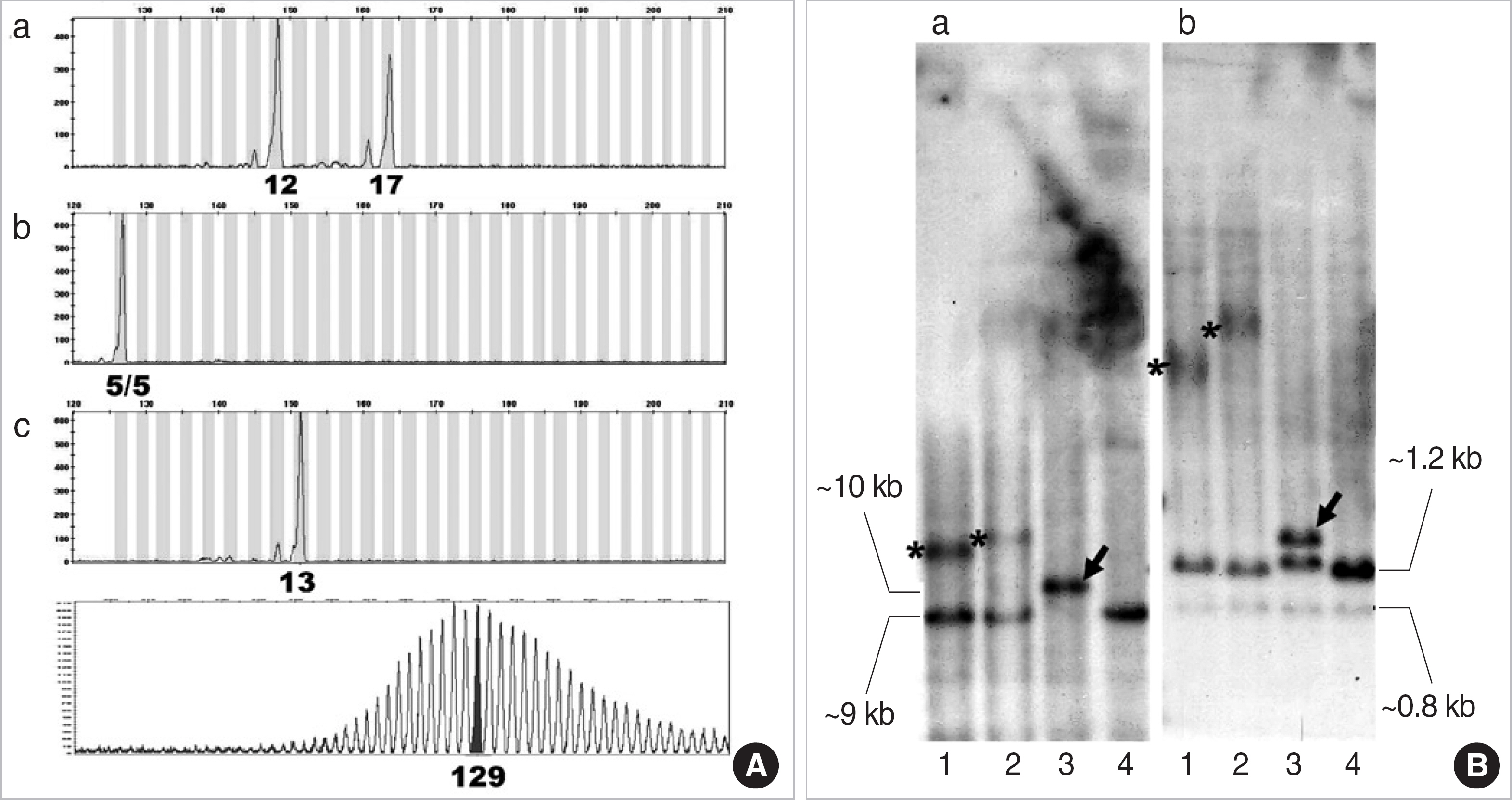
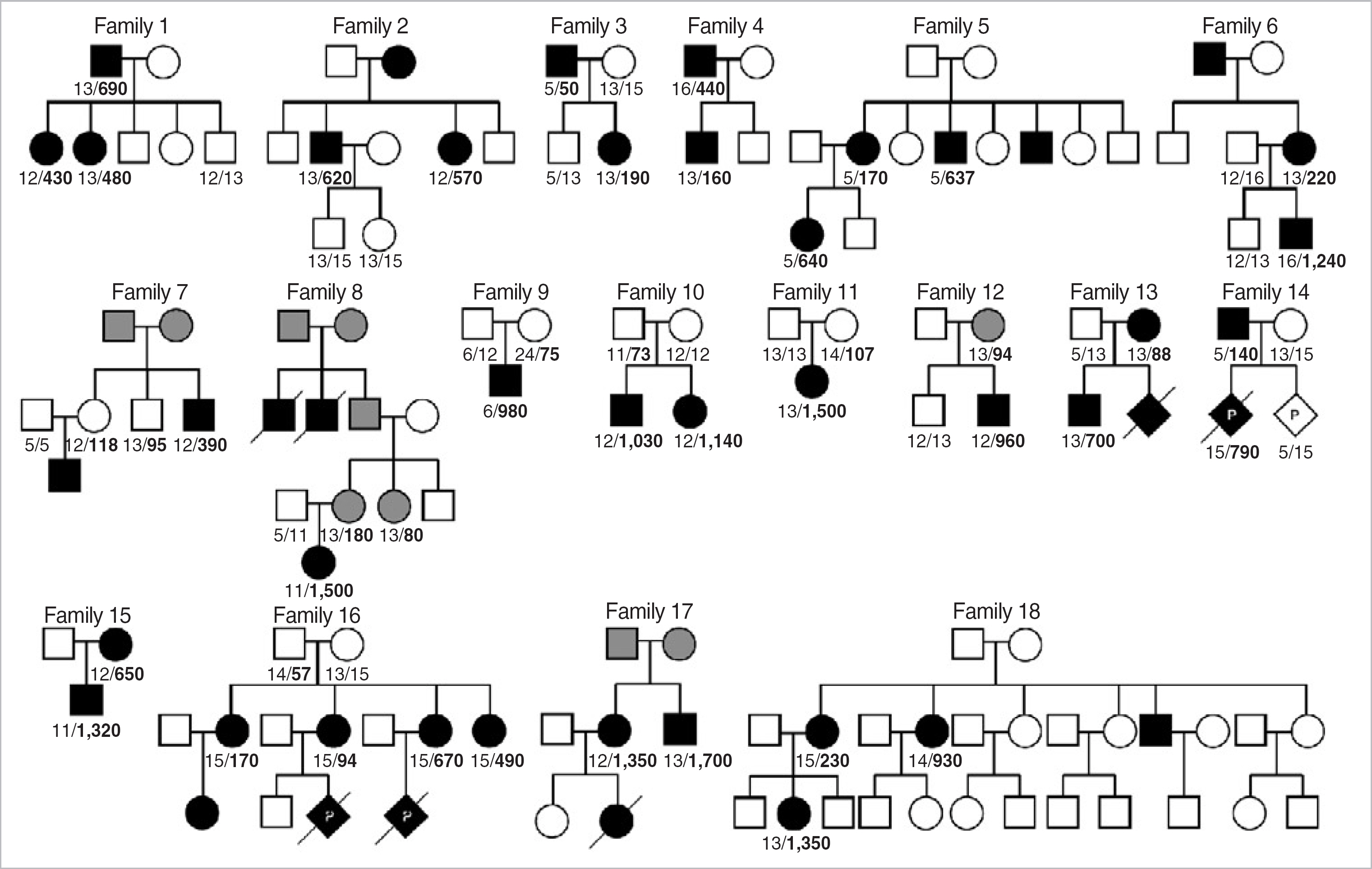
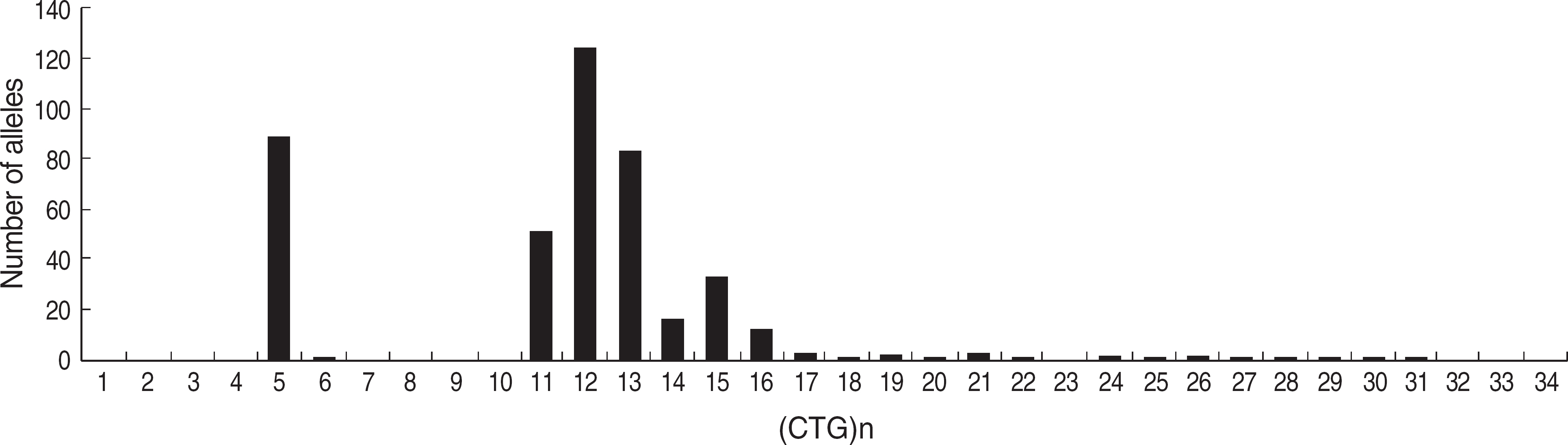
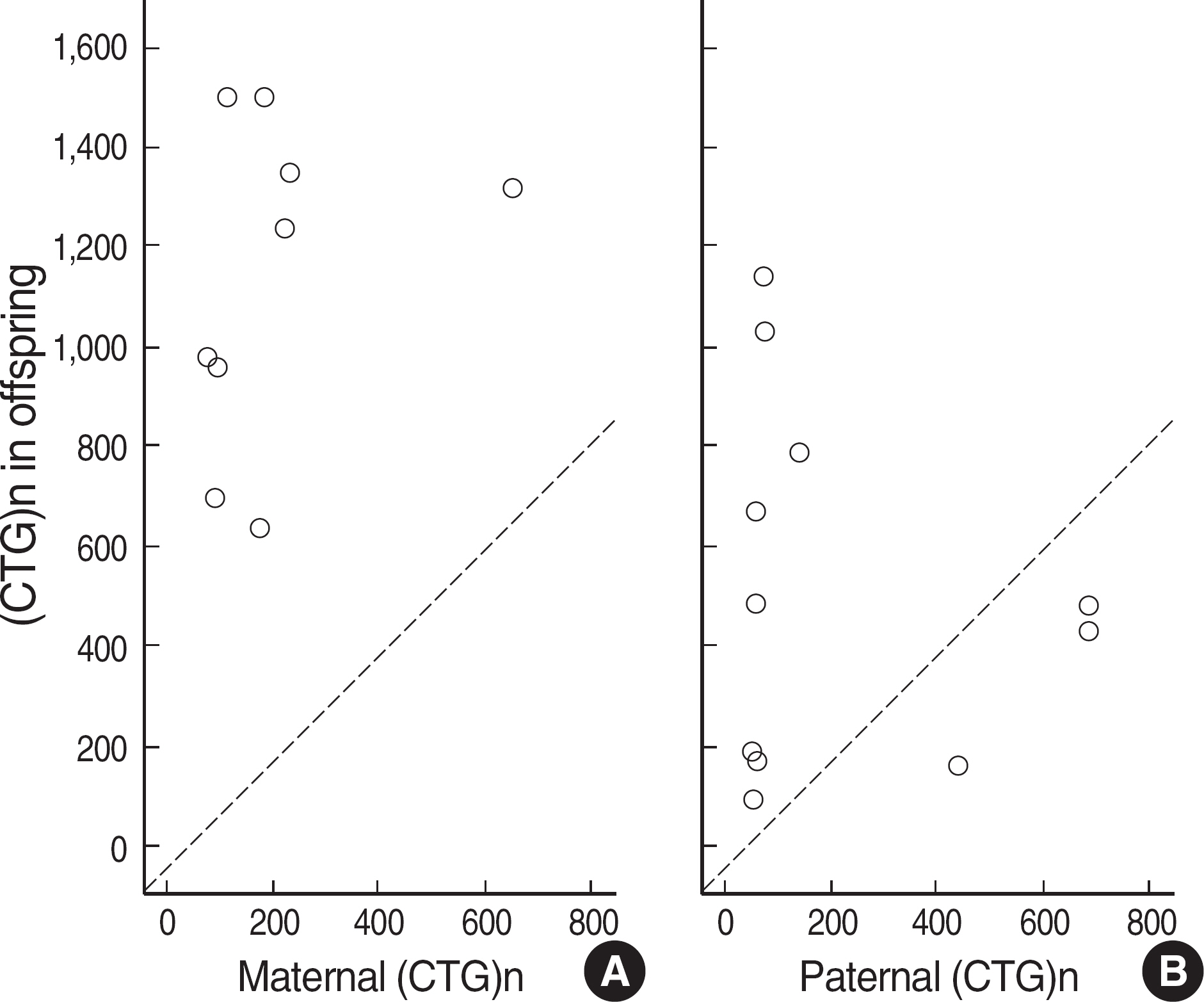
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is an autosomal-dominant muscular dystrophy caused by expansion of cytosine-thymine-guanine (CTG) trinucleotide repeats in the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase (DMPK) gene. The clinical features of DM1 are multisystemic and highly variable, and the unstable nature of CTG expansion causes wide genotypic and phenotypic presentations. The aim of this study was to characterize the molecular and clinical spectra of DM1 in Koreans. METHODS: The CTG repeats of 283 Korean individuals were tested by PCR fragment analysis and Southern blot. The following characteristics were assessed retrospectively: spectrum of CTG expansions, clinical findings, genotype-phenotype correlation, anticipation, and genetic instability. RESULTS: One-hundred twenty-four patients were confirmed as DM1 by molecular tests, and the CTG expansions ranged from 50 to 2,770 repeats (median 480 repeats). The most frequent clinical features were myotonia, muscular weakness, and family history. Patients with muscular weakness or dysfunction of the central nervous system harbored larger CTG expansions than those without each symptom (P<0.05). The age of onset was inversely correlated with the size of the CTG expansion (gamma=-0.422, P<0.001). The instability of CTG expansion representing as the maximum difference between sibships was observed from 50 to 700 repeats in nine families. Clinical anticipation and the increase in CTG repeat were significantly higher in maternally transmitted alleles (P=0.002). CONCLUSIONS: Molecular genetic tests are not only essential for diagnosis, but also helpful for suggesting the spectrum and relationship between genotype and phenotype in Korean DM1 patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Kurihara T. New classification and treatment for myotonic disorders. Intern Med. 2005. 44:1027–32.
Article2.Brook JD., McCurrach ME., Harley HG., Buckler AJ., Church D., Aburatani H, et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992. 68:799–808.
Article3.Machuca-Tzili L., Brook D., Hilton-Jones D. Clinical and molecular aspects of the myotonic dystrophies: a review. Muscle Nerve. 2005. 32:1–18.
Article4.Day JW., Ranum LP. RNA pathogenesis of the myotonic dystrophies. Neuromuscul Disord. 2005. 15:5–16.
Article5.Harper PS, editor. Myotonic dystrophy. 3rd ed.London: WB Saunders;2001. p. 47–86. p. 324–49.6.The International Myotonic Dystrophy Consortium (IDMC). New nomenclature and DNA testing guidelines for myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). Neurology. 2000. 54:1218–21.7.Deka R., Majumder PP., Shriver MD., Stivers DN., Zhong Y., Yu LM, et al. Distribution and evolution of CTG repeats at the myotonin protein kinase gene in human populations. Genome Res. 1996. 6:142–54.
Article8.Martorell L., Monckton DG., Sanchez A., Lopez De Munain A., Baiget M. Frequency and stability of the myotonic dystrophy type 1 premutation. Neurology. 2001. 56:328–35.
Article9.Shim SH., Cho YH., Choi SK., Chung SR. The CTG repeat polymorphisms of myotonic dystrophy (DM) gene in Korean population. J Genet Med. 1997. 1:23–6.10.Choi BO., SunWoo IN., Kim SM., Lee JS., Lee EK., Park KD, et al. Clinical significance of CTG repeat expansion in Korean myotonic dystrophy patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1999. 17:548–53. (최병옥, 선우일남, 김승민, 이진성, 이은경, 박기덕 등. 한국인 근긴장성 이양증에서CTG 반복확장의임상적의의. 대한신경과학회지 1999;17: 548-53.).11.Shojasaffar B., Moradin N., Kahrizi K., Cobo AM., Najmabadi H. CTG expansion & haplotype analysis in DM1 gene in healthy Iranian population. Can J Neurol Sci. 2008. 35:216–9.12.Pan H., Lin HM., Ku WY., Li TC., Li SY., Lin CC, et al. Haplotype analysis of the myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) locus in Taiwan: implications for low prevalence and founder mutations of Taiwanese myotonic dystrophy type 1. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001. 9:638–41.
Article13.Tishkoff SA., Goldman A., Calafell F., Speed WC., Deinard AS., Bonne-Tamir B, et al. A global haplotype analysis of the myotonic dystrophy locus: implications for the evolution of modern humans and for the origin of myotonic dystrophy mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. 62:1389–402.
Article14.Culjkovic B., Stojkovic O., Vukosavic S., Savic D., Rakocevic V., Apostolski S, et al. CTG repeat polymorphism in DMPK gene in healthy Yugoslav population. Acta Neurol Scand. 2002. 105:55–8.15.Marchini C., Lonigro R., Verriello L., Pellizzari L., Bergonzi P., Damante G. Correlations between individual clinical manifestations and CTG repeat amplification in myotonic dystrophy. Clin Genet. 2000. 57:74–82.
Article16.Gharehbaghi-Schnell EB., Finsterer J., Korschineck I., Mamoli B., Binder BR. Genotype-phenotype correlation in myotonic dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1998. 53:20–6.
Article17.Savic D., Rakocvic-Stojanovic V., Keckarevic D., Culjkovic B., Stojkovic O., Mladenovic J, et al. 250 CTG repeats in DMPK is a threshold for correlation of expansion size and age at onset of juvenile-adult DM1. Hum Mutat. 2002. 19:131–9.18.Brisson D., Tremblay M., Prevost C., Laberge C., Puymirat J., Mathieu J. Sibship stability of genotype and phenotype in myotonic dystrophy. Clin Genet. 2002. 62:220–5.
Article19.Ashizawa T., Anvret M., Baiget M., Barcelo JM., Brunner H., Cobo AM, et al. Characteristics of intergenerational contractions of the CTG repeat in myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1994. 54:414–23.20.Amiel J., Raclin V., Jouannic JM., Morichon N., Hoffman-Radvanyi H., Dommergues M, et al. Trinucleotide repeat contraction: a pitfall in prenatal diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy. J Med Genet. 2001. 38:850–2.
Article21.Harley HG., Rundle SA., MacMillan JC., Myring J., Brook JD., Crow S, et al. Size of the unstable CTG repeat sequence in relation to phenotype and parental transmission in myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1993. 52:1164–74.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 With Brain MRI Lesions Involving White Matters in Anterior Temporal Pole and Insula
- Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation with Myotonic Dystrophy and Achalasia-like Esophageal Dilatation
- Accidentally Diagnosed Myotonic Dystrophy after Cholecystectomy
- A Case of Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy Diagnosed by Molecular Genetics
- A Case of Myotonic Dystrophy with Prolonged Atrial Flutter