Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Oct;28(5):353-361. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.5.353.
Detection of Anti-ENA and anti-dsDNA Antibodies Using Line Immunoassay in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. jmkim@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1781567
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.5.353
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Detection of antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs) and dsDNA is needed for the diagnosis of and predicting prognosis in systemic autoimmune diseases. Recently introduced line immunoassay (LIA) has the advantage of detecting several autoantibodies simultaneously, and we evaluated its usefulness in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases in comparison with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
METHODS
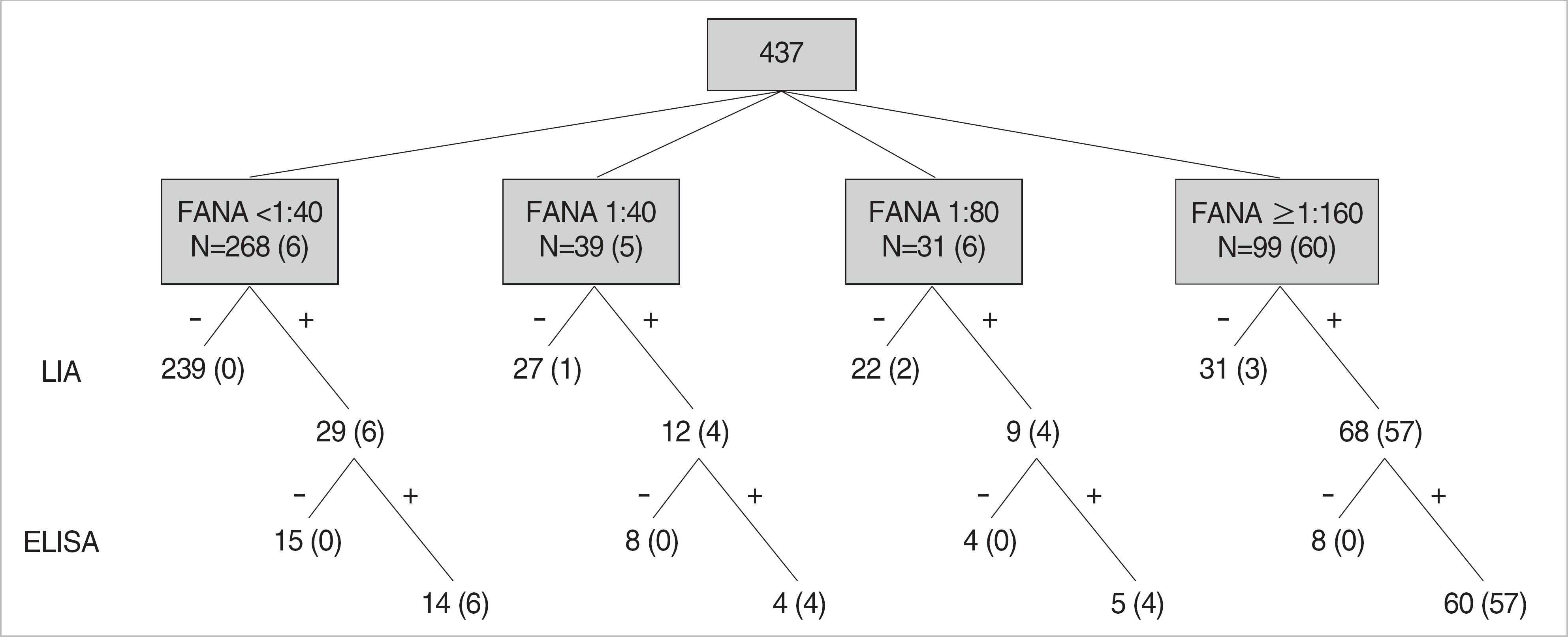
Samples were collected from 437 patients referred by rheumatologists. FANA (fluorescent antinuclear antibody) test and LIA for the detection of 13 different autoantibodies, including 6 ENAs and dsDNA were performed. LIA-positive samples for ENA or dsDNA antibodies were further tested with ELISA. Final diagnosis was made by rheumatologists according to the diagnostic criteria. Agreement of results between LIA and ELISA was analyzed in 53 selected patients with systemic autoimmune diseases.
RESULTS
The LIA detected antibodies to ENA and dsDNA in 118 and 22 patients, respectively, and ELISA detected 70.3% (83/118) and 45.5% (10/22) of LIA positive samples. Especially, 60.2% (71/118) of patients with positive ENA antibody on LIA was diagnosed as systemic autoimmune diseases. Patients having strong FANA titer and homogenous/speckled pattern showed higher prevalence of autoantibodies, but a small proportion of FANA negative patients also showed positive reactivity (LIA 10.8%, ELISA 5.2%). LIA showed a good agreement with ELISA for the anti-ENA antibodies (> or =80%), and a lower agreement for the anti-dsDNA antibody (67.9%).
CONCLUSIONS
LIA detecting several autoantibodies simultaneously might replace ELISA for anti-ENA antibodies, but not for anti-dsDNA antibodies. When LIA is performed considering clinical manifestations and FANA, it could contribute to the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Agreement of three commercial anti-extractable nuclear antigen tests: EUROASSAY Anti-ENA Profile, Polycheck Autoimmune Test and FIDIS Connective Profile
Namhee Kim, In-Suk Kim, Chulhun L Chang, Hyung-Hoi Kim, Eun Yup Lee
Kosin Med J. 2018;33(3):307-317. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2018.33.3.307.
Reference
-
1.Reisner BS., DiBlasi J., Goel N. Comparison of an enzyme immunoassay to an indirect fluorescent immunoassay for the detection of antinuclear antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1999. 111:503–6.
Article2.Fenger M., Wiik A., Hoier-Madsen M., Lykkegaard JJ., Rozenfeld T., Hansen MS, et al. Detection of antinuclear antibodies by solid-phase immunoassays and immunofluorescence analysis. Clin Chem. 2004. 50:2141–7.
Article3.Homburger HA. Cascade testing for autoantibodies in connective tissue disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1995. 70:183–4.4.Hoffman IE., Peene I., Veys EM., De Keyser F. Detection of specific antinuclear reactivities in patients with negative anti-nuclear antibody immunofluorescence screening tests. Clin Chem. 2002. 48:2171–6.
Article5.Bossuyt X., Luyckx A. Antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens in antinuclear antibody-negative samples. Clin Chem. 2005. 51:2426–7.
Article6.Delpech A., Gilbert D., Daliphard S., Le Loet X., Godin M., Tron F. Antibodies to Sm, RNP and SSB detected by solid-phase ELISAs using recombinant antigens: a comparison study with counter immunoelectrophoresis and immunoblotting. J Clin Lab Anal. 1993. 7:197–202.7.Lopez-Longo FJ., Rodriguez-Mahou M., Escalona-Monge M., Gonzalez CM., Monteagudo I., Carreno-Perez L. Simultaneous identification of various antinuclear antibodies using an automated multi-parameter line immunoassay system. Lupus. 2003. 12:623–9.
Article8.Vitali C., Bombardieri S., Jonsson R., Moutsopoulos HM., Alexander EL., Carsons SE, et al. Classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002. 61:554–8.
Article9.Hu PQ., Fertig N., Medsger TA Jr., Wright TM. Correlation of serum anti-DNA topoisomerase I antibody levels with disease severity and activity in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 48:1363–73.
Article10.Damoiseaux J., Boesten K., Giesen J., Austen J., Tervaert JW. Evaluation of a novel line-blot immunoassay for the detection of antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. 1050:340–7.
Article11.Rouquette AM., Desgruelles C., Laroche P. Evaluation of the new multiplexed immunoassay, FIDIS, for simultaneous quantitative determination of antinuclear antibodies and comparison with conventional methods. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003. 120:676–81.
Article12.Villalta D., Bizzaro N., Tonutti E., Visentin D., Manoni F., Piazza A, et al. Detection of anti-ENA autoantibodies in patients with systemic connective tissue disease. Analytical variability and diagnostic sensitivity of 4 methods. Recenti Prog Med. 1999. 90:579–84.13.Damoiseaux JG., Tervaert JW. From ANA to ENA: how to proceed? Autoimmun Rev. 2006. 5:10–7.
Article14.Arbuckle MR., McClain MT., Rubertone MV., Scofield RH., Dennis GJ., James JA, et al. Development of autoantibodies before the clinical onset of systemic lupus eythematosus. N Eng J Med. 2003. 349:1526–33.15.Sanchez-Guerrero J., Lew RA., Fossel AH., Schur PH. Utility of anti-Sm, anti-RNP, anti-Ro/SS-A, and anti-La/SS-B (extractable nuclear antigens) detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996. 39:1055–61.16.Vos PA., Bast EJ., Derksen RH. Cost-effective detection of non-anti-double-stranded DNA antinuclear antibody specificities in daily clinical practice. Rheumatology. 2006. 45:629–35.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Agreement of three commercial anti-extractable nuclear antigen tests: EUROASSAY Anti-ENA Profile, Polycheck Autoimmune Test and FID(IS) Connective Profile
- A Study of the Standardization and the External Quality Assessment for Antinuclear Antibody, Anti-Double-Stranded DNA, and AntiExtractable Nuclear Antigen Antibody Testing
- A Case of ANA-negative, Anti-dsDNA Negative, and Anti-Ro/SSA Positive Membranous Lupus Nephropathy
- Degree of Agreement between Phadia EliA ENA and Euroimmun line Immunoassay; Comparison of Two Methods to Evaluate the Ability to Detect ENA Antibodies
- Detection Of Antibodies To Ena In The Systemic Lupus Erythematosus By Immunoblotting: A Cornparision Of Irnmunoblotting And Double Immunodiffusion