J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Feb;25(2):257-264. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.257.
Hepatitis B Viral Surface Mutations in Patients with Adefovir Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B with A181T/V Polymerase Mutations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. 93haan@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1779257
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.257
Abstract
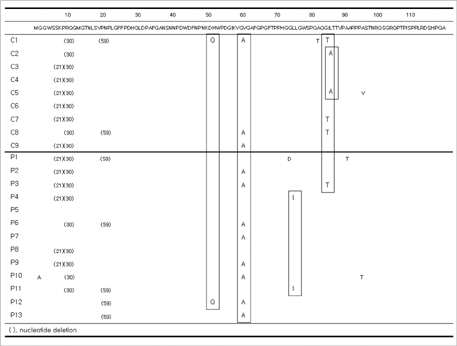
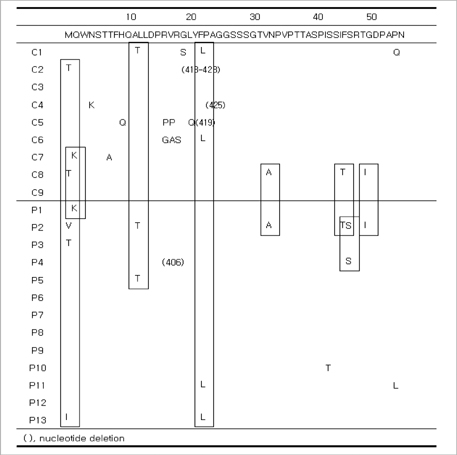
- The hepatitis B virus (HBV) polymerase gene has overlapping reading frames with surface genes, which allows to alter the amino acid codon of the surface genes. In adefovir (ADV) treated chronic hepatitis B patients carrying rtA181T/rtA181V mutations, overlap with surface gene mutations such as sW172stop/sL173F has been reported. However, the clinical consequences of such surface mutations have not been determined. The aim of this study was to determine the surface gene sequence in ADV-resistant patients carrying the A181T/V mutation and to describe the clinical significance. Of the 22 patients included in this study, 13 were ADV-resistant with rtA181T/V mutations (polymerase mutation group, Group P) and nine were antiviral treatment-naive (control group, Group C). The Pre-S1 gene mutation, V60A, was detected in 11 patients (Group P=8, Group C=3). A start codon mutation in the Pre-S2 gene was found in five patients (Group P=3, Group C=2). An S gene mutation, sA184V, was found in nine patients, all of whom were in group P. Although sW172stop and sL173F mutations were detected, reduced HBsAg titer was not observed. Further study of these mutations and their clinical implications are needed.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenine/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Adult
Aged
Amino Acid Sequence
Amino Acid Substitution
Antiviral Agents/*therapeutic use
Codon, Initiator
DNA-Directed DNA Polymerase/*genetics
Demography
Drug Resistance, Viral/genetics
Female
Genotype
Hepatitis B Surface Antigens/*genetics/metabolism
Hepatitis B, Chronic/*drug therapy
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Molecular Sequence Data
Organophosphonates/*therapeutic use
Point Mutation
Viral Proteins/*genetics
Antiviral Agents
Codon, Initiator
Hepatitis B Surface Antigens
Organophosphonates
Viral Proteins
Adenine
DNA-Directed DNA Polymerase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bartholomeusz A, Locarnini S. Hepatitis B virus mutations associated with antiviral therapy. J Med Virol. 2006. 78:Suppl 1. S52–S55.
Article2. Locarnini S, Mason WS. Cellular and virological mechanisms of HBV drug resistance. J Hepatol. 2006. 44:422–431.
Article3. Torresi J. The virological and clinical significance of mutations in the overlapping envelope and polymerase genes of hepatitis B virus. J Clin Virol. 2002. 25:97–106.
Article4. Hsu CW, Yeh CT, Chang ML, Liaw YF. Identification of a hepatitis B virus S gene mutant in lamivudine-treated patients experiencing HBsAg seroclearance. Gastroenterology. 2007. 132:543–550.
Article5. Lee SY, Choi MS, Lee D, Lee JH, Koh KC, Paik SW, Yoo BC. Overlapping gene mutations of hepatitis B virus in a chronic hepatitis B patient with hepatitis B surface antigen loss during lamivudine therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2005. 20:433–437.
Article6. Yeon JE, Yoo W, Hong SP, Chang YJ, Yu SK, Kim JH, Seo YS, Chung HJ, Moon MS, Kim SO, Byun KS, Lee CH. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil in lamivudine resistant chronic hepatitis B patients treated with adefovir dipivoxil. Gut. 2006. 55:1488–1495.
Article7. Rozanov M, Plikat U, Chappey C, Kochergin A, Tatusova T. A web-based genotyping resource for viral sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. 32:W654–W659.
Article8. Summers J, O'Connell A, Millman I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1975. 72:4597–4601.
Article9. Michel ML, Tiollais P. Structure and expression of the hepatitis B virus genome. Hepatology. 1987. 7:1 Suppl. 61S–63S.
Article10. Tiollais P, Pourcel C, Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985. 317:489–495.
Article11. Torresi J, Earnest-Silveira L, Deliyannis G, Edgtton K, Zhuang H, Locarnini SA, Fyfe J, Sozzi T, Jackson DC. Reduced antigenicity of the hepatitis B virus HBsAg protein arising as a consequence of sequence changes in the overlapping polymerase gene that are selected by lamivudine therapy. Virology. 2002. 293:305–313.
Article12. Angus P, Vaughan R, Xiong S, Yang H, Delaney W, Gibbs C, Brosgart C, Colledge D, Edwards R, Ayres A, Bartholomeusz A, Locarnini S. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil therapy associated with the selection of a novel mutation in the HBV polymerase. Gastroenterology. 2003. 125:292–297.
Article13. Choi MS, Kim DY, Lee DH, Lee JH, Koh KC, Paik SW, Rhee JC, Yoo BC. Clinical significance of pre-S mutations in patients with genotype C hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat. 2007. 14:161–168.
Article14. Chen CH, Hung CH, Lee CM, Hu TH, Wang JH, Wang JC, Lu SN, Changchien CS. Pre-S deletion and complex mutations of hepatitis B virus related to advanced liver disease in HBeAg-negative patients. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133:1466–1474.
Article15. Raimondo G, Costantino L, Caccamo G, Pollicino T, Squadrito G, Cacciola I, Brancatelli S. Non-sequencing molecular approaches to identify preS2-defective hepatitis B virus variants proved to be associated with severe liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2004. 40:515–519.
Article16. Preikschat P, Gunther S, Reinhold S, Will H, Budde K, Neumayer HH, Kruger DH, Meisel H. Complex HBV populations with mutations in core promoter, C gene, and pre-S region are associated with development of cirrhosis in long-term renal transplant recipients. Hepatology. 2002. 35:466–477.
Article17. Fan YF, Lu CC, Chen WC, Yao WJ, Wang HC, Chang TT, Lei HY, Shiau AL, Su IJ. Prevalence and significance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) pre-S mutants in serum and liver at different replicative stages of chronic HBV infection. Hepatology. 2001. 33:277–286.
Article18. Pollicino T, Zanetti AR, Cacciola I, Petit MA, Smedile A, Campo S, Sagliocca L, Pasquali M, Tanzi E, Longo G, Raimondo G. Pre-S2 defective hepatitis B virus infection in patients with fulminant hepatitis. Hepatology. 1997. 26:495–499.
Article19. Chen BF, Liu CJ, Jow GM, Chen PJ, Kao JH, Chen DS. High prevalence and mapping of pre-S deletion in hepatitis B virus carriers with progressive liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 2006. 130:1153–1168.
Article20. Sugauchi F, Ohno T, Orito E, Sakugawa H, Ichida T, Komatsu M, Kuramitsu T, Ueda R, Miyakawa Y, Mizokami M. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the development of preS deletions and advanced liver disease. J Med Virol. 2003. 70:537–544.
Article21. Mun HS, Lee SA, Jee Y, Kim H, Park JH, Song BC, Yoon JH, Kim YJ, Lee HS, Hyun JW, Hwang ES, Kook YH, Kim BJ. The prevalence of hepatitis B virus preS deletions occurring naturally in Korean patients infected chronically with genotype C. J Med Virol. 2008. 80:1189–1194.
Article22. Caselmann WH, Meyer M, Kekule AS, Lauer U, Hofschneider PH, Koshy R. A trans-activator function is generated by integration of hepatitis B virus preS/S sequences in human hepatocellular carcinoma DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990. 87:2970–2974.
Article23. Olinger CM, Weber B, Otegbayo JA, Ammerlaan W, van der Taelem-Brule N, Muller CP. Hepatitis B virus genotype E surface antigen detection with different immunoassays and diagnostic impact of mutations in the preS/S gene. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2007. 196:247–252.
Article24. Carman WF, Zanetti AR, Karayiannis P, Waters J, Manzillo G, Tanzi E, Zuckerman AJ, Thomas HC. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet. 1990. 336:325–329.
Article25. Koyanagi T, Nakamuta M, Sakai H, Sugimoto R, Enjoji M, Koto K, Iwamoto H, Kumazawa T, Mukaide M, Nawata H. Analysis of HBs antigen negative variant of hepatitis B virus: unique substitutions, Glu129 to Asp and Gly145 to Ala in the surface antigen gene. Med Sci Monit. 2000. 6:1165–1169.26. Ohnuma H, Machida A, Okamoto H, Tsuda F, Sakamoto M, Tanaka T, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M. Allelic subtypic determinants of hepatitis B surface antigen (i and t) that are distinct from d/y or w/r. J Virol. 1993. 67:927–932.
Article27. Yamamoto K, Horikita M, Tsuda F, Itoh K, Akahane Y, Yotsumoto S, Okamoto H, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M. Naturally occurring escape mutants of hepatitis B virus with various mutations in the S gene in carriers seropositive for antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1994. 68:2671–2676.
Article28. Okamoto H, Yano K, Nozaki Y, Matsui A, Miyazaki H, Yamamoto K, Tsuda F, Machida A, Mishiro S. Mutations within the S gene of hepatitis B virus transmitted from mothers to babies immunized with hepatitis B immune globulin and vaccine. Pediatr Res. 1992. 32:264–268.
Article29. Kohno H, Inoue T, Tsuda F, Okamoto H, Akahane Y. Mutations in the envelope gene of hepatitis B virus variants co-occurring with antibody to surface antigen in sera from patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Gen Virol. 1996. 77(Pt 8):1825–1831.
Article30. Tatti KM, Korba BE, Stang HL, Peek S, Gerin JL, Tennant BC, Schinazi RF. Mutations in the conserved woodchuck hepatitis virus polymerase FLLA and YMDD regions conferring resistance to lamivudine. Antiviral Res. 2002. 55:141–150.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Resistance to Adefovir in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Efficacy of New Anti-viral Agent in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B
- Antiviral Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B and C: Current Update
- Lamivudine-Resistance in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B and/or Cirrhosis and Detection of Mutations in YMDD Motif of Hepatitis B Virus Genome
- Long-Term Outcomes and Dynamics of Mutants Associated with Lamivudine-Adefovir Rescue Therapy in Patients with Lamivudine-Resistant Chronic Hepatitis B