J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Nov;25(11):1574-1581. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.11.1574.
Disruption of Microtubules Sensitizes the DNA Damage-induced Apoptosis Through Inhibiting Nuclear Factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) DNA-binding Activity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmacology, Research Institute for Medical Science, Daejeon Regional Cancer Center, Daejeon, Korea. gmhur@cnu.ac.kr
- 2Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 1779226
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.11.1574
Abstract
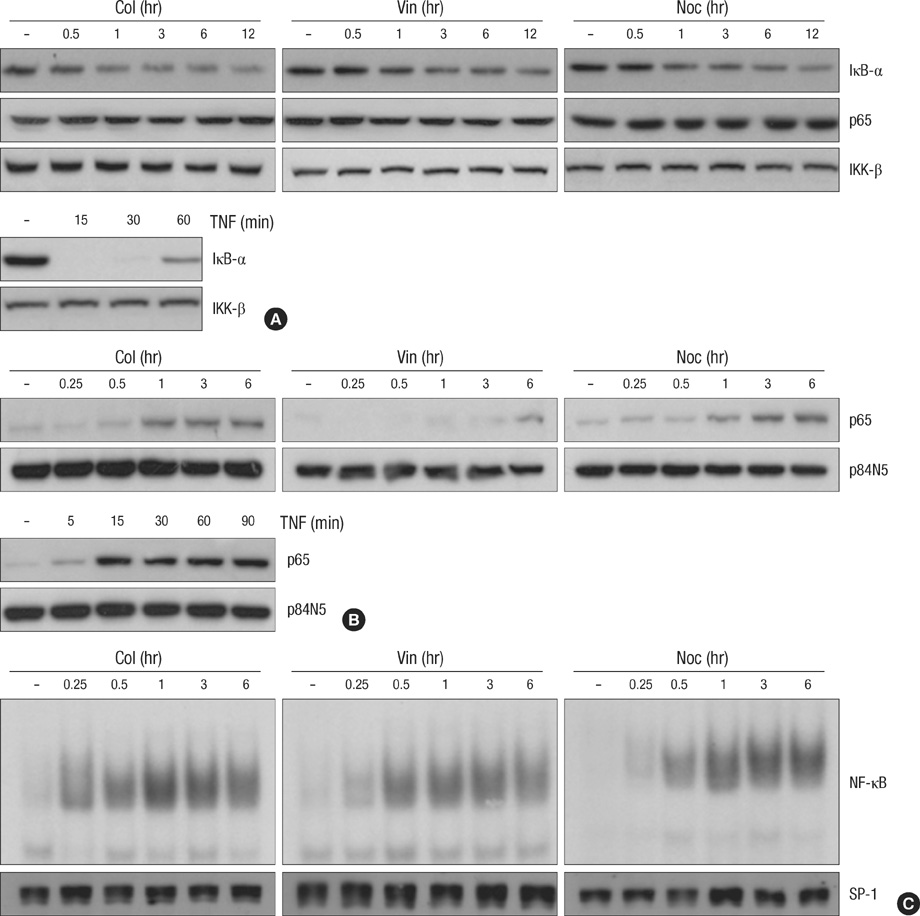
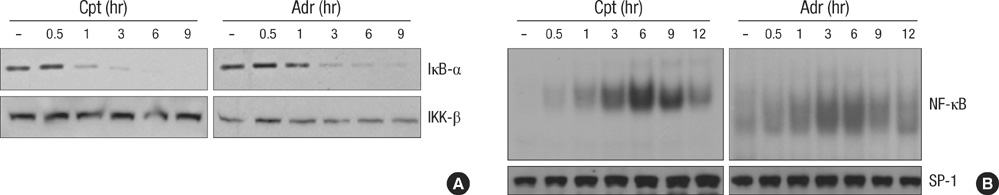
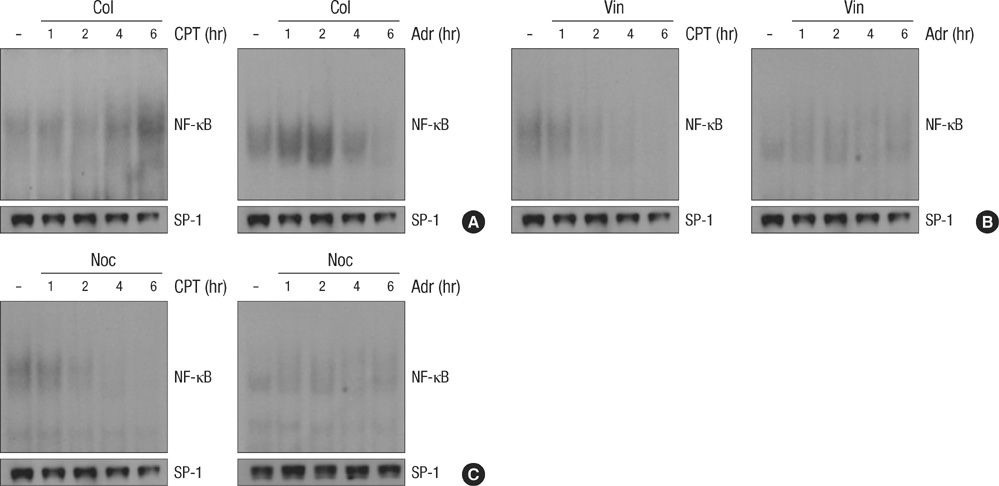
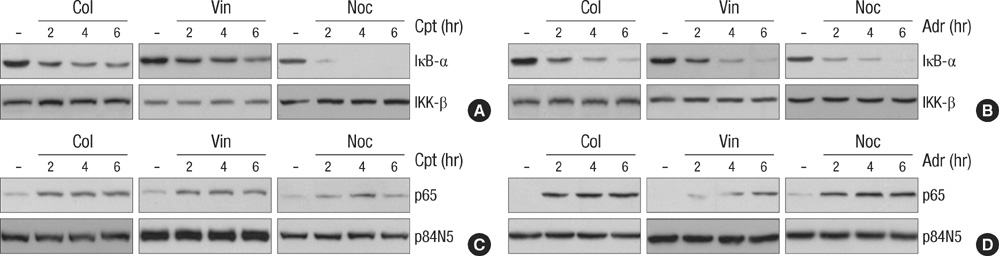
- The massive reorganization of microtubule network involves in transcriptional regulation of several genes by controlling transcriptional factor, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) activity. The exact molecular mechanism by which microtubule rearrangement leads to NF-kappaB activation largely remains to be identified. However microtubule disrupting agents may possibly act in synergy or antagonism against apoptotic cell death in response to conventional chemotherapy targeting DNA damage such as adriamycin or comptothecin in cancer cells. Interestingly pretreatment of microtubule disrupting agents (colchicine, vinblastine and nocodazole) was observed to lead to paradoxical suppression of DNA damage-induced NF-kappaB binding activity, even though these could enhance NF-kappaB signaling in the absence of other stimuli. Moreover this suppressed NF-kappaB binding activity subsequently resulted in synergic apoptotic response, as evident by the combination with Adr and low doses of microtubule disrupting agents was able to potentiate the cytotoxic action through caspase-dependent pathway. Taken together, these results suggested that inhibition of microtubule network chemosensitizes the cancer cells to die by apoptosis through suppressing NF-kappaB DNA binding activity. Therefore, our study provided a possible anti-cancer mechanism of microtubule disrupting agent to overcome resistance against to chemotherapy such as DNA damaging agent.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibiotics, Antineoplastic/therapeutic use
*Apoptosis
Caspases/metabolism
Cell Line
Colchicine/pharmacology
DNA/metabolism
*DNA Damage
Doxorubicin/therapeutic use
Humans
Mice
Microtubules/chemistry/*drug effects/metabolism
NF-kappa B/antagonists & inhibitors/*metabolism
Neoplasms/drug therapy
Nocodazole/pharmacology
Protein Binding
Signal Transduction
Tubulin Modulators/*pharmacology
Vinblastine/pharmacology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karin M, Greten FR. NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005. 5:749–759.2. Lin Y, Bai L, Chen W, Xu S. The NF-kappaB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. 14:45–55.3. Brown K, Gerstberger S, Carlson L, Franzoso G, Siebenlist U. Control of I kappa B-alpha proteolysis by site-specific, signal-induced phosphorylation. Science. 1995. 267:1485–1488.
Article4. Hur GM, Lewis J, Yang Q, Lin Y, Nakano H, Nedospasov S, Liu ZG. The death domain kinase RIP has an essential role in DNA damage-induced NF-kappaB activation. Genes Dev. 2003. 17:873–882.5. Waddick KG, Uckun FM. Innovative treatment programs against cancer: II. Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) as a molecular target. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. 57:9–17.6. Daroczi B, Kari G, Ren Q, Dicker AP, Rodeck U. Nuclear factor kappaB inhibitors alleviate and the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 exacerbates radiation toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009. 8:2625–2634.7. Li F, Sethi G. Targeting transcription factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. 1805:167–180.8. Egan LJ, Eckmann L, Greten FR, Chae S, Li ZW, Myhre GM, Robine S, Karin M, Kagnoff MF. IkappaB-kinasebeta-dependent NF-kappaB activation provides radioprotection to the intestinal epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004. 101:2452–2457.9. Starenki D, Namba H, Saenko V, Ohtsuru A, Yamashita S. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB cascade potentiates the effect of a combination treatment of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. 89:410–418.10. Ahmed KM, Li JJ. ATM-NF-kappaB connection as a target for tumor radiosensitization. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007. 7:335–342.11. Fan Y, Dutta J, Gupta N, Fan G, Gélinas C. Regulation of programmed cell death by NF-kappaB and its role in tumorigenesis and therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. 615:223–250.12. Nadiminty N, Lou W, Sun M, Chen J, Yue J, Kung HJ, Evans CP, Zhou Q, Gao AC. Aberrant activation of the androgen receptor by NF-kappaB2/p52 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010. 70:3309–3319.13. Puvvada SD, Funkhouser WK, Greene K, Deal A, Chu H, Baldwin AS, Tepper JE, O'Neil BH. NF-kB and Bcl-3 activation are prognostic in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2010. 78:181–188.14. Rosette C, Karin M. Cytoskeletal control of gene expression: depolymerization of microtubules activates NF-kappaB. J Cell Biol. 1995. 128:1111–1119.15. Das KC, White CW. Activation of NF-kappaB by antineoplastic agents. Role of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:14914–14920.16. Mackenzie GG, Keen CL, Oteiza PI. Microtubules are required for NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in neuroblastoma IMR-32 cells: modulation by zinc. J Neurochem. 2006. 99:402–415.17. Mikenberg I, Widera D, Kaus A, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C. Transcription factor NF-kappaB is transported to the nucleus via cytoplasmic dynein/dynactin motor complex in hippocampal neurons. PLoS One. 2007. 2:e589.18. Devary Y, Rosette C, DiDonato JA, Karin M. NF-kappaB activation by ultraviolet light not dependent on a nuclear signal. Science. 1993. 261:1442–1445.19. Doostzadeh-Cizeron J, Terry NH, Goodrich DW. The nuclear death domain protein p84N5 activates a G2/M cell cycle checkpoint prior to the onset of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2001. 276:1127–1132.
Article20. Kim R, Emi M, Tanabe K. Caspase-dependent and -independent cell death pathways after DNA damage (Review). Oncol Rep. 2005. 14:595–599.
Article21. Berenson JR, Ma HM, Vescio R. The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the biology and treatment of multiple myeloma. Semin Oncol. 2001. 28:626–633.22. Um JH, Kang CD, Lee BG, Kim DW, Chung BS, Kim SH. Increased and correlated nuclear factor-kappa B and Ku autoantigen activities are associated with development of multidrug resistance. Oncogene. 2001. 20:6048–6056.
Article23. Meulmeester E, Jochemsen AG. p53: a guide to apoptosis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008. 8:87–97.
Article24. Green DR, Kroemer G. Cytoplasmic functions of the tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 2009. 458:1127–1130.
Article25. Schuler M, Green DR. Mechanisms of p53-dependent apoptosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. 29:684–688.
Article26. Shen Y, White E. p53-dependent apoptosis pathways. Adv Cancer Res. 2001. 82:55–84.
Article27. el-Deiry WS. Role of oncogenes in resistance and killing by cancer therapeutic agents. Curr Opin Oncol. 1997. 9:79–87.
Article28. Pérez-Tomás R. Multidrug resistance: retrospect and prospects in anti-cancer drug treatment. Curr Med Chem. 2006. 13:1859–1876.29. Németh ZH, Deitch EA, Davidson MT, Szabó C, Vizi ES, Haskó G. Disruption of the actin cytoskeleton results in nuclear factor-kappaB activation and inflammatory mediator production in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2004. 200:71–81.30. Mikenberg I, Widera D, Kaus A, Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C. TNF-alpha mediated transport of NF-kappaB to the nucleus is independent of the cytoskeleton-based transport system in non-neuronal cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. 85:529–536.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differential Regulation of NF-kappaB Signaling during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection
- Rifampicin Inhibits the LPS-induced Expression of Toll-like Receptor 2 via the Suppression of NF-kappaB DNA-binding Activity in RAW 264.7 Cells
- The Proteasome Inhibitor MG132 Sensitizes Lung Cancer Cells to TRAIL-induced Apoptosis by Inhibiting NF-kappaB Activation
- beta-Lapachone suppresses radiation-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB
- The Inhibitory Effect of Epicatechin on IL-1beta -induced iNOS Expression and NO Production in RINm5F Cell