J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Jun;20(3):390-396. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.390.
Pharaoh Ant (Monomorium pharaonis): Newly Identified Important Inhalant Allergens in Bronchial Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cshong@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 3Institute of Allergy, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1778495
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.390
Abstract
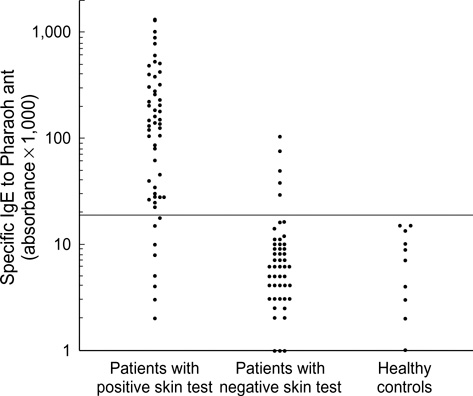
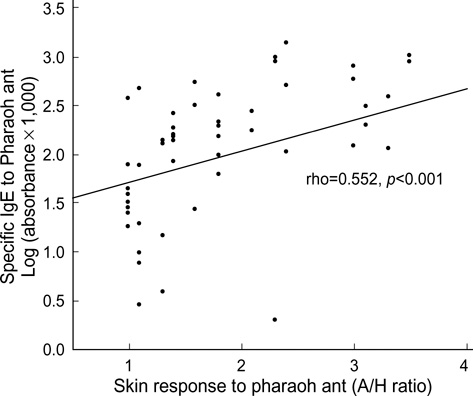
- The nonstinging house ant, Monomorium pharaonis (pharaoh ant), was recently identified as a cause of respiratory allergy. This study was performed to evaluate the extent of sensitization to pharaoh ant, and its clinical significance in asthmatic patients. We carried out skin prick tests in 318 patients with asthma. Specific IgE (sIgE) to pharaoh ant was measured by ELISA, and cross-reactivity was evaluated by ELISA inhibition tests. Bronchial provocation testing was performed using pharaoh ant extracts. Fifty-eight (18.2%) of 318 patients showed positive skin responses to pharaoh ant, and 25 (7.9%) had an isolated response to pharaoh ant. Positive skin responses to pharaoh ant were significantly higher among patients with non-atopic asthma than among those with atopic asthma (26.0% vs. 14.9%, p<0.05). There was significant correlation between sIgE level and skin responses to pharaoh ant (rho=0.552, p<0.001). The ELISA inhibition tests indicated that pharaoh ant allergens had various pattern of cross-reactivity to house dust mites and cockroaches. Bronchial provocation tests to pharaoh ant were conducted for 9 patients, and eight showed typical asthmatic reactions. In conclusion, pharaoh ant is an important source of aeroallergens, and it should be included in the skin test battery for screening the causative allergens in patients with asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lierl MB, Riordan MM, Fischer TJ. Prevalence of insect allergen-specific IgE in allergic asthmatic children in Cincinnati, Ohio. Ann Allergy. 1994. 72:45–50.2. Tee RD, Gordon DJ, Hawkins ER, Nunn AJ, Lacey J, Venables KM, Cooter RJ, McCaffery AR, Newman Taylor AJ. Occupational allergy to locusts: an investigation of the sources of the allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988. 81:517–525.
Article3. Bagenstose AH III, Mathews KP, Homburger HA, Saaveard-Delgado AP. Inhalant allergy due to crickets. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980. 65:71–74.4. Komase Y, Sakata M, Azuma T, Tanaka A, Nakagawa T. IgE antibodies against midge and moth found in Japanese asthmatic subjects and comparison of allergenicity between these insects. Allergy. 1997. 52:75–81.
Article5. Focke M, Hemmer W, Wohrl S, Gotz M, Jarisch R, Kofler H. Specific sensitization to the common housefly (Musca domestica) not related to insect panallergy. Allergy. 2003. 58:448–451.
Article6. van Wijnen JH, Verhoeff AP, Mulder-Folkerts DK, Brachel HJ, Schou C. Cockroach allergen in house dust. Allergy. 1997. 52:460–464.
Article7. Rosenstreich DL, Eggleston P, Kattan M, Baker D, Slavin RG, Gergen P, Mitchell H, McNiff-Mortimer K, Lynn H, Ownby D, Malveaux F. The role of cockroach allergy and exposure to cockroach allergen in causing morbidity among inner-city children with asthma. N Engl J Med. 1997. 336:1356–1363.
Article8. Lewis SA, Weiss ST, Platts-Mills TA, Burge H, Gold DR. The role of indoor allergen sensitization and exposure in causing morbidity in women with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:961–966.
Article9. Kim CW, Choi SY, Park JW, Hong CS. Respiratory allergy to the indoor ant (Monomorium pharaonis) not related to sting allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005. 94:301–306.
Article10. Swanson MC, Agarwal MK, Reed CE. An immunochemical approach to indoor aeroallergen quantitation with a new volumetric air sampler: studies with mite, roach, cat, mouse, and guinea pig antigens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985. 76:724–729.
Article11. Kino T, Chihara J, Fukuda K, Sasaki Y, Shogaki Y, Oshima S. Allergy to insects in Japan. III. High frequency of IgE antibody responses to insects (moth, butterfly, caddis fly, and chironomid) in patients with bronchial asthma and immunochemical quantitation of the insect-related airborne particles smaller than 10 microns in diameter. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1987. 79:857–866.12. Wynn SR, Swanson MC, Reed CE, Penny ND, Showers WB, Smith JM. Immunochemical quantitation, size distribution, and cross-reactivity of lepidoptera (moth) aeroallergens in southeastern Minnesota. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988. 82:47–54.
Article13. Holldobler B, Wilson EO. The ants: classification and origins. 1990. Cambridge (MA): The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press;4–141.14. Choi BM, Masaki K, Choi MK. Study on distribution of ants (Formicidae) from Korea (II): formic fauna in Mt. Halla [in Korean]. Cheong Ju Tea Coll. 1985. 22:439–462.15. Hoffman DR, Dove DE, Moffitt JE, Stafford CT. Allergens in Hymenoptera venom. XXI. Cross-reactivity and multiple reactivity between fire ant venom and bee and wasp venoms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988. 82:828–834.
Article16. Witteman AM, Akkerdaas JH, van Leeuwen J, van der Zee JS, Aalberse RC. Identification of a cross-reactive allergen (presumably tropomyosin) in shrimp, mite and insects. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1994. 105:56–61.
Article17. Panzani RC, Ariano R. Arthropods and invertebrates allergy (with the exclusion of mites): the concept of panallergy. Allergy. 2001. 56:Suppl 69. 1–22.
Article18. Gupta S, Jain S, Chaudhry S, Agarwal MK. Role of insects as inhalant allergens in bronchial asthma with special reference to the clinical characteristics of patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 1990. 20:519–524.
Article19. Tariq SM, Matthews SM, Hakim EA, Stevens M, Arshad SH, Hide DW. The prevalence of and risk factors for atopy in early childhood: a whole population birth cohort study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 101:587–593.
Article20. Nickel R, Kulig M, Forster J, Bergmann R, Bauer CP, Lau S, Guggenmoos-Holzmann I, Wahn U. Sensitization to hen's egg at the age of twelve months is predictive for allergic sensitization to common indoor and outdoor allergens at the age of three years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. 99:613–617.
Article21. Reed CE. The natural history of asthma in adults: the problem of irreversibility. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 103:539–547.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Newly sensitization to house dust mite in an isocyanate-induced asthmatic patient
- A comparison of Sensitization to Major Indoor & Outdoor Inhalant Allergens in Children with Respiratory Allergic Diseases
- Changing sensitization rate to common inhalant allergens in our environment
- Changing patterns of skin reactivity to inhalant allergens in asthmatic patients
- Prevalence and Clinical Significance of New Sensitization to Inhalant Allergens in Toluene Diisocyanate-induced Asthmatic Patients