J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Jun;21(3):577-580. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.577.
Langerhans Cell Sarcoma Arising from Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea. jhlee@gaechuk.gsnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 1778449
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.577
Abstract
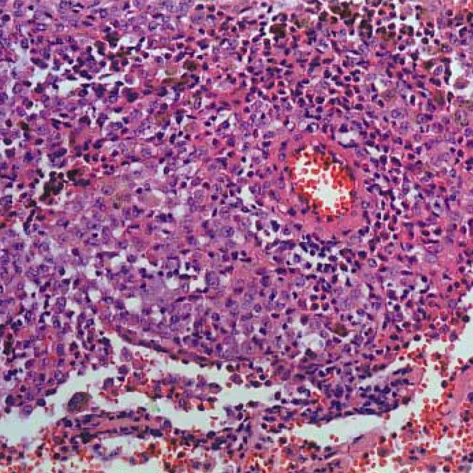
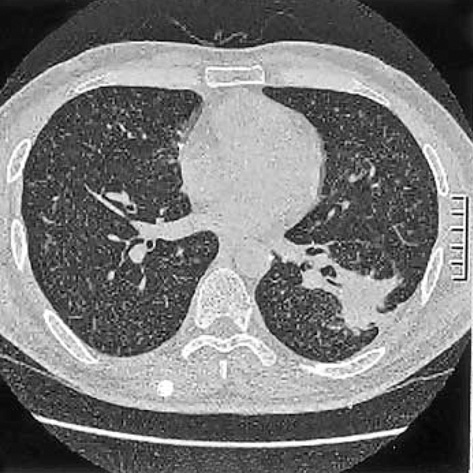
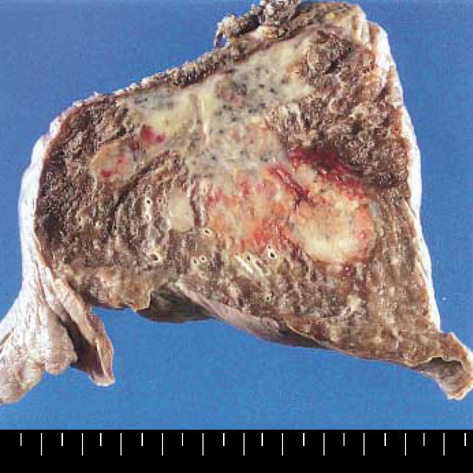
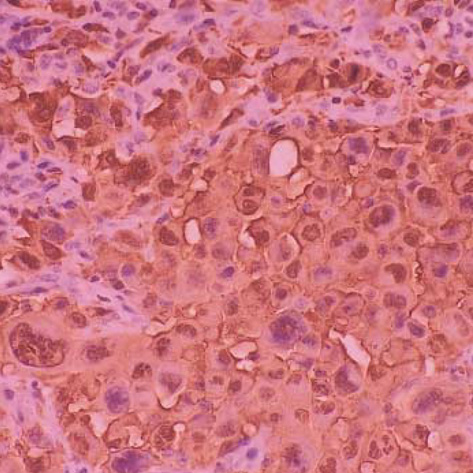
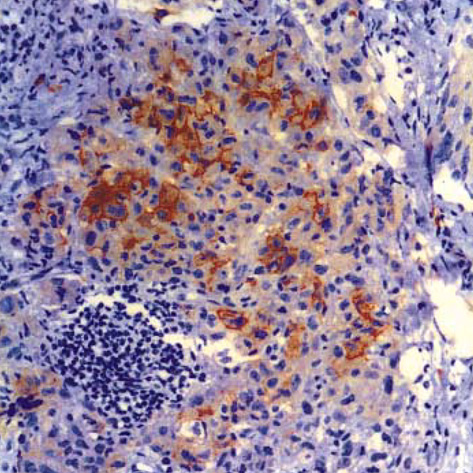
- Langerhans cell sarcoma (LCS) is a neoplastic proliferation of Langerhans cells that have overtly malignant cytologic features. It is a very rare disease and theoretically, it can present de novo or progress from an antecedent Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH). However, to our knowledge, LCS arising from an antecedent LCH has not been reported on. We present here a case of LCS arising from a pulmonary LCH. A 34 yr-old man who was a smoker, had a fever and a chronic cough. Computed tomographic (CT) scan revealed multiple tiny nodules in both lungs. The thoracoscopic lung biopsy revealed LCH. The patient quit smoking, but he received no other specific treatment. One year later, the follow up chest CT scan showed a 4 cm-sized mass in the left lower lobe of the lung. A lobectomy was then performed. Microscopic examination of the mass revealed an infiltrative proliferation of large cells that had malignant cytologic features. Immunohistochemical stains showed a strong reactivity for S-100 and CD68, and a focal reactivity for CD1a. We think this is the first case of LCS arising from LCH.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Sarcoma/*pathology
S100 Proteins/biosynthesis
Radiography, Thoracic
Pancreatic Neoplasms/*pathology
Male
Langerhans Cells/*pathology
Immunohistochemistry
Humans
Histiocytosis, Langerhans-Cell/diagnosis/*pathology
Gene Expression Regulation, Neoplastic
Antigens, Differentiation, Myelomonocytic/biosynthesis
Antigens, CD1/biosynthesis
Antigens, CD/biosynthesis
Adult
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Langerhans Cell Sarcoma Presenting as Submandibular Gland Mass
Geonho Lee, Kunho Song, Ki Wan Park, Bon Seok Koo
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2019;62(9):520-523. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2018.00661.
Reference
-
1. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW. WHO classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 2001. Lyon: IARCPress;283.2. Ben-Ezra J, Bailey A, Azumi N, Delsol G, Stroup R, Sheibani K, Rappaport H. Malignant histiocytosis X. A distinct clinicopathologic entity. Cancer. 1991. 68:1050–1060.
Article3. Imamura M, Sakamoto S, Hanazono H. Malignant histiocytosis: a case of generalized histiocytosis with infiltration of Langerhans' granule-containing histiocytes. Cancer. 1971. 28:467–475.
Article4. Henderson DW, Sage RE. Malignant histiocytosis with eosinophilia. Cancer. 1973. 32:1421–1428.
Article5. Wood C, Wood GS, Deneau DG, Oseroff A, Beckstead JH, Malin J. Malignant histiocytosis X. Report of a rapidly fatal case in an elderly man. Cancer. 1984. 54:347–352.
Article6. Bonetti F, Knowles DM, Chilosi M, Pisa R, Fiaccavento S, Rizzuto N, Zamboni G, Menestrina F, Fiore-Donati L. A distinctive cutaneous malignant neoplasm expressing the Langerhans cell phenotype: synchronous occurrence with B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer. 1985. 55:2417–2425.
Article7. Goldberg NS, Bauer K, Rosen ST, Caro WA, Marder RJ, Zugerman C, Rao S, Variakojis D. Histiocytosis X. Flow cytometric DNA-content and immunohistochemical and ultrastructural analysis. Arch Dermatol. 1986. 122:446–450.
Article8. Delabie J, De Wolf-Peeters C, De Vos R, Vandenberghe E, Kennes K, De Jonge I, Desmet V. True histiocytic neoplasm of Langerhans' cell type. J Pathol. 1991. 163:217–223.
Article9. Tani M, Ishii N, Kumagai M, Ban M, Sasase A, Mishima Y. Malignant Langerhans cell tumor. Br J Dermatol. 1992. 126:398–403.10. Itoh H, Miyaguni H, Kataoka H, Akiyama Y, Tateyama S, Marutsuka K, Asada Y, Ogata K, Koono M. Primary cutaneous Langerhans cell histiocytosis showing malignant phenotype in an elderly woman: report of a fatal case. J Cutan Pathol. 2001. 28:371–378.
Article11. Misery L, Godard W, Hamzeh H, Levigne V, Vincent C, Perrot JL, Gentil-Perret A, Schmitt D, Cambazard F. Malignant Langerhans cell tumor: a case with a favorable outcome associated with the absence of blood dendritic cell proliferation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003. 49:527–529.
Article12. Risdall RJ, Dehner LP, Duray P, Kobrinsky N, Robison L, Nesbit ME Jr. Histiocytosis X (Langerhans' cell histiocytosis). Prognostic role of histopathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983. 107:59–63.13. Frederiksen P, Thommesen P. Histiocytosis X: II. Histologic appearance correlated to prognosis and extent of disease. Acta Radiol Oncol Radiat Phys Biol. 1978. 17:10–16.
Article14. Howarth DM, Gilchrist GS, Mullan BP, Wiseman GA, Edmonson JH, Schomberg PJ. Langerhans cell histiocytosis: diagnosis, natura history, management, and outcome. Cancer. 1999. 85:2278–2290.15. Shinzato M, Shamoto M, Hosokawa S, Kaneko C, Osada A, Shimizu M, Yoshida A. Differentiation of Langerhans cells from interdigitating cells using CD1a and S-100 protein antibodies. Biotech Histochem. 1995. 70:114–118.
Article16. Lee JR, Choi GS, Koo SW, Lee SC, Kim YK. Langerhans cell histiocytosis presenting as a solitary nodule. Korean J Dermatol. 2001. 39:459–462.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax due to Pulmonary Invasion in Multisystemic Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A case report
- A Case of Orbital Langerhans' cell histiocytosis
- A Case of Pulmonary Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis with Pneumothorax
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis With Secondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst in a 9-Year-Old Boy’s Femur: A Case Report
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis Presenting as a Solitary Nodule