J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Jun;21(3):412-417. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.412.
Circulating Autoantibodies in Patients with Aspirin-intolerant Asthma: An Epiphenomenon Related to Airway Inflammation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pulmonology and Allergy, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1778420
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.3.412
Abstract
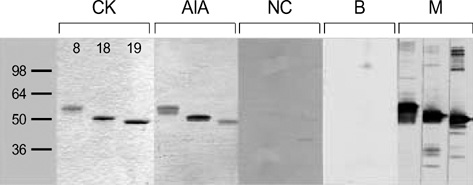
- Several studies have suggested the involvement of an autoimmune mechanism in aspirin (ASA)-intolerant asthma. To test this hypothesis, we measured the levels of circulating autoantibodies, such as IgG and IgA to tissue transglutaminase (TGase), IgG to cytokeratins (CKs) 8, 18, and 19, Clq-binding immune complex (CIC), and antinuclear antibody (ANA), in the sera of 79 patients with ASA-intolerant asthma (Group I) and those of two control groups, consisting of 61 patients with ASA-tolerant asthma (Group II) and 88 healthy control subjects (Group III) by means of ELISA. Significantly higher prevalences of IgG antibodies to CK18 (13.9%) and CK19 (17.7%) were noted in Group I, as compared with Group III (p<0.05 for all) not with Group II. Regarding the prevalences of other autoantibodies, the levels of ANA (1.3%), IgG to TGase (3.8%), and CIC (24.7%) in Group I were not significantly different from those in Groups II and III. Significant correlations were found between positivities for the anti-CK18 and anti-CK19 autoantibodies and the PC20 methacholine values in the analysis of asthma Groups I and II vs. normal controls, (p=0.001 and p=0.003, respectively). Further studies are needed to explore the potential involvement of an autoantibody-mediated mechanism in the clinical manifestation of bronchial asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park HS. Aspirin-sensitive asthma. BioDrugs. 2000. 13:29–33.
Article2. Park HS, Cho YH, Kim SS, Kim HY, Nahm DH, Suh CH, Hahn MH. Prevalence of sensitivity to aspirin (ASA) and food additives in subjects diagnosed as having intrinsic asthma. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 18:662–671.3. Delaney JC. The diagnosis of aspirin idiosyncrasy by analgesic challenge. Clin Allergy. 1976. 6:177–181.
Article4. Szczeklik A, Nizankowska E, Duplaga M. Natural history of aspirin-induced asthma. AIANE Investigators. European Network on Aspirin-Induced Asthma. Eur Respir J. 2000. 16:432–436.5. Szczeklik A, Stevenson DD. Aspirin-induced asthma: advances in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:913–921.
Article6. Jawien J. A new insight into aspirin-induced asthma. Eur J Clin Invest. 2002. 32:134–138.
Article7. Venter JC, Fraser CM, Harrison LC. Autoantibodies to beta2-adrenergic receptors: a possible cause of adrenergic hyporesponsiveness in allergic rhinitis and asthma. Science. 1980. 207:1361–1363.8. Menon P, Menon V, Hilman BC, Wolf R, Bairnsfather L. Antinuclear antibodies and anticytoplasmic antibodies in bronchial asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1989. 84:937–943.
Article9. Szczeklik A, Nizankowska E, Serafin A, Dyczek A, Duplaga M, Musial J. Autoimmune phenomena in bronchial asthma with special reference to aspirin intolerance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 152:1753–1756.
Article10. Choi JH, Lee KW, Oh HB, Lee KJ, Suh YJ, Park CS, Park HS. HLA association in aspirin-intolerant asthma: DPB1*0301 as a strong marker in a Korean population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 113:562–564.11. Dekker JW, Nizankowska E, Schmitz-Schumann M, Pile K, Bochenek G, Dyczek A, Cookson WO, Szczeklik A. Aspirin-induced asthma and HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DPB1 genotypes. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997. 27:574–577.
Article12. Nahm DH, Lee YE, Yim EJ, Park HS, Yim HE, Kan Y, Kim JK. Identification of cytokeratin 18 as a bronchial epithelial autoantigen associated with nonallergic asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:1536–1539.
Article13. Micheli L, Cerretani D, Fiaschi AI, Giorgi G, Romeo MR, Runci FM. Effect of acetaminophen on glutathione levels in rat testis and lung. Environ Health Perspect. 1994. 102:Suppl 9. 63–64.
Article14. Bucchier F, Puddicombe SM, Lordan JL, Richter A, Buchanan D, Wilson SJ, Ward J, Zummo G, Howarth PH, Djukanovic R, Holgate ST, Davies DE. Asthmatic bronchial epithelium is more susceptible to oxidant-induced apoptosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. 27:179–185.
Article15. Caulin C, Salvesen GS, Oshima RG. Caspase cleavage of keratin 18 and reorganization of intermediate filaments during epithelial cell apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1997. 22:379–394.16. Leers MP, Kolgen W, Bjorklund V, Bergman T, Tribbick G, Persson B, Bjorklund P, Ramaekers FC, Bjorklund B, Nap M, Jornvall H, Schutte B. Immunocytochemical detection and mapping of a cytokeratin 18 neo-epitope exposed during early apoptosis. J Pathol. 1999. 187:567–572.
Article17. Chu PG, Weiss LM. Keratin expression in human tissues and neoplasms. Histology. 2002. 40:403–439.
Article18. Wisnewski AV, Srivastava R, Herick C, Xu L, Lemus R, Cain H, Magoski NM, Karol MH, Bottomly K, Redlich CA. Identification of human lung and skin proteins conjugated with hexamethylene diisocyanate in vitro and in vivo. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:2330–2336.19. Choi JH, Nahm DH, Kim SH, Kim YS, Suh CH, Park HS, Ahn SW. Increased levels of IgG to cytokeratin 19 in sera of patients with toluene diisocyanate-induced asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004. 93:293–298.
Article20. Schutte B, Henfling M, Kolgen W, Bouman M, Meex S, Leers MP, Nap M, Bjorklund V, Bjorklund P, Bjorklund B, Lane EB, Omary MB, Jornvall H, Ramaekers FC. Keratin 8/18 breakdown and reorganization during apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2004. 297:11–26.
Article21. Hintner H, Romani N, Stanzl U, Grubauner G, Fritsck P, Lawley TJ. Phagocytosis of keratin filament aggregates following opsonization with IgG-anti-keratin filament autoantibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1987. 88:176–182.
Article22. Szczeklik A. Aspirin-induced asthma as a viral disease. Clin Allergy. 1988. 18:15–20.
Article23. Martinet N, Bonnard L, Regnault V, Picard E, Burke L, Siat J, Grosdidier G, Martinet Y, Vignaud JM. In vivo transglutaminase type 1 expression in normal lung, preinvasive bronchial lesions, and lung cancer. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. 28:428–435.24. Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM. Transglutaminases: Nature's biological glues. Biochem J. 2002. 368:377–396.
Article25. Dobashi N, Fujita J, Murota M, Ohtsuki Y, Yamadori I, Yoshinouchi T, Ueda R, Bandoh S, Kamei T, Nishioka M, Ishida T, Takahara J. Elevation of anti-cytokeratin 18 antibody and circulating cytokeratin 18: anti-cytokeratin 18 antibody immune complexes in sera of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lung. 2000. 178:171–179.
Article26. Blobel GA, Moll R, Franke WW, Vogt-Moykopf I. Cytokeratins in normal lung and lung carcinomas. I. Adenocarcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas and cultured cell lines. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984. 45:407–429.27. Murota M, Nishioka M, Fujita J, Dobashi N, Wu F, Ohtsuki Y, Hojo S, Takahara J, Kuriyama S. Anti-cytokeratin antibodies in sera of the patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. 125:291–299.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- IL-13 Gene Polymorphisms are Associated With Rhinosinusitis and Eosinophilic Inflammation in Aspirin Intolerant Asthma
- IgG Subclass Distribution of Circulating IgG Autoantibodies to Airway Epithelial Cell Proteins in Adult Asthmatic Patients
- Analysis of Airway Epithelial Cell Autoantigens Recognized by IgG Autoantibodies from Patients with Severe Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Comparison of Plasma Eotaxin Family Level in Aspirin-Intolerant and Aspirin-Tolerant Asthma Patients
- Differences in MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and eosinophil inflammatory markers of nasal polyp homogenates between aspirin intolerant and tolerant asthma