J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Jan;24(Suppl 1):S183-S188. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S183.
Effects of Celecoxib and Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid on Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Nephrosis in the Rat
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea. iskwak@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea.
- 3Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1778160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S183
Abstract
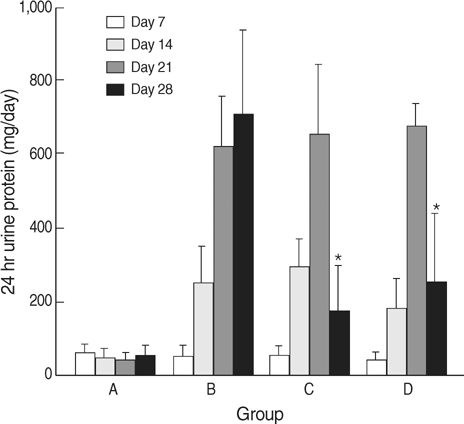
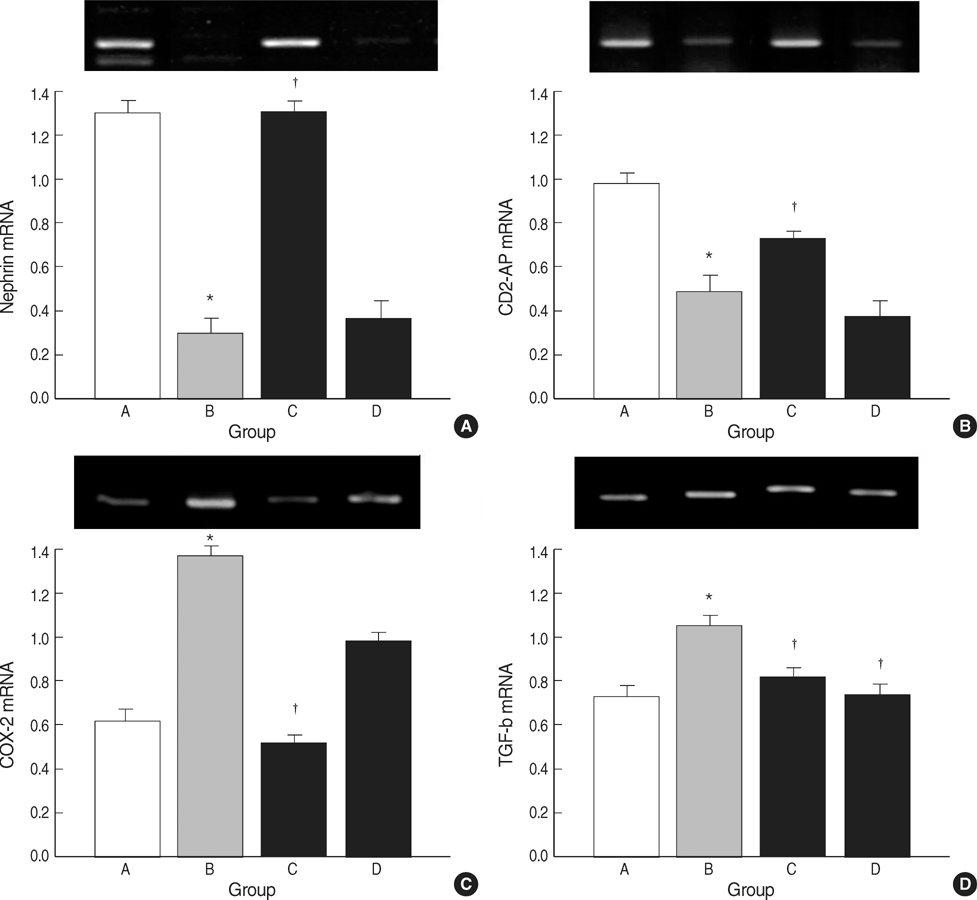
- The selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (LOX) inhibitors might inhibit prostaglandin synthesis and reduce proteinuria. The present study was designed to investigate the anti-proteinuric effects of nordihydroguaiaretic acid (NDGA) as compared with celecoxib in puromycin aminonucleoside (PAN) nephrosis rats. Fifty five male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 4 groups; A, normal control; B, PAN group; C, PAN+COX-2 inhibitor (celecoxib) group; and D, PAN+5-LOX inhibitor (NDGA) group. After induction of PAN nephrosis through repeated injections of PAN (7.5 and 15 mg/100 g body weight), rats were treated with celecoxib, NDGA, or vehicle for 2 weeks. Twenty four hour urine protein excretions were significantly lower in PAN+celecoxib and PAN+NDGA groups than in PAN group. Serum creatinine (SCr) concentrations and 24 hr urine creatinine clearances (CCr) were not significantly different in the four groups. Electron microscopy showed that podocyte morphology was changed after the induction of PAN nephrosis and was recovered after celecoxib or NDGA administration. Celecoxib significantly recovered the expressions of nephrin, CD2AP, COX-2, and TGF-beta. NDGA also recovered TGF-betaexpression, but did not alter the expressions of nephrin, CD2AP and COX-2. The present study suggested that celecoxib and NDGA might effectively reduce proteinuria in nephrotic syndrome without impairing renal function.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal/pharmacology
Body Weight
Creatinine/blood
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors/pharmacology
Male
Microscopy, Electron
Nephrosis/*chemically induced/drug therapy
Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid/*pharmacology
Podocytes/metabolism
Puromycin Aminonucleoside/pharmacology/*toxicity
Pyrazoles/*pharmacology
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Sulfonamides/*pharmacology
Time Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shankland SJ. The podocyte's response to injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2006. 69:2131–2147.
Article2. Mahan JD, Sisson RS, Vernier RL. Glomerular basement membrane anionic charge site change early in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Am J Pathol. 1986. 125:393–401.3. Furness PN, Turner DR, Cotton RE. Basement membrane charge in human glomerular disease. J Pathol. 1986. 150:267–278.
Article4. Washizawa K, Kasai S, Mori T, Komiyama A, Shigematsu H. Ultrastructural alteration of glomerular anionic sites in nephrotic patients. Pediatr Nephrol. 1993. 7:1–5.
Article5. Blume C, Heise G, Mhlfeld A, Bach D, Schrr K, Gerhardz CD, Grabensee B, Heering P. Effects of flosulide, a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, on passive Heymann nephritis in the rat. Kidney Int. 1999. 56:1770–1778.6. Emery P, Vane J, Botting J, Botting R, editors. Pharmacology, safety data and therapeutics of COX-2 inhibitors. Improved non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, COX-2 enzyme inhibitors. 1996. Hingham, MA: Kluwer;229–241.
Article7. Arteaga S, Andrade-Cetto A, Crdenas R. Larrea tridentata (Creosote bush), an abundant plant of Mexican and US-American deserts and its metabolite nordihydroguaiaretic acid. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005. 98:231–239.
Article8. Tries S, Laufer S, Radziwon P, Breddin HK. Antithrombotic and platelet function inhibiting effects of ML3000, a new anti-inflammatory drug with COX/5-LOX inhibitory activity. Inflamm Res. 2002. 51:129–134.
Article9. Salari H, Braquet P, Borgeat P. Comparative effects of indomethacin, acetylenic acids, 15-HETE, NDGA and BW755C on the metabolism of arachidonic acid in human leukocytes and platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1984. 13:53–60.10. Anjaneyulu M, Chopra K. Nordihydroguairetic acid, a lignin prevents oxidative stress and the development of diabetic nephropathy in rats. Pharmacology. 2004. 72:42–50.
Article11. Frenk S, Antonowicz I, Craig JM, Metcoff J. Experimental nephrotic syndrome induced in rats by aminonucleoside. Renal lesion and body electrolyte composition. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955. 89:424–427.12. Fishman JA, Karnovsky MJ. Effects of the aminonucleoside: puromycin on glomerular epithelial cells in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1985. 118:398–407.13. Bertram JF, Messina A, Ryan GB. In vitro effects of puromycin aminonucleoside on the ultrastructure of rat glomerular podocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1990. 260:555–563.
Article14. Farquhar MG, Palade GE. Glomerular permeability: II. ferritin transfer across the glomerular capillary wall in nephrotic rats. J Exp Med. 1961. 114:699–716.15. Furness PN, Harris K. An evaluation of experimental models of glomerulonephritis. Int J Exp Pathol. 1994. 75:9–22.16. Grond J, Weening JJ, Elema JD. Glomerular sclerosis in nephrotic rats. Comparison of the long-term effects of adriamycin and aminonucleoside. Lab Invest. 1984. 51:277–285.17. Marinides GN, Groggel GC, Cohen AH, Border WA. Enalapril and low protein reverse chronic puromycin aminonucleoside nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1990. 37:749–757.
Article18. Liu S, Li Y, Zhao H, Chen D, Huang Q, Wang S, Zou W, Zhang Y, Li X, Huang H. Increase in extracellular cross-linking by tissue transglutaminase and reduction in expression of MMP-9 contribute differentially to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006. 284:9–17.
Article19. Hagiwara M, Yamagata K, Capaldi RA, Koyama A. Mitochondrial dysfunction in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis of puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 2006. 69:1146–1152.
Article20. Wang JL, Cheng HF, Zhang MZ, McKanna JA, Harris RC. Selective increase of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in a model of renal ablation. Am J Physiol. 1998. 275:F613–F622.21. Wang JL, Cheng HF, Shappell S, Harris RC. A selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor decreases proteinuria and retards progressive renal injury in rats. Kidney Int. 2000. 57:2334–2342.
Article22. Cheng HF, Wang CJ, Moeckel GW, Zhang MZ, McKanna JA, Harris RC. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor blocks expression of mediators of renal injury in a model of diabetes and hypertension. Kidney Int. 2002. 62:929–939.23. Ezberci F, Tekin E, Onuk E. Protective effect of a lipoxygenase inhibitor, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, on the ileal motor disturbances induced by Serratia marcescens endotoxin in rats. Surg Today. 2001. 31:497–501.24. Kollman-Bauerly KA, Thomas DL, Adrian TE, Lien EL, Vanderhoof JA. The role of eicosanoids in the process of adaptation following massive bowel resection in the rat. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2001. 25:275–281.
Article25. Marchenko HI, Kotsiuruba VM, Butovych IA, Sorochyns'kyi AE, Zrazhevs'ka VK, Tumanovs'ka LV. The correction of disorders in arachidonic acid metabolism in coronary spasm of an immune origin. Fiziol Zh. 1994. 40:81–87.26. Cheng H, Wang S, Jo YI, Hao CM, Zhang M, Fan X, Kennedy C, Breyer MD, Moeckel GW, Harris RC. Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 predisposes to podocyte injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007. 18:551–559.
Article27. Poncelet AC, Schnaper HW. Regulation of human mesangial cell collagen expression by transforming growth factor-β1. Am J Physiol. 1998. 275:F458–F466.28. Suzuki S, Ebihara I, Tomino Y, Koide H. Transcriptional activation of matrix genes by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in mesangial cells. Exp Nephrol. 1993. 1:229–237.29. McKay NG, Khong TF, Haites NE, Power DA. The effects of transforming growth factor-beta 1 on mesangial cell fibronectin synthesis: increased incorporation into the extracellular matrix and reduced pI but no effect on alternative splicing. Exp Mol Pathol. 1993. 59:211–224.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of puromycin aminonucleoside on the cytoskeletal changes of glomerular epithelial cells
- Effect of Puromycin Aminonucleoside on Podocyte P-Cadherin
- Morphological Changes in Glomerular Epithelial Cells and Basement Membranes in Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induced Nephropathy
- The effects of lovastatin on puromycin aminonucleoside-induced focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in rats
- Effects of Dietary Salt Restriction on Puromycin Aminonucleoside Nephrosis: Preliminary Data