Electrolyte Blood Press.
2011 Dec;9(2):55-62. 10.5049/EBP.2011.9.2.55.
Effects of Dietary Salt Restriction on Puromycin Aminonucleoside Nephrosis: Preliminary Data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimgh@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2168385
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2011.9.2.55
Abstract
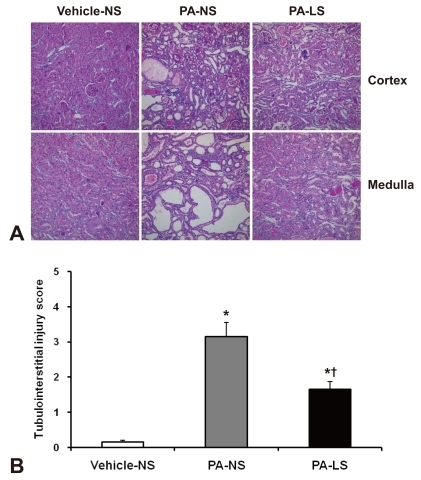
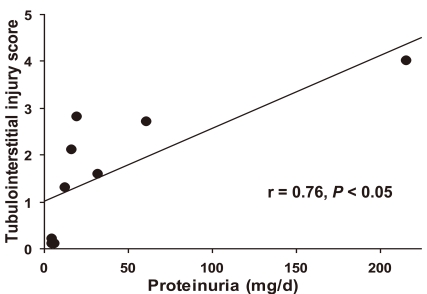
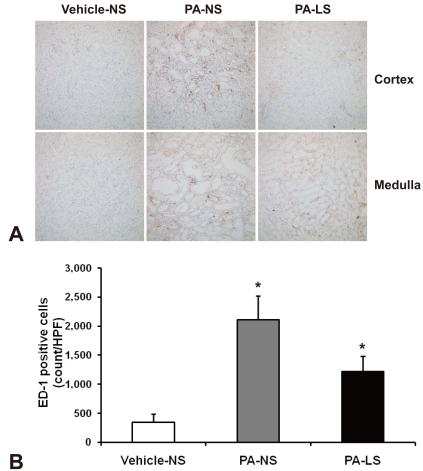
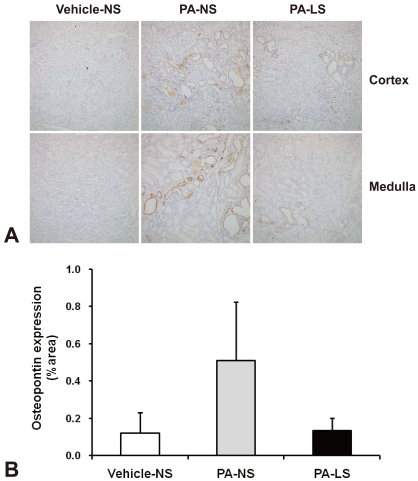
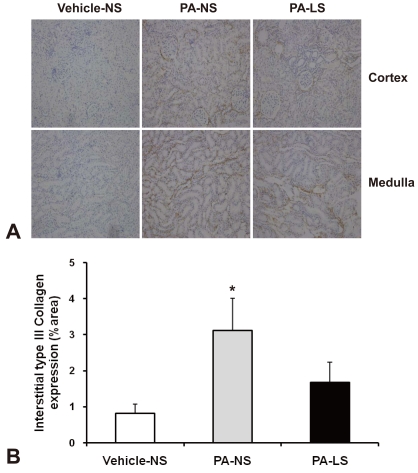
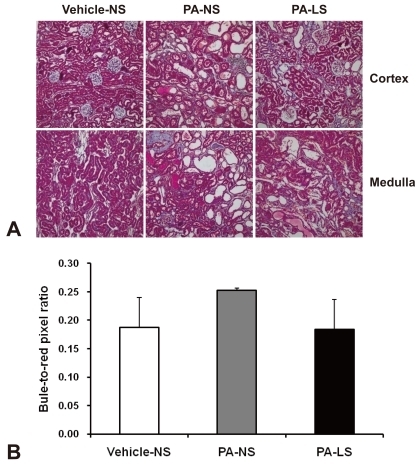
- Proteinuria is a major promoter that induces tubulointerstitial injury in glomerulopathy. Dietary salt restriction may reduce proteinuria, although the mechanism is not clear. We investigated the effects of dietary salt restriction on rat kidneys in an animal model of glomerular proteinuria. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were used and divided into 3 groups: vehicle-treated normal-salt controls, puromycin aminonucleoside (PA)-treated normal-salt rats, and PA-treated low-salt rats. PA was given at a dose of 150 mg/kg BW at time 0, followed by 50 mg/kg BW on days 28, 35, and 42. Sodium-deficient rodent diet with and without additional NaCl (0.5%) were provided for normal-salt rats and low-salt rats, respectively. On day 63, kidneys were harvested for histopathologic examination and immunohistochemistry. PA treatment produced overt proteinuria and renal damage. Dietary salt restriction insignificantly reduced proteinuria in PA-treated rats, and PA-treated low-salt rats had lower urine output and lower creatinine clearance than vehicle-treated normal-salt controls. When tubulointerstitial injury was semiquantitatively evaluated, it had a positive correlation with proteinuria. The tubulointerstitial injury score was significantly increased by PA treatment and relieved by low-salt diet. ED1-positive infiltrating cells and immunostaining for interstitial collagen III were significantly increased by PA treatment. These changes appeared to be less common in PA-treated low-salt rats, although the differences in PA-treated normal-salt versus low-salt rats did not reach statistical significance. Our results suggest that renal histopathology in PA nephrosis may potentially be improved by dietary salt restriction. Non-hemodynamic mechanisms induced by low-sodium diet might contribute to renoprotection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bohle A, Mackensen-Haen S, von Gise H. Significance of tubulointerstitial changes in the renal cortex for the excretory function and concentration ability of the kidney: a morphometric contribution. Am J Nephrol. 1987; 7:421–433. PMID: 3439552.
Article2. Risdon RA, Sloper JC, De Wardener HE. Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in renal-biopsy specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet. 1968; 2:363–366. PMID: 4173786.
Article3. Schainuck LI, Striker GE, Cutler RE, Benditt EP. Structural-functional correlations in renal disease. II. The correlations. Hum Pathol. 1970; 1:631–641. PMID: 5521736.4. Hirschberg R, Wang S. Proteinuria and growth factors in the development of tubulointerstitial injury and scarring in kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005; 14:43–52. PMID: 15586015.
Article5. Krikken JA, Laverman GD, Navis G. Benefits of dietary sodium restriction in the management of chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009; 18:531–538. PMID: 19713840.
Article6. Ying WZ, Sanders PW. Dietary salt modulates renal production of transforming growth factor-beta in rats. Am J Physiol. 1998; 274:F635–F641. PMID: 9575885.7. Ying WZ, Sanders PW. Dietary salt enhances glomerular endothelial nitric oxide synthase through TGF-beta1. Am J Physiol. 1998; 275:F18–F24. PMID: 9689000.8. Ying WZ, Sanders PW. Dietary salt intake activates MAP kinases in the rat kidney. FASEB J. 2002; 16:1683–1684. PMID: 12206991.9. Ying WZ, Aaron K, Sanders PW. Mechanism of dietary salt-mediated increase in intravascular production of TGF-beta1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008; 295:F406–F414. PMID: 18562633.10. Schiffer M, von Gersdorff G, Bitzer M, Susztak K, Bottinger EP. Smad proteins and transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000; 77:S45–S52. PMID: 10997690.11. Wang W, Koka V, Lan HY. Transforming growth factor-beta and Smad signalling in kidney diseases. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005; 10:48–56. PMID: 15705182.12. Nangaku M, Pippin J, Couser WG. Complement membrane attack complex (C5b-9) mediates interstitial disease in experimental nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:2323–2331. PMID: 10541291.
Article13. Hamrick MW, Arounleut P, Kellum E, Cain M, Immel D, Liang LF. Recombinant myostatin (GDF-8) propeptide enhances the repair and regeneration of both muscle and bone in a model of deep penetrant musculoskeletal injury. J Trauma. 2010; 69:579–583. PMID: 20173658.
Article14. Yu XQ, Wu LL, Huang XR, et al. Osteopontin expression in progressive renal injury in remnant kidney: role of angiotensin II. Kidney Int. 2000; 58:1469–1480. PMID: 11012882.
Article15. Magil AB, Pichler RH, Johnson RJ. Osteopontin in chronic puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997; 8:1383–1390. PMID: 9294829.
Article16. Jones CL, Buch S, Post M, McCulloch L, Liu E, Eddy AA. Pathogenesis of interstitial fibrosis in chronic purine aminonucleoside nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1991; 40:1020–1031. PMID: 1762303.
Article17. Bigazzi R, Bianchi S, Baldari D, Sgherri G, Baldari G, Campese VM. Microalbuminuria in salt-sensitive patients. A marker for renal and cardiovascular risk factors. Hypertension. 1994; 23:195–199. PMID: 8307628.
Article18. Swift PA, Markandu ND, Sagnella GA, He FJ, MacGregor GA. Modest salt reduction reduces blood pressure and urine protein excretion in black hypertensives: a randomized control trial. Hypertension. 2005; 46:308–312. PMID: 15983240.19. Konishi Y, Okada N, Okamura M, et al. Sodium sensitivity of blood pressure appearing before hypertension and related to histological damage in immunoglobulin a nephropathy. Hypertension. 2001; 38:81–85. PMID: 11463764.
Article20. Vogt L, Waanders F, Boomsma F, de Zeeuw D, Navis G. Effects of dietary sodium and hydrochlorothiazide on the antiproteinuric efficacy of losartan. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 19:999–1007. PMID: 18272844.
Article21. Krikken JA, Lely AT, Bakker SJ, Navis G. The effect of a shift in sodium intake on renal hemodynamics is determined by body mass index in healthy young men. Kidney Int. 2007; 71:260–265. PMID: 17091123.
Article22. Heeg JE, de Jong PE, van der Hem GK, de Zeeuw D. Efficacy and variability of the antiproteinuric effect of ACE inhibition by lisinopril. Kidney Int. 1989; 36:272–279. PMID: 2550696.
Article23. Buter H, Hemmelder MH, Navis G, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D. The blunting of the antiproteinuric efficacy of ACE inhibition by high sodium intake can be restored by hydrochlorothiazide. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998; 13:1682–1685. PMID: 9681711.
Article24. Verhave JC, Hillege HL, Burgerhof JG, et al. Sodium intake affects urinary albumin excretion especially in overweight subjects. J Intern Med. 2004; 256:324–330. PMID: 15367175.
Article25. Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Garcia Garcia G. The role of tubulointerstitial inflammation in the progression of chronic renal failure. Nephron Clin Pract. 2010; 116:c81–c88. PMID: 20502043.
Article26. Tamaki K, Okuda S, Nakayama M, Yanagida T, Fujishima M. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 in hypertensive renal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1996; 7:2578–2589. PMID: 8989736.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The effects of lovastatin on puromycin aminonucleoside-induced focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in rats
- Ultrastructural Changes in Glomerular Anionic Sites in Puromycin Aminonucleoside Nephropathy
- Morphological Changes in Glomerular Epithelial Cells and Basement Membranes in Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induced Nephropathy
- Effects of puromycin aminonucleoside on the cytoskeletal changes of glomerular epithelial cells
- The Effect of a-Tocopherol in Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induced Nephropathy in Rats