J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Jan;24(Suppl 1):S176-S182. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S176.
Hypoxia Induces Connective Tissue Growth Factor mRNA Expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Cardiology Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ygkim26@skku.edu
- KMID: 1778159
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S176
Abstract
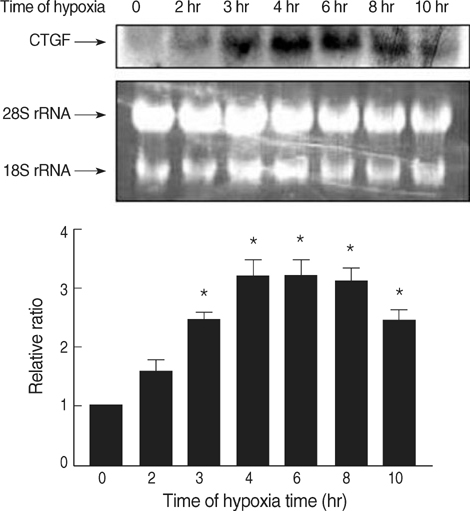
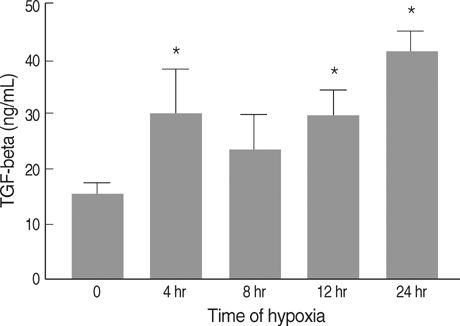
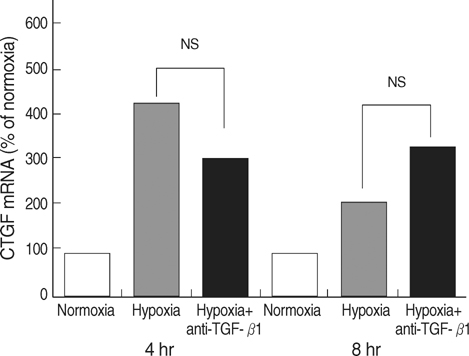
- Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) is known to be a profibrotic growth factor, which mediate the fibrotic effect of transforming growth factor-beta(TGF-beta) and to stimulate cell proliferation and matrix production. CTGF has been shown to be hypoxiainducible in several cell types. Here we investigated the effect of hypoxia on CTGF gene expression in cultured mouse renal tubular cells (MTC). Quiescent cultures of MTC were exposed to hypoxia (1% O2) or normoxia in serum-free medium. The effects on hypoxia-induced CTGF expression were evaluated by Northern blot and real-time PCR. The roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and TGF-beta were also determined using specific biochemical inhibitors. Exposure of quiescent tubular cells to hypoxia for 24 hr in a conditioned medium resulted in a significant increase TGF-beta. Hypoxia caused a significant increase in CTGF mRNA expression in MTC. Either JNK or ERK inhibitor did not block the hypoxia-induced stimulation of CTGF, whereas an inhibitor of p38 MAPK reduced the hypoxia-induced changes of CTGF. Although hypoxia stimulated TGF-betaproduction, neutralizing anti-TGF-beta1 antibody did not abolish the hypoxia-induced CTGF mRNA expression. The data suggest that hypoxia up-regulates CTGF gene expression, and that p38 MAPK plays a role in hypoxic-stimulation of CTGF. We also demonstrated that hypoxia induces CTGF mRNA expression via a TGF-beta1-independent mechanism.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
*Anoxia
Connective Tissue Growth Factor/*metabolism
Culture Media, Conditioned/metabolism
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
*Gene Expression Regulation
Kidney/metabolism
Kidney Tubules/cytology
MAP Kinase Signaling System
Mice
Models, Biological
RNA, Messenger/*metabolism
Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction
Time Factors
Transforming Growth Factor beta/metabolism
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Inhibition of Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction of Rats by Carbon Monoxide
Hae Young Yoo, Su Jung Park, Jae Hyon Bahk, Sung Joon Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(10):1411-1417. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.10.1411.
Reference
-
1. Nangaku M. Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: a final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. 17:17–25.
Article2. Fine LG, Bandyopadhay D, Norman JT. Is there a common mechanism for the progression of different types of renal diseases other than proteinuria? Towards the unifying theme of chronic hypoxia. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000. 75:S22–S26.
Article3. Norman JT, Orphanides C, Garcia P, Fine LG. Hypoxia-induced changes in extracellular matrix metabolism in renal cells. Exp Nephrol. 1999. 7:463–469.
Article4. Kim SB, Kang SA, Park JS, Lee JS, Hong CD. Effect of hypoxia on the extracellular matrix production of cultured rat mesangial cells. Nephron. 1996. 72:275–280.5. Sahai A, Mei C, Pattison TA, Tannen RL. Chronic hypoxia induces proliferation of cultured mesangial cells: role of calcium and protein kinase C. Am J Physiol. 1997. 273:F954–F960.6. Norman JT, Clark IM, Garcia PL. Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in human renal fibroblasts. Kidney Int. 2000. 58:2351–2366.
Article7. Manotham K, Tanaka T, Matsumoto M, Ohse T, Inagi R, Miyata T, Kurokawa K, Fujita T, Ingelfinger JR, Nangaku M. Transdifferentiation of cultured tubular cells induced by hypoxia. Kidney Int. 2004. 65:871–880.
Article8. Matsumoto M, Tanaka T, Yamamoto T, Noiri E, Miyata T, Inagi R, Fujita T, Nangaku M. Hypoperfusion of peritubular capillaries induces chronic hypoxia before progression of tubulointerstitial injury in a progressive model of rat glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004. 15:1574–1581.
Article9. Choi YJ, Chakraborty S, Nguyen V, Nguyen C, Kim BK, Shim SI, Suki WN, Truong LD. Peritubular capillary loss is associated with chronic tubulointerstitial injury in human kidney: altered expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Hum Pathol. 2000. 31:1491–1497.
Article10. Sahai A, Mei C, Schrier RW, Tannen RL. Mechanisms of chronic hypoxia-induced renal cell growth. Kidney Int. 1999. 56:1277–1281.
Article11. Blom IE, Goldschmeding R, Leask A. Gene regulation of connective growth factor: new targets for antifibrotic therapy? Matrix Biol. 2002. 21:473–482.12. Chen Y, Blom IE, Sa S, Goldschmeding R, Abraham DJ, Leask A. CTGF expression in mesangial cells: involvement of SMADs, MAP kinase, and PKC. Kidney Int. 2002. 62:1149–1159.
Article13. Kondo S, Kubota S, Shimo T, Nishida T, Yosimichi G, Eguchi T, Sugahara T, Takigawa M. Connective tissue growth factor increased by hypoxia may initiate angiogenesis in collaboration with matrix metalloproteinases. Carcinogenesis. 2002. 23:769–776.
Article14. Higgins DF, Biju MP, Akai Y, Wutz A, Johnson RS, Haase VH. Hypoxic induction of CTGF is directly mediated by Hif-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. 287:F1223–F1232.15. Haverty TP, Kelly CJ, Hines WH, Amenta PS, Watanabe M, Harper RA, Kefalides NA, Neilson EG. Characterization of a renal tubular epithelial cell line which secretes theautologous target antigen of autoimmune experimental interstitial nephritis. J Cell Biol. 1988. 107:1359–1368.16. Hayashida T, Poncelet AC, Hubchak SC, Schnaper HW. TGF-beta1 activates MAP kinase in human mesangial cells: a possible role in collagen expression. Kidney Int. 1999. 56:1710–1720.17. Hartsough MT, Mulder KM. Transforming growth factor beta activation of p44mapk in proliferating cultures of epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1995. 270:7117–7124.18. Ravanti L, Häkkinen L, Larjava H, Saarialho-Kere U, Foschi M, Han J, Kähäri VM. Transforming growth factor-beta induces collagenase-3 expression by human gingival fibroblasts via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:37292–37300.19. Kucich U, Rosenbloom JC, Herrick DJ, Abrams WR, Hamilton AD, Sebti SM, Rosenbloom J. Signaling events required for transforming growth factor-β stimulation of connective tissue growth factor expression by cultured human lung fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. 395:103–112.
Article20. Paradis V, Dargere D, Bonvoust F, Vidaud M, Segarini P, Bedossa P. Effects and regulation of connective tissue growth factor on hepatic stellate cells. Lab Invest. 2002. 82:767–774.
Article21. Zhang H, Akman HO, Smith EL, Zhao J, Murphy-Ullrich JE, Batuman OA. Cellular response to hypoxia involves signaling via Smad proteins. Blood. 2003. 101:2253–2260.
Article22. Maxwell P. HIF-1: an oxygen response system with special relevance to the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003. 14:2712–2722.
Article23. Marx J. Cell biology. How cells endure low oxygen. Science. 2004. 303:1454–1456.
Article24. Cummins EP, Comerford KM, Scholz C, Bruning U, Taylor CT. Hypoxic regulation of NF-kappaB signaling. Methods Enzymol. 2007. 435:479–492.25. Minchenko A, Bauer T, Salceda S, Caro J. Hypoxic stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in vitro and in vivo. Lab Invest. 1994. 71:374–379.26. Nakagawa T, Lan HY, Zhu HJ, Kang DH, Schreiner GF, Johnson RJ. Differential regulation of VEGF by TGF-β and hypoxia in rat proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. 287:F658–F664.
Article27. Orphanides C, Fine LG, Norman JT. Hypoxia stimulates proximal tubular cell matrix production via a TGF-beta1-independent mechanism. Kidney Int. 1997. 52:637–647.28. Gupta S, Clarkson MR, Duggan J, Brady HR. Connective tissue growth factor: potential role in glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2000. 58:1389–1399.
Article29. Xu J, Smock SL, Safadi FF, Rosenzweig AB, Odgren PR, Marks SC Jr, Owen TA, Popoff SN. Cloning the full-length cDNA for rat connective tissue growth factor: implications for skeletal development. J Cell Biochem. 2000. 77:103–115.
Article30. Mottet D, Michel G, Renard P, Ninane N, Raes M, Michiels C. Role of ERK and calcium in the hypoxia-induced activation of HIF-1. J Cell Physiol. 2002. 194:30–44.
Article31. Sodhi CP, Batlle D, Sahai A. Osteopontin mediates hypoxia-induced proliferation of cultured mesangial cells: role of PKC and p38 MAPK. Kidney Int. 2000. 58:691–700.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hypoxia Induces the Expression of Connective Tissue Growth Factor in Dermal Fibroblasts
- Hypoxia Induces Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF) in Cultured Tubular Cells
- Control of Scarring in Adult Wounds using Antisense Connective Tissue Growth Factor Ollgodeoxynucleotides
- The Role of CTGF in Osteosarcoma Progression
- The Role and Relation of VEGF, TGF-beta1 and CTGF in the Scar Formation of the Rat