J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Nov;28(11):1595-1602. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.11.1595.
Post-Progression Survival in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Clinically Acquired Resistance to Gefitinib
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hemato-oncology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Lung Cancer Branch, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. hmotakyun@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 1777655
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.11.1595
Abstract
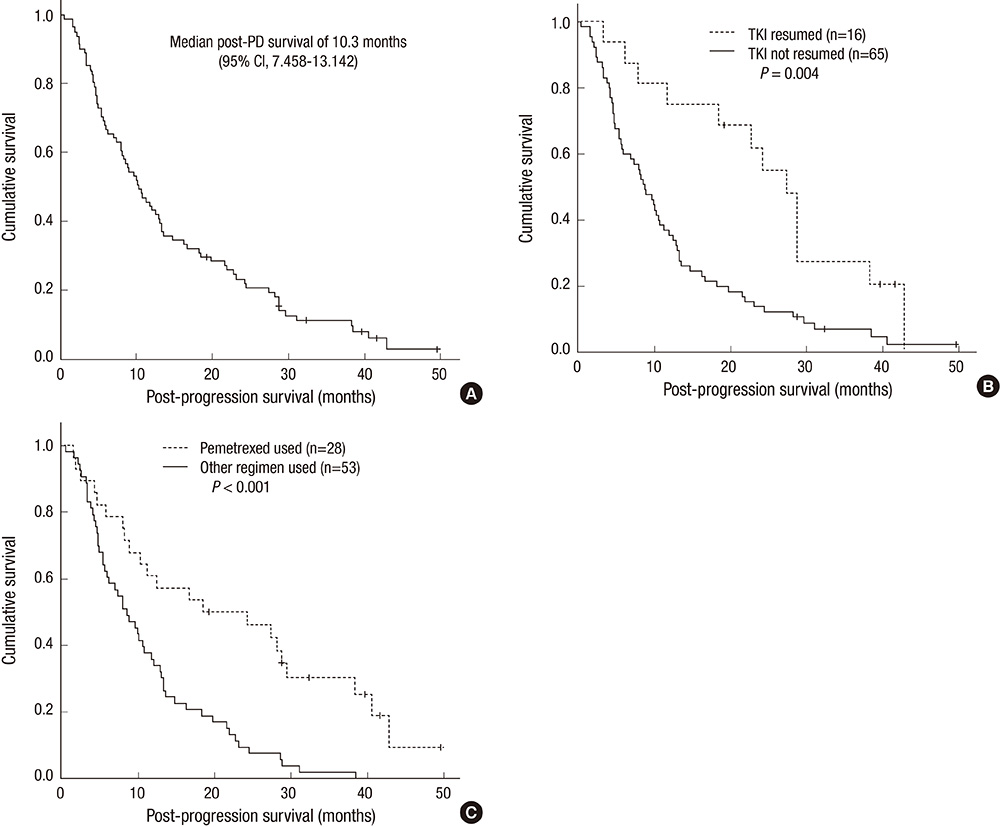
- Most patients with tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-sensitive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) eventually develop acquired resistance to TKIs. Factors that affect TKI-sensitive patient survival after progression during TKI treatment remain unknown. We attempted to identify factors that affected post-progression survival. We retrospectively reviewed 81 advanced NSCLC patients with disease progression following tumor response and durable (> or = 6 months) disease stabilization with first-line or second-line gefitinib. Post-progression survival (PPS) and characteristics were investigated and compared in patients who did (n = 16) and did not (n = 65) resume TKIs. Most patients were female never-smokers with adenocarcinoma. Median overall PPS was 10.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.458-13.142). Age, gender, smoking history, histology, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status at gefitinib initiation, initial stage, and platinum-based chemotherapy after gefitinib were not significant predictors of PPS. Pemetrexed use after gefitinib significantly improved PPS (18.5 vs 8.6 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.45; P = 0.008). Gefitinib reuse tended to lengthen PPS but was insignificant in multivariate analysis (27.4 vs 8.8 months; HR, 0.53; P = 0.095). NSCLC patients assumed to have clinically acquired resistance to TKIs had relatively long PPS. TKIs reuse or pemetrexed use after progression with gefitinib may improve PPS.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma/drug therapy/*mortality
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Antineoplastic Agents/therapeutic use
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung/drug therapy/*mortality
Disease-Free Survival
Drug Resistance, Neoplasm
Female
Glutamates/*therapeutic use
Guanine/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Humans
Lung Neoplasms/drug therapy/*mortality
Male
Middle Aged
Protein Kinase Inhibitors/*therapeutic use
Quinazolines/*therapeutic use
Retrospective Studies
Survival
Treatment Outcome
Antineoplastic Agents
Glutamates
Guanine
Protein Kinase Inhibitors
Quinazolines
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, et al. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:123–132.2. Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, Socinski MA, Gervais R, Wu YL, Li LY, Watkins CL, Sellers MV, Lowe ES, et al. Gefitinib versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (INTEREST): a randomised phase III trial. Lancet. 2008; 372:1809–1818.3. Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch TJ Jr, Prager D, Belani CP, Schiller JH, Kelly K, Spiridonidis H, Sandler A, et al. Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2003; 290:2149–2158.4. Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Zhu CQ, Kamel-Reid S, Squire J, Lorimer I, Zhang T, Liu N, Daneshmand M, et al. Erlotinib in lung cancer - molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:133–144.5. Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004; 304:1497–1500.6. Jänne PA, Johnson BE. Effect of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain mutations on the outcome of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2006; 12:4416s–4420s.7. Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S, Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et al. West Japan Oncology Group. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:121–128.8. Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:947–957.9. Jackman DM, Miller VA, Cioffredi LA, Yeap BY, Jänne PA, Riely GJ, Ruiz MG, Giaccone G, Sequist LV, Johnson BE. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor and KRAS mutations on clinical outcomes in previously untreated non-small cell lung cancer patients: results of an online tumor registry of clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:5267–5273.10. Costa DB, Kobayashi S, Tenen DG, Huberman MS. Pooled analysis of the prospective trials of gefitinib monotherapy for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 2007; 58:95–103.11. Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I, et al. North-East Japan Study Group. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2380–2388.12. Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M, et al. Spanish Lung Cancer Group. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:958–967.13. Jackman D, Pao W, Riely GJ, Engelman JA, Kris MG, Jänne PA, Lynch T, Johnson BE, Miller VA. Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:357–360.14. Sequist LV, Besse B, Lynch TJ, Miller VA, Wong KK, Gitlitz B, Eaton K, Zacharchuk C, Freyman A, Powell C, et al. Neratinib, an irreversible pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor: results of a phase II trial in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3076–3083.15. Miller VA, Hirsh V, Cadranel J, Chen YM, Park K, Kim SW, Zhou C, Su WC, Wang M, Sun Y, et al. Afatinib versus placebo for patients with advanced, metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of erlotinib, gefitinib, or both, and one or two lines of chemotherapy (LUX-Lung 1): a phase 2b/3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:528–538.16. Costa DB. To re-treat or not with gefitinib/erlotinib: This is the question for tyrosine kinase inhibitor-responsive lung cancers that progress. Lung Cancer. 2007; 57:251–252.17. Yokouchi H, Yamazaki K, Kinoshita I, Konishi J, Asahina H, Sukoh N, Harada M, Akie K, Ogura S, Ishida T, et al. Clinical benefit of readministration of gefitinib for initial gefitinib-responders with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2007; 7:51.18. Kaira K, Naito T, Takahashi T, Ayabe E, Shimoyama R, Kaira R, Ono A, Igawa S, Shukuya T, Murakami H, et al. Pooled analysis of the reports of erlotinib after failure of gefitinib for non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010; 68:99–104.19. Zhou W, Ercan D, Chen L, Yun CH, Li D, Capelletti M, Cortot AB, Chirieac L, Iacob RE, Padera R, et al. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Nature. 2009; 462:1070–1074.20. Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Soria JC, Jappe A, Jehl V, Klimovsky J, Johnson BE. Everolimus and erlotinib as second- or third-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:1594–1601.21. Sequist LV, von Pawel J, Garmey EG, Akerley WL, Brugger W, Ferrari D, Chen Y, Costa DB, Gerber DE, Orlov S, et al. Randomized phase II study of erlotinib plus tivantinib versus erlotinib plus placebo in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:3307–3315.22. Sun JM, Lee KW, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Yoon HI, Lee JH, Lee CT, Lee JS. Efficacy and toxicity of pemetrexed as a third-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009; 39:27–32.23. Wu SG, Yang CH, Yu CJ, Lee JH, Hsu YC, Chang YL, Shih JY, Yang PC. Good response to pemetrexed in patients of lung adenocarcinoma with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. Lung Cancer. 2011; 72:333–339.24. Giovannetti E, Lemos C, Tekle C, Smid K, Nannizzi S, Rodriguez JA, Ricciardi S, Danesi R, Giaccone G, Peters GJ. Molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic interaction of erlotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, with the multitargeted antifolate pemetrexed in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2008; 73:1290–1300.25. Lee JC, Jang SH, Lee KY, Kim YC. Treatment of non-small cell lung carcinoma after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 45:79–85.26. Tomizawa Y, Fujita Y, Tamura A, Shirai M, Shibata S, Kawabata T, Shibayama T, Fukai S, Kawahra M, Saito R. Effect of gefitinib re-challenge to initial gefitinib responder with non-small cell lung cancer followed by chemotherapy. Lung Cancer. 2010; 68:269–272.27. Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, Riely GJ, Chmielecki J, Kris MG, Pao W, Ladanyi M, Miller VA. Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 17:1616–1622.28. Hayashi H, Okamoto I, Morita S, Taguri M, Nakagawa K. Postprogression survival for first-line chemotherapy of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23:1537–1541.29. Agelaki S, Hatzidaki D, Kotsakis A, Papakotoulas P, Polyzos A, Ziras N, Gioulbasanis I, Karampeazis A, Agelidou A, Tsiafaki X, et al. Non-platinum-based first-line followed by platinum-based second-line chemotherapy or the reverse sequence in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis by the lung cancer group of the Hellenic Oncology Research Group. Oncology. 2010; 78:229–236.30. Han JY, Lee DH, Song JE, Lee SY, Kim HY, Kim HT, Lee JS. Randomized phase 2 study of irinotecan plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus vinorelbine as first-line chemotherapy with second-line crossover in patients with advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2008; 113:388–395.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inhibition of Ubiquitin-specific Peptidase 8 Suppresses Growth of Gefitinib-resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Inducing Apoptosis
- A case of leptomeningeal metastasis from adenocarcinoma of the lung improved by treatment with Gefitinib
- Overcoming the Intrinsic Gefitinib-resistance via Downregulation of AXL in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Enhancement of Sensitivity of Human Lung Cancer Cell Line to TRAIL and Gefitinib by IGF-1R Blockade
- Comparison of the therapeutic outcome between gefitinib and erlotinib in female patients with non-small-cell lung cancer