Clin Orthop Surg.
2011 Sep;3(3):238-244. 10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.238.
The First Clinical Trial of Beta-Calcium Pyrophosphate as a Novel Bone Graft Extender in Instrumented Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bschang@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Incheon Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1743915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.3.238
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
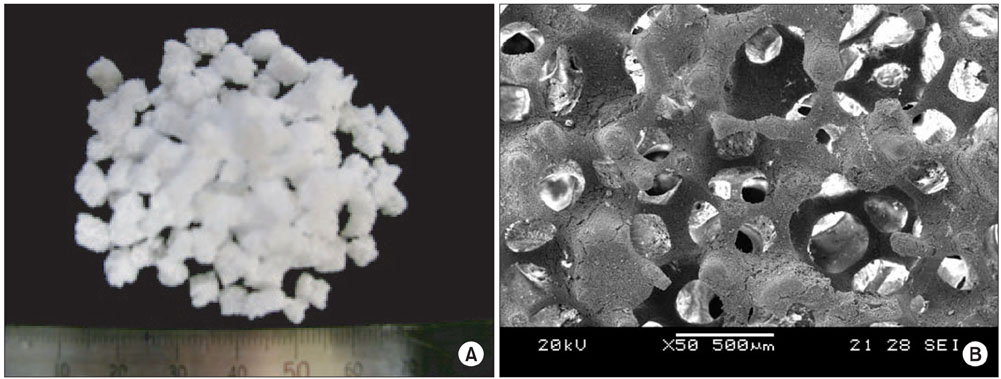
Porous beta-calcium pyrophosphate (beta-CPP) was developed to improve the fusion success of posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF). The possibility of accomplishing PLF using a mixture of porous beta-CPP and iliac bone was studied. This paper reports the radiologic results of PLF using the beta-CPP plus autograft for lumbar degenerative disease as a bone graft extender.
METHODS
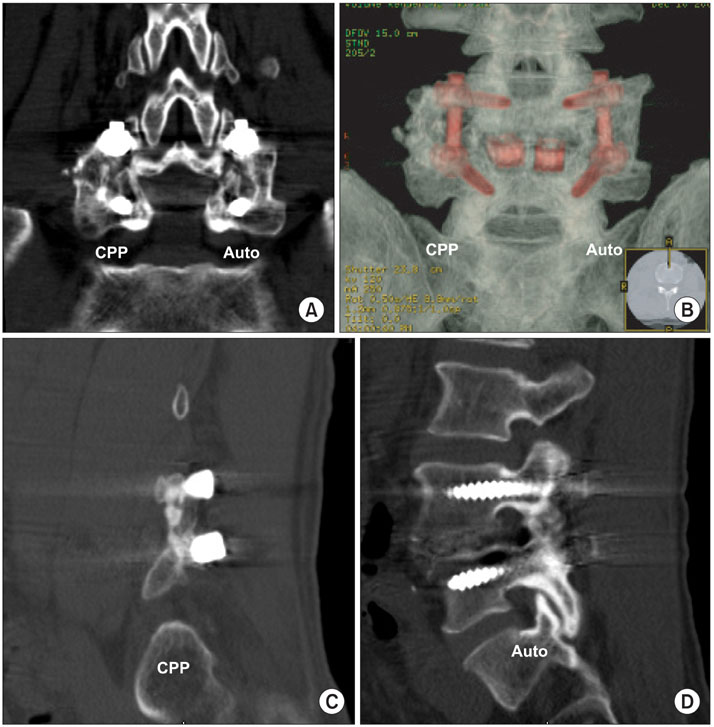
A prospective, case-matched, radiographic study evaluating the results of short segment lumbar fusion using a beta-CPP plus autograft was performed to compare the efficacy of beta-CPP plus autograft with that of an autograft alone for short segment lumbar fusion. Thirty one consecutive patients (46 levels) underwent posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation and additional posterior lumbar interbody fusion. In all patients, 3 mL of beta-CPP plus 3 mL of autogenous bone graft was placed randomly in one side of a posterolateral gutter, and 6 mL of autogenous iliac bone graft was placed on the other. The fusion rates, volumes of fusion masses, and bone absorption percentage were evaluated postoperatively using simple radiographs and 3 dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) scans.
RESULTS
The control sides treated with an autograft showed significantly better Lenke scores than the study sides treated with beta-CPP at 3 and 6 months postoperatively, but there was no difference between the two sides at 12 months. The fusion rates (confirmed by 3D-CT) were 87.0% in the beta-CPP group and 89.1% in the autograft group, which were not significantly different. The fusion mass volumes and bone absorption percentage at 12 months postoperatively were 2.49 mL (58.4%) and 1.89 mL (69.5%) for the beta-CPP and autograft groups, respectively, and mean fusion mass volume was significantly higher in the beta-CPP group.
CONCLUSIONS
beta-CPP combined with an autograft is as effective as autologous bone for grafting during instrumented posterolateral spinal fusion. These findings suggest that beta-CPP bone chips can be used as a novel bone graft extender for short-segment posterolateral spinal fusion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arrington ED, Smith WJ, Chambers HG, Bucknell AL, Davino NA. Complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. (329):300–309.
Article2. Goulet JA, Senunas LE, DeSilva GL, Greenfield ML. Autogenous iliac crest bone graft: complications and functional assessment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. (339):76–81.
Article3. Banwart JC, Asher MA, Hassanein RS. Iliac crest bone graft harvest donor site morbidity: a statistical evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. 20(9):1055–1060.4. Boden SD, Grob D, Damien C. Ne-Osteo bone growth factor for posterolateral lumbar spine fusion: results from a nonhuman primate study and a prospective human clinical pilot study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29(5):504–514.
Article5. Lee JH, Lee DH, Ryu HS, Chang BS, Hong KS, Lee CK. Porous beta-calcium pyrophosphate as a bone graft substitute in a canine bone defect model. Key Eng Mater. 2003. 240-2:399–402.
Article6. Lee DH, Ryu HS, Lee SL, et al. Comparison of oteosyntheses in various types of porous calcium phosphate compounds: an experimental study by posterolateral fusion of rabbits' lumbar vertebrae. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001. 8(4):455–467.
Article7. Lee JH, Chang BS, Ryu HS, Lee CK. A 90-day subchronic toxicity study of beta-calcium pyrophosphate in rat. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2009. 32(3):277–282.
Article8. Lee JH, Ryu HS, Lee DS, Hong KS, Chang BS, Lee CK. Biomechanical and histomorphometric study on the bone-screw interface of bioactive ceramic-coated titanium screws. Biomaterials. 2005. 26(16):3249–3257.
Article9. Lee JH, Hwang CJ, Song BW, Koo KH, Chang BS, Lee CK. A prospective consecutive study of instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion using synthetic hydroxyapatite (Bongros-HA) as a bone graft extender. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009. 90(3):804–810.
Article10. Fujibayashi S, Shikata J, Tanaka C, Matsushita M, Nakamura T. Lumbar posterolateral fusion with biphasic calcium phosphate ceramic. J Spinal Disord. 2001. 14(3):214–221.
Article11. Gunzburg R, Szpalski M. Use of a novel beta-tricalcium phosphate-based bone void filler as a graft extender in spinal fusion surgeries. Orthopedics. 2002. 25:5 Suppl. s591–s595.12. Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73(6):802–808.
Article13. Alexander DI, Manson NA, Mitchell MJ. Efficacy of calcium sulfate plus decompression bone in lumbar and lumbosacral spinal fusion: preliminary results in 40 patients. Can J Surg. 2001. 44(4):262–266.14. Singh K, Smucker JD, Gill S, Boden SD. Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 as an adjunct in posterolateral lumbar spine fusion: a prospective CT-scan analysis at one and two years. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006. 19(6):416–423.
Article15. Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Bullis D, Betz RR, Baldus C, Schoenecker PL. Results of in situ fusion for isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992. 5(4):433–442.
Article16. Hench LL, Wilson J. Surface-active biomaterials. Science. 1984. 226(4675):630–636.
Article17. Kitsugi T, Yamamuro T, Nakamura T, Kotani S, Kokubo T, Takeuchi H. Four calcium phosphate ceramics as bone substitutes for non-weight-bearing. Biomaterials. 1993. 14(3):216–224.
Article18. Kitsugi T, Yamamuro T, Nakamura T, Oka M. Transmission electron microscopy observations at the interface of bone and four types of calcium phosphate ceramics with different calcium/phosphorus molar ratios. Biomaterials. 1995. 16(14):1101–1107.
Article19. Kasuga T, Sawada M, Nogami M, Abe Y. Bioactive ceramics prepared by sintering and crystallization of calcium phosphate invert glasses. Biomaterials. 1999. 20(15):1415–1420.
Article20. Ducheyne P. Bioceramics: material characteristics versus in vivo behavior. J Biomed Mater Res. 1987. 21:A2 Suppl. 219–236.21. Lin FH, Lin CC, Lu CM, Liu HC, Sun JS, Wang CY. Mechanical properties and histological evaluation of sintered beta-Ca2P2O7 with Na4P2O7.10H2O addition. Biomaterials. 1995. 16(10):793–802.
Article22. Sun JS, Tsuang YH, Liao CJ, Liu HC, Hang YS, Lin FH. The effects of calcium phosphate particles on the growth of osteoblasts. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997. 37(3):324–334.
Article23. Klein CP, Driessen AA, de Groot K, van den Hooff A. Biodegradation behavior of various calcium phosphate materials in bone tissue. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983. 17(5):769–784.
Article24. Dimar JR, Glassman SD, Burkus KJ, Carreon LY. Clinical outcomes and fusion success at 2 years of single-level instrumented posterolateral fusions with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2/compression resistant matrix versus iliac crest bone graft. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006. 31(22):2534–2539.
Article25. Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Baldus C. The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord. 1993. 6(6):461–472.
Article26. Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997. 22(24):2807–2812.27. Nork SE, Hu SS, Workman KL, Glazer PA, Bradford DS. Patient outcomes after decompression and instrumented posterior spinal fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999. 24(6):561–569.
Article28. Rechtine GR, Sutterlin CE, Wood GW, Boyd RJ, Mansfield FL. The efficacy of pedicle screw/plate fixation on lumbar/lumbosacral autogenous bone graft fusion in adult patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disord. 1996. 9(5):382–391.
Article29. Bono CM, Lee CK. Critical analysis of trends in fusion for degenerative disc disease over the past 20 years: influence of technique on fusion rate and clinical outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29(4):455–463.
Article30. Blokhuis TJ, Termaat MF, den Boer FC, Patka P, Bakker FC, Haarman HJ. Properties of calcium phosphate ceramics in relation to their in vivo behavior. J Trauma. 2000. 48(1):179–186.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Calcium Sulfate Pellets as Bone Graft Substitute in Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion
- Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion Using Demineralized Bone Matrix
- Bone Union Rate Following Instrumented Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion: Comparison between Demineralized Bone Matrix versus Hydroxyapatite
- Comparison of the Result of Lumbar Posterolateral Bone Fusion using Autogenous Bone Graft with Allobone Graft
- Union Rates of Local Autobone and beta-Tricalcium Phosphate Mixed Graft in Lumbar Posterolateral Fusion