J Vet Sci.
2014 Mar;15(1):81-89. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.1.81.
Elucidating the role of ApxI in hemolysis and cellular damage by using a novel apxIA mutant of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 10
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate Institute of Veterinary Pathobiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung 402, Taiwan, R.O.C. hsuan@nchu.edu.tw
- 2Graduate Institute of Microbiology and Public Health, College of Veterinary Medicine, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung 402, Taiwan, R.O.C.
- 3Division of Animal Medicine, Animal Technology Institute Taiwan, Miaoli, 350, Taiwan, R.O.C.
- KMID: 1737613
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.1.81
Abstract
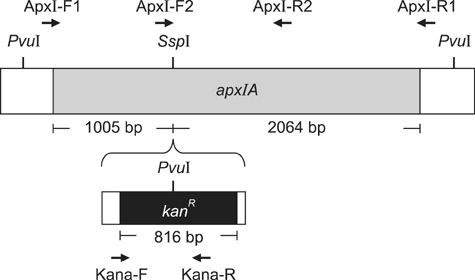
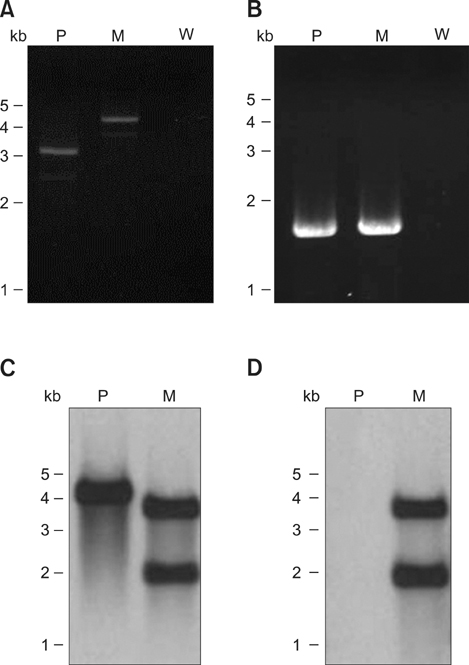
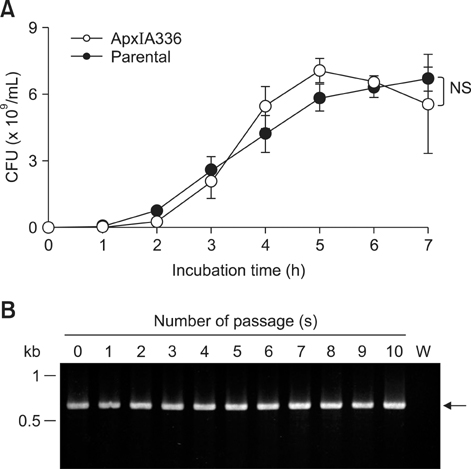
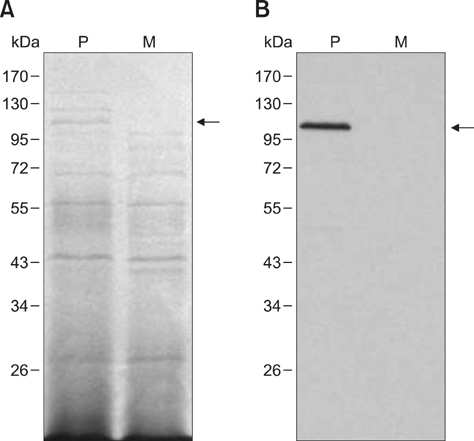
- Exotoxins produced by Actinobacillus (A.) pleuropneumoniae (Apx) play major roles in the pathogenesis of pleuropneumonia in swine. This study investigated the role of ApxI in hemolysis and cellular damage using a novel apxIA mutant, ApxIA336, which was developed from the parental strain A. pleuropneumoniae serotype 10 that produces only ApxI in vitro. The genotype of ApxIA336 was confirmed by PCR, Southern blotting, and gene sequencing. Exotoxin preparation derived from ApxIA336 was analyzed for its bioactivity towards porcine erythrocytes and alveolar macrophages. Analysis results indicated that ApxIA336 contained a kanamycin-resistant cassette inserted immediately after 1005 bp of the apxIA gene. Phenotype analysis of ApxIA336 revealed no difference in the growth rate as compared to the parental strain. Meanwhile, ApxI production was abolished in the bacterial culture supernatant, i.e. exotoxin preparation. The inability of ApxIA336 to produce ApxI corresponded to the loss of hemolytic and cytotoxic bioactivity in exotoxin preparation, as demonstrated by hemolysis, lactate dehydrogenase release, mitochondrial activity, and apoptosis assays. Additionally, the virulence of ApxIA336 appeared to be attenuated by 15-fold in BALB/c mice. Collectively, ApxI, but not other components in the exotoxin preparation of A. pleuropneumoniae serotype 10, was responsible for the hemolytic and cytotoxic effects on porcine erythrocytes and alveolar macrophages.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae/genetics/*pathogenicity/*physiology
Animals
*Apoptosis
Bacterial Proteins/genetics/metabolism
Blotting, Southern
Exotoxins/*genetics
Hemolysin Proteins/genetics/metabolism
*Hemolysis
Macrophages, Alveolar/metabolism/*microbiology
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Swine
Virulence
Bacterial Proteins
Exotoxins
Hemolysin Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bandara AB, Lawrence ML, Veit HP, Inzana TJ. Association of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae capsular polysaccharide with virulence in pigs. Infect Immun. 2003; 71:3320–3328.
Article2. Chen ZW, Chien MS, Chang NY, Chen TH, Wu CM, Huang C, Lee WC, Hsuan SL. Mechanisms underlying Actinobacillus plefuropneumoniae exotoxin ApxI induced expression of IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α in porcine alveolar macrophages. Vet Res. 2011; 42:25.3. Chiang CH, Huang WF, Huang LP, Lin SF, Yang WJ. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of ApxIA and ApxIIA DNA vaccine against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae lethal challenge in murine model. Vaccine. 2009; 27:4565–4570.
Article4. Chien MS, Chan YY, Chen ZW, Wu CM, Liao JW, Chen TH, Lee WC, Yeh KS, Hsuan SL. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 10 derived ApxI induces apoptosis in porcine alveolar macrophages. Vet Microbiol. 2009; 135:327–333.
Article5. Czuprynski CJ, Welch RA. Biological effects of RTX toxins: the possible role of lipopolysaccharide. Trends Microbiol. 1995; 3:480–483.
Article6. Devenish J, Rosendal S. Identification of the heat-labile hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1. Can J Vet Res. 1989; 53:251–254.7. Dubreuil JD, Jacques M, Mittal KR, Gottschalk M. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae surface polysaccharides: their role in diagnosis and immunogenicity. Anim Health Res Rev. 2000; 1:73–93.
Article8. Frey J. Virulence in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae and RTX toxins. Trends Microbiol. 1995; 3:257–261.9. Frey J, Nicolet J. Hemolysin patterns of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1990; 28:232–236.
Article10. Frey J, Beck M, Stucki U, Nicolet J. Analysis of hemolysin operons in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Gene. 1993; 123:51–58.
Article11. Frey J, Bosse JT, Chang YF, Cullen JM, Fenwick B, Gerlach GF, Gygi D, Haesebrouck F, Inzana TJ, Jansen R, Kamp EM, Macdonald J, MacInnes JI, Mittal KR, Nicolet J, Rycroft AN, Segers RPAM, Smits MA, Stenbaek E, Struck DK, van den Bosch JF, Willson PJ, Young R. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae RTX-toxins: uniform designation of haemolysins, cytolysins, pleurotoxin and their genes. J Gen Microbiol. 1993; 139:1723–1728.
Article12. Jansen R, Briaire J, Smith HE, Dom P, Haesebrouck F, Kamp EM, Gielkens ALJ, Smits MA. Knockout mutants of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 that are devoid of RTX toxins do not activate or kill porcine neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1995; 63:27–37.
Article13. Kamp EM, van Leengoed LAMG. Serotype-related differences in production and type of heat-labile hemolysin and heat-labile cytotoxin of Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1989; 27:1187–1191.
Article14. Kamp EM, Popma JK, Anakotta J, Smits MA. Identification of hemolytic and cytotoxic proteins of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae by use of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1991; 59:3079–3085.
Article15. Kamp EM, Stockhofe-Zurwieden N, van Leengoed LAMG, Smits MA. Endobronchial inoculation with Apx toxins of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae leads to pleuropneumonia in pigs. Infect Immun. 1997; 65:4350–4354.
Article16. Kim JM, Jung DI, Eom YJ, Park SM, Yoo HS, Jang YS, Yang MS, Kim DH. Surface-displayed expression of a neutralizing epitope of ApxIIA exotoxin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and oral administration of it for protective immune responses against challenge by Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010; 74:1362–1367.
Article17. Leite F, Gyles S, Atapattu D, Maheswaran SK, Czuprynski CJ. Prior exposure to Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin or LPS enhances β2-integrin expression by bovine neutrophils and augments LKT cytotoxicity. Microb Pathog. 2003; 34:267–275.
Article18. Liao CW, Chiou HY, Yeh KS, Chen JR, Weng CN. Oral immunization using formalin-inactivated Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae antigens entrapped in microspheres with aqueous dispersion polymers prepared using a co-spray drying process. Prev Vet Med. 2003; 61:1–15.
Article19. Maier E, Reinhard N, Benz R, Frey J. Channel-forming activity and channel size of the RTX toxins ApxI, ApxII, and ApxIII of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1996; 64:4415–4423.
Article20. Reed LJ, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Hyg. 1938; 27:493–497.21. Rosendal S, Devenish J, MacInnes JI, Lumsden JH, Watson S, Xun H. Evaluation of heat-sensitive, neutrophil-toxic, and hemolytic activity of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1988; 49:1053–1058.22. Schaller A, Kuhn R, Kuhnert P, Nicolet J, Anderson TJ, MacInnes JI, Segers RPAM, Frey J. Characterization of apxIVA, a new RTX determinant of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Microbiology. 1999; 145:2105–2116.
Article23. Strathdee CA, Lo RYC. Extensive homology between the leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987; 55:3233–3236.
Article24. Welch RA. Pore-forming cytolysins of gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1991; 5:521–528.
Article25. Wu CM, Chen ZW, Chen TH, Liao JW, Lin CC, Chien MS, Lee WC, Hsuan SL. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p38 and JNK mediate Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae exotoxin ApxI-induced apoptosis in porcine alveolar macrophages. Vet Microbiol. 2011; 151:372–378.
Article26. Xu F, Chen X, Shi A, Yang B, Wang J, Li Y, Guo X, Blackall PJ, Yang H. Characterization and immunogenicity of an apxIA mutant of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Vet Microbiol. 2006; 118:230–239.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence and Characterization of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Isolated from Korean Pigs
- Role of the ApxIB/ApxID exporter in secretion of the ApxII and ApxIII toxins in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
- Enhancement of protective immune responses by oral vaccination with Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing recombinant Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae ApxIA or ApxIIA in mice
- Expression of apxIA of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Construction and immunization with double mutant ΔapxIBD Δpnp forms of Oryctolagus cuniculus serotypes 1 and 5