Human Bocavirus in Patients with Respiratory Tract Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cklee@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1735851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2011.31.3.179
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Human bocavirus (HBoV) is a newly identified viral pathogen, and its clinical epidemiology and significance in respiratory infections have not yet been completely elucidated. We investigated the prevalence of HBoV infection and the association between viral (HBoV) load and clinical features of the infection in patients of all age-groups.
METHODS
Nasopharyngeal aspirates from patients with symptoms of respiratory infection were tested for presence of HBoV by using real-time polymerase chain reaction. HBoV-positive patients were categorized into low- and high-viral-load groups using 1.0x10(6) copies/mL as the threshold value of viral load.
RESULTS
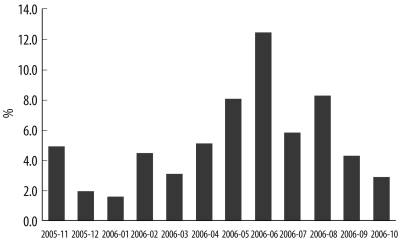
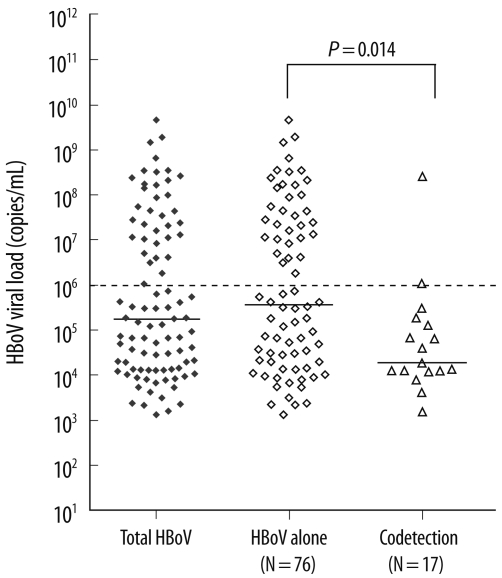
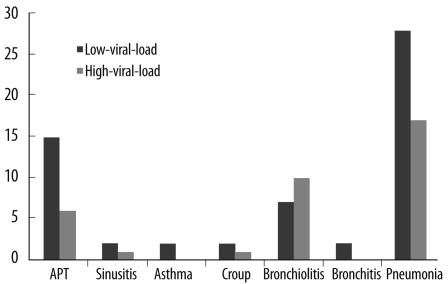
Detection rate of HBoV was 4.8% (N=93) in a total of 1,926 samples with peak incidence of infection being observed in patients aged 6-12 months. HBoV infection was more frequently observed in young children, especially, in children aged less than 5 yr, and the HBoV load decreased with increase in age. HBoV was codetected with other respiratory viruses in 17 (18.3%) of the 93 HBoV-positive patients and 15 patients (88.2%) belonged to the low-viral-load group. Patients infected with HBoV alone showed a higher viral load than those patients in whom HBoV was codetected with other respiratory viruses (median load, 3.78x10(5) copies/mL vs. 1.94x10(4) copies/mL, P=0.014). Higher pulse rate (P=0.007) and respiratory rate (P=0.021) were observed in patients with a high-viral-load.
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggest that HBoV may be the causative agent of respiratory infection in the high-viral-load group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Child
Child, Preschool
DNA, Viral/analysis
Female
Human bocavirus/*isolation & purification
Humans
Infant
Male
Middle Aged
Nasopharynx/virology
Parvoviridae Infections/diagnosis/*epidemiology/virology
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Prevalence
Respiratory Tract Infections/diagnosis/*epidemiology/virology
Viral Load
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Phylogenetic Analysis of Human Bocavirus in Hospitalized Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Infection in Korea
Jong Gyun Ahn, Seong Yeol Choi, Dong Soo Kim, Ki Hwan Kim
Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2012;19(2):71-78. doi: 10.14776/kjpid.2012.19.2.71.Clinical characteristics of respiratory viral infection in children during spring/summer: focus on human bocavirus
Kwang Jin Kwak, Yeo Hyang Kim, Hee Joung Choi
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(6):410-416. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.6.410.Evaluation of a Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay for the Detection of Respiratory Viruses in Clinical Specimens
Insoo Rheem, Joowon Park, Tae-Hyun Kim, Jong Wan Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2012;32(6):399-406. doi: 10.3343/alm.2012.32.6.399.Prevalence of Human Astrovirus in Patients with Acute Gastroenteritis
Heejin Ham, Seah Oh, Jungim Jang, Sukju Jo, Sungmin Choi, Sonil Pak
Ann Lab Med. 2014;34(2):145-147. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.2.145.
Reference
-
1. Allander T, Tammi MT, Eriksson M, Bjerkner A, Tiveljung-Lindell A, Andersson B. Cloning of a human parvovirus by molecular scr-eening of respiratory tract samples. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005; 102:12891–12896. PMID: 16118271.2. Ma X, Endo R, Ishiguro N, Ebihara T, Ishiko H, Ariga T, et al. Detection of human bocavirus in Japanese children with lower respiratory tract infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:1132–1134. PMID: 16517912.
Article3. Sloots TP, McErlean P, Speicher DJ, Arden KE, Nissen MD, Mack-ay IM. Evidence of human coronavirus HKU1 and human bocavirus in Australian children. J Clin Virol. 2006; 35:99–102. PMID: 16257260.
Article4. Choi EH, Lee HJ, Kim SJ, Eun BW, Kim NH, Lee JA, et al. The association of newly identified respiratory viruses with lower respiratory tract infections in Korean children, 2000-2005. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 43:585–592. PMID: 16886150.
Article5. Weissbrich B, Neske F, Schubert J, Tollmann F, Blath K, Blessing K, et al. Frequent detection of bocavirus DNA in German children with respiratory tract infections. BMC Infect Dis. 2006; 6:109. PMID: 16834781.
Article6. Dijkman R, Koekkoek SM, Molenkamp R, Schildgen O, van der Hoek L. Human bocavirus can be cultured in differentiated human airway epithelial cells. J Virol. 2009; 83:7739–7748. PMID: 19474096.
Article7. Mackay IM. Real-time PCR in the microbiology laboratory. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004; 10:190–212. PMID: 15008940.
Article8. Bastien N, Chui N, Robinson JL, Lee BE, Dust K, Hart L, et al. Detection of human bocavirus in Canadian children in a 1-year study. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:610–613. PMID: 17122013.
Article9. Kahn J. Human bocavirus: clinical significance and implications. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2008; 20:62–66. PMID: 18197041.
Article10. Manning A, Russell V, Eastick K, Leadbetter GH, Hallam N, Templeton K, et al. Epidemiological profile and clinical associations of human bocavirus and other human parvoviruses. J Infect Dis. 2006; 194:1283–1290. PMID: 17041855.
Article11. Kesebir D, Vazquez M, Weibel C, Shapiro ED, Ferguson D, Landry ML, et al. Human bocavirus infection in young children in the United States: molecular epidemiological profile and clinical characteristics of a newly emerging respiratory virus. J Infect Dis. 2006; 194:1276–1282. PMID: 17041854.
Article12. Naghipour M, Cuevas LE, Bakhshinejad T, Dove W, Hart CA. Human bocavirus in Iranian children with acute respiratory infections. J Med Virol. 2007; 79:539–543. PMID: 17385723.
Article13. Arden KE, McErlean P, Nissen MD, Sloots TP, Mackay IM. Frequent detection of human rhinoviruses, paramyxoviruses, coronaviruses, and bocavirus during acute respiratory tract infections. J Med Virol. 2006; 78:1232–1240. PMID: 16847968.
Article14. Allander T, Jartti T, Gupta S, Niesters HG, Lehtinen P, Osterback R, et al. Human bocavirus and acute wheezing in children. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 44:904–910. PMID: 17342639.
Article15. Kleines M, Scheithauer S, Rackowitz A, Ritter K, Häusler M. High prevalence of human bocavirus detected in young children with severe acute lower respiratory tract disease by use of a standard PCR protocol and a novel real-time PCR protocol. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:1032–1034. PMID: 17215343.
Article16. Bastien N, Brandt K, Dust K, Ward D, Li Y. Human bocavirus infection, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006; 12:848–850. PMID: 16704852.
Article17. Fry AM, Lu X, Chittaganpitch M, Peret T, Fischer J, Dowell SF, et al. Human bocavirus: a novel parvovirus epidemiologically associated with pneumonia requiring hospitalization in Thailand. J Infect Dis. 2007; 195:1038–1045. PMID: 17330795.
Article18. Endo R, Ishiguro N, Kikuta H, Teramoto S, Shirkoohi R, Ma X, et al. Seroepidemiology of human bocavirus in Hokkaido prefecture, Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:3218–3223. PMID: 17699639.
Article19. Lau SK, Yip CC, Que TL, Lee RA, Au-Yeung RK, Zhou B, et al. Clinical and molecular epidemiology of human bocavirus in respiratory and fecal samples from children in Hong Kong. J Infect Dis. 2007; 196:986–993. PMID: 17763318.
Article20. Christensen A, Nordbø SA, Krokstad S, Rognlien AG, Døllner H. Human bocavirus in children: mono-detection, high-viral-load and viraemia are associated with respiratory tract infection. J Clin Virol. 2010; 49:158–162. PMID: 20833582.21. Blessing K, Neske F, Herre U, Kreth HW, Weissbrich B. Prolonged detection of human bocavirus DNA in nasopharyngeal aspirates of children with respiratory tract disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2009; 28:1018–1019. PMID: 19730155.
Article22. Franz A, Adams O, Willems R, Bonzel L, Neuhausen N, Schweizer-Krantz S, et al. Correlation of viral load of respiratory pathogens and co-infections with disease severity in children hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infection. J Clin Virol. 2010; 48:239–245. PMID: 20646956.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phylogenetic Analysis of Human Bocavirus in Hospitalized Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Infection in Korea
- Clinical manifestation of human bocavirus infection in children
- Acute viral lower respiratory tract infections in children
- Epidemiologic Characteristics of Human Bocavirus-Associated Respiratory Infection in Children
- Recurrent Wheezing After Human Bocavirus Lower Respiratory Tract Illnesses in Early Life