J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Mar;29(3):311-319. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.3.311.
Cell Therapy for Wound Healing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pshan@kumc.or.kr
- KMID: 1734915
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.3.311
Abstract
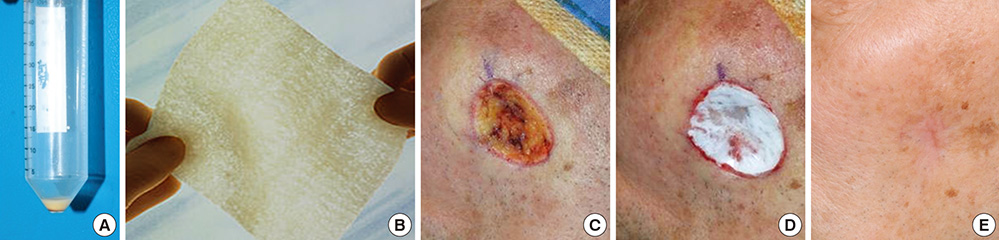
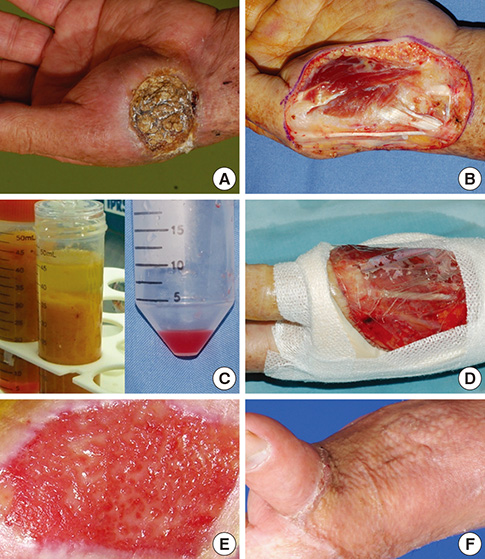
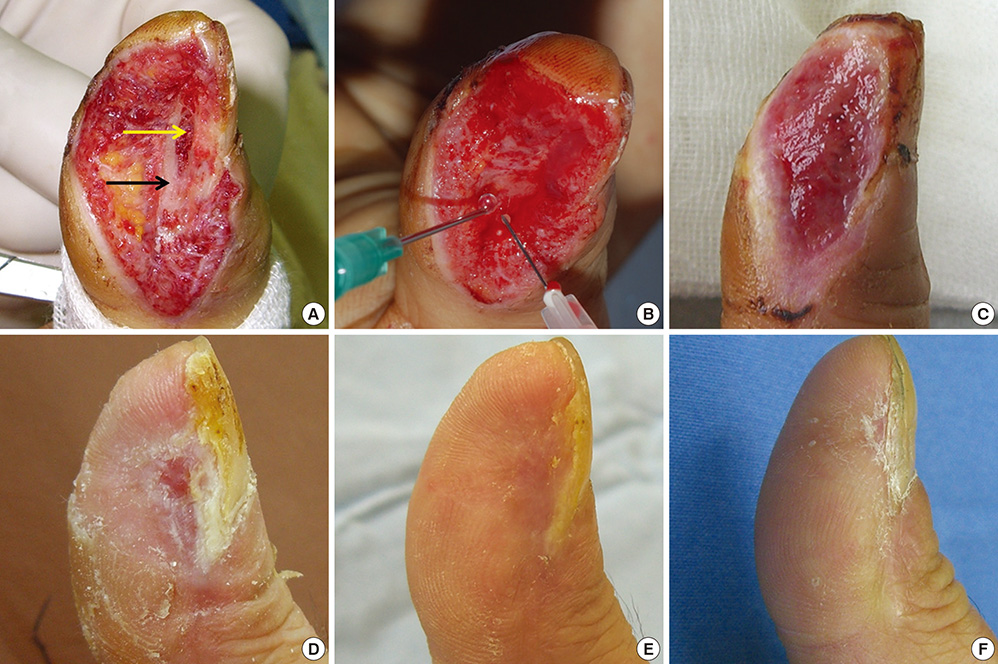
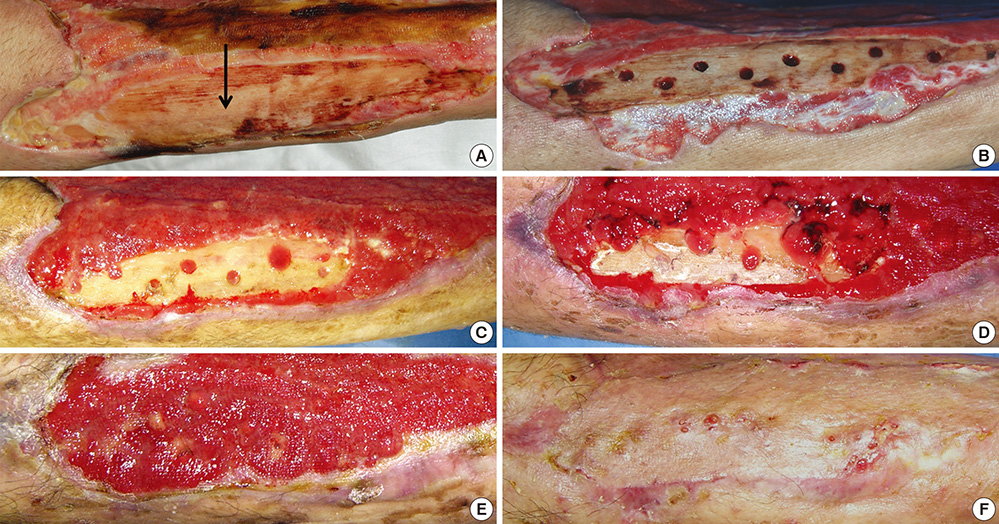
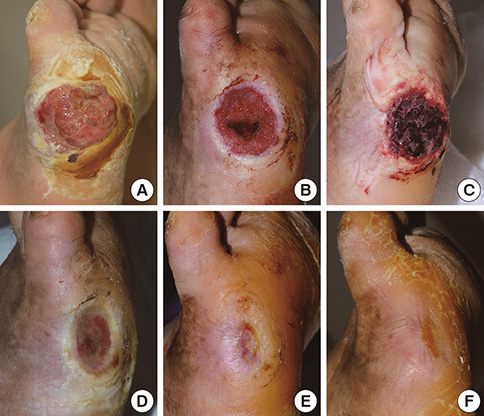
- In covering wounds, efforts should include utilization of the safest and least invasive methods with goals of achieving optimal functional and cosmetic outcome. The recent development of advanced wound healing technology has triggered the use of cells to improve wound healing conditions. The purpose of this review is to provide information on clinically available cell-based treatment options for healing of acute and chronic wounds. Compared with a variety of conventional methods, such as skin grafts and local flaps, the cell therapy technique is simple, less time-consuming, and reduces the surgical burden for patients in the repair of acute wounds. Cell therapy has also been developed for chronic wound healing. By transplanting cells with an excellent wound healing capacity profile to chronic wounds, in which wound healing cannot be achieved successfully, attempts are made to convert the wound bed into the environment where maximum wound healing can be achieved. Fibroblasts, keratinocytes, adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells, bone marrow stem cells, and platelets have been used for wound healing in clinical practice. Some formulations are commercially available. To establish the cell therapy as a standard treatment, however, further research is needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Large-scale Isolation, Expansion and Characterization of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells
Sanjay Gottipamula, K. N Sridhar
Int J Stem Cells. 2018;11(1):87-95. doi: 10.15283/ijsc18001.
Reference
-
1. Moon HS, Burm JS, Yang WY, Kang SY. Prognosis of full-thickness skin defects in premature infants. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:463–468.2. Park YS, Lee JW, Huh GY, Koh JH, Seo DK, Choi JK, Jang YC. Algorithm for primary full-thickness skin grafting in pediatric hand burns. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:483–488.3. Yun MJ, Park JU, Kwon ST. Surgical options for malignant skin tumors of the hand. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:238–243.4. Bae SH, Bae YC, Nam SB, Choi SJ. A skin fixation method for decreasing the influence of wound contraction on wound healing in a rat model. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:457–462.5. Han SK, Yoon WY, Jeong SH, Kim WK. Facial dermis grafts after removal of basal cell carcinomas. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1895–1897.6. Han SK, You HJ. Wound coverage using advanced technology in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2011; 54:594–603.7. Gu JH, Han SK, Jeong SH, Kim WK. Hand coverage using venous island flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012; 65:e366–e367.8. Han SK, Lee BI, Kim WK. The reverse digital artery island flap: an update. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 113:1753–1755.9. Han SK, Lee BI, Kim WK. The reverse digital artery island flap: clinical experience in 120 fingers. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998; 101:1006–1011.10. Ghanem AM, Hachach-Haram N, Leung CC, Myers SR. A systematic review of evidence for education and training interventions in microsurgery. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:312–319.11. Myers SR, Froschauer S, Akelina Y, Tos P, Kim JT, Ghanem AM. Microsurgery training for the twenty-first century. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:302–303.12. Whang KK, Kim MJ, Song WK, Cho S. Comparative treatment of giant congenital melanocytic nevi with curettage or Er: YAG laser ablation alone versus with cultured epithelial autografts. Dermatol Surg. 2005; 31:1660–1667.13. Sood R, Roggy D, Zieger M, Balledux J, Chaudhari S, Koumanis DJ, Mir HS, Cohen A, Knipe C, Gabehart K, et al. Cultured epithelial autografts for coverage of large burn wounds in eighty-eight patients: the Indiana University experience. J Burn Care Res. 2010; 31:559–568.14. Kim HR, Han SK, Rha SW, Kim HS, Kim WK. Effect of percutaneous transluminal angioplasty on tissue oxygenation in ischemic diabetic feet. Wound Repair Regen. 2011; 19:19–24.15. Park DJ, Han SK, Kim WK. Is the foot elevation the optimal position for wound healing of a diabetic foot? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010; 63:561–564.16. Seo YK, Song KY, Kim YJ, Park JK. Wound healing effect of acellular artificial dermis containing extracellular matrix secreted by human skin fibroblasts. Artif Organs. 2007; 31:509–520.17. Erdag G, Sheridan RL. Fibroblasts improve performance of cultured composite skin substitutes on athymic mice. Burns. 2004; 30:322–328.18. Morimoto N, Saso Y, Tomihata K, Taira T, Takahashi Y, Ohta M, Suzuki S. Viability and function of autologous and allogeneic fibroblasts seeded in dermal substitutes after implantation. J Surg Res. 2005; 125:56–67.19. Yates CC, Whaley D, Wells A. Transplanted fibroblasts prevents dysfunctional repair in a murine CXCR3-deficient scarring model. Cell Transplant. 2012; 21:919–931.20. El-Ghalbzouri A, Gibbs S, Lamme E, Van Blitterswijk CA, Ponec M. Effect of fibroblasts on epidermal regeneration. Br J Dermatol. 2002; 147:230–243.21. Kang BS, Na YC, Jin YW. Comparison of the wound healing effect of cellulose and gelatin: an in vivo study. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:317–321.22. Kim H, Son D, Choi TH, Jung S, Kwon S, Kim J, Han K. Evaluation of an amniotic membrane-collagen dermal substitute in the management of full-thickness skin defects in a pig. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:11–18.23. Gallego L, Junquera L, Villarreal P, Peña I, Meana A. Use of cultured human epithelium for coverage: a defect of radial forearm free flap donor site. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010; 15:e58–e60.24. Yanaga H, Udoh Y, Yamauchi T, Yamamoto M, Kiyokawa K, Inoue Y, Tai Y. Cryopreserved cultured epidermal allografts achieved early closure of wounds and reduced scar formation in deep partial-thickness burn wounds (DDB) and split-thickness skin donor sites of pediatric patients. Burns. 2001; 27:689–698.25. Rheinwald JG, Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975; 6:331–343.26. You HJ, Han SK, Lee JW, Chang H. Treatment of diabetic foot ulcers using cultured allogeneic keratinocytes: a pilot study. Wound Repair Regen. 2012; 20:491–499.27. Zou SB, Yoon WY, Han SK, Jeong SH, Cui ZJ, Kim WK. Cytotoxicity of silver dressings on diabetic fibroblasts. Int Wound J. 2013; 10:306–312.28. Han SK, Choi KJ, Kim WK. Clinical application of fresh fibroblast allografts for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: a pilot study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 114:1783–1789.29. Han SK, Kim WK. Revisiting fresh fibroblast allograft as a treatment for diabetic foot ulcers. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 123:88e–89e.30. Han SK, Kim HS, Kim WK. Efficacy and safety of fresh fibroblast allografts in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Dermatol Surg. 2009; 35:1342–1348.31. Castro-Govea Y, De La Garza-Pineda O, Lara-Arias J, Chacón-Martínez H, Mecott-Rivera G, Salazar-Lozano A, Valdes-Flores E. Cell-assisted lipotransfer for the treatment of parry-romberg syndrome. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:659–662.32. Choi J, Minn KW, Chang H. The efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma and adipose-derived stem cells: an update. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:585–592.33. Lee JH, Lee KH, Kim MH, Kim JP, Lee SJ, Yoon J. Possibility of undifferentiated human thigh adipose stem cells differentiating into functional hepatocytes. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:593–599.34. Lee SK, Kim DW, Dhong ES, Park SH, Yoon ES. Facial soft tissue augmentation using autologous fat mixed with stromal vascular fraction. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:534–539.35. Sung HM, Suh IS, Lee HB, Tak KS, Moon KM, Jung MS. Case reports of adipose-derived stem cell therapy for nasal skin necrosis after filler injection. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:51–54.36. Han SK, Kim HR, Kim WK. The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers with uncultured, processed lipoaspirate cells: a pilot study. Wound Repair Regen. 2010; 18:342–348.37. Shin HS, Oh HY. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on wounds of OLETF rats using expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 mRNA. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:106–112.38. Jeong SH, Han SK, Kim WK. Treatment of diabetic foot ulcers using a blood bank platelet concentrate. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010; 125:944–952.39. Han SK, Kim DW, Jeong SH, Hong YT, Woo HS, Kim WK, Gottrup F. Potential use of blood bank platelet concentrates to accelerate wound healing of diabetic ulcers. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 59:532–537.40. Suga H, Matsumoto D, Inoue K, Shigeura T, Eto H, Aoi N, Kato H, Abe H, Yoshimura K. Numerical measurement of viable and nonviable adipocytes and other cellular components in aspirated fat tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 122:103–114.41. Kim JB, Chun KW, Han SK, Kim WK. Effect of human bone marrow stromal cell allograft on proliferation and collagen synthesis of diabetic fibroblasts in vitro. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010; 63:1030–1035.42. Lee CH, Han SK, Choi WI, Kim WK. Effect of human bone marrow stromal cells and dermal fibroblasts on collagen synthesis and epithelization. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 59:713–719.43. Han SK, Chun KW, Gye MS, Kim WK. The effect of human bone marrow stromal cells and dermal fibroblasts on angiogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 117:829–835.44. Han SK, Yoon TH, Lee DG, Lee MA, Kim WK. Potential of human bone marrow stromal cells to accelerate wound healing in vitro. Ann Plast Surg. 2005; 55:414–419.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nutritional Support and Wound Healing
- Impaired Wound Healing in Diabetes Mellitus
- Wound coverage using advanced technology in Korea
- Effects of Adipose-derived Stromal Cells and of their Extract on Wound Healing in a Mouse Model
- Deciphering the Role of Non-Coding RNAs as Regulators in the Wound Healing Process