Yonsei Med J.
2005 Apr;46(2):252-259. 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.2.252.
Behavioral Characteristics of a Mouse Model of Cancer Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical Research Center, Department of Physiology, Brain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jsseong@yumc.yonsei. ac.kr
- KMID: 1734052
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2005.46.2.252
Abstract
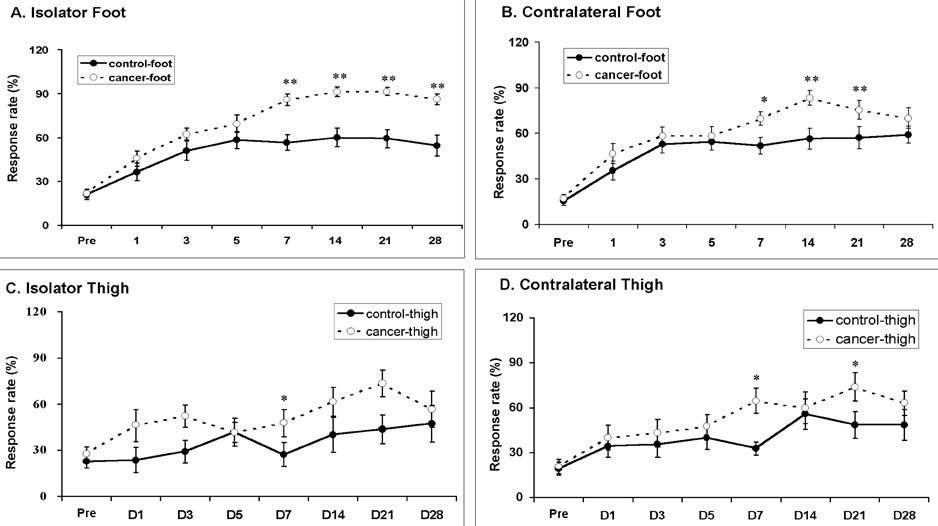
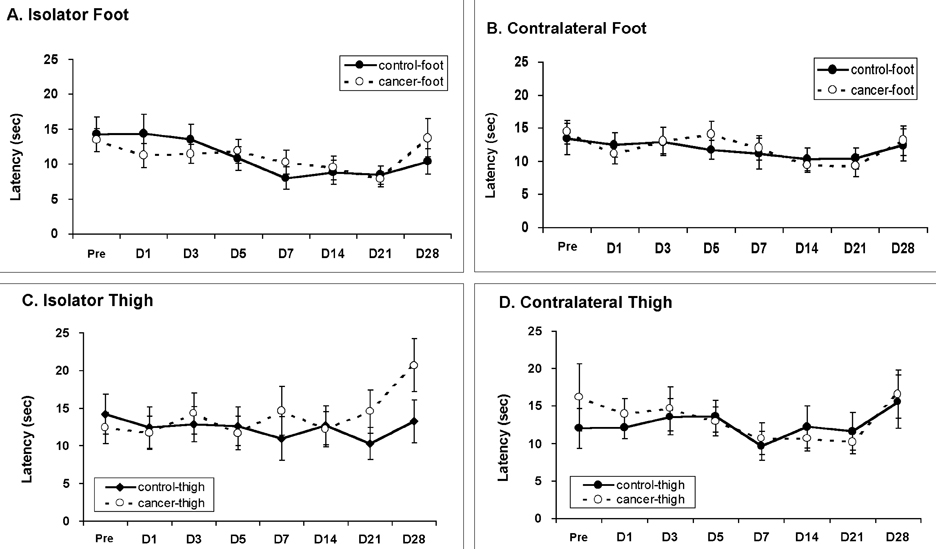
- Pain is a major symptom in cancer patients, and most cancer patients with advanced or terminal cancers suffer from chronic pain related to treatment failure and/or tumor progression. In the present study, we examined the development of cancer pain in mice. Murine hepatocarcinoma cells, HCa-1, were inoculated unilaterally into the thigh or the dorsum of the foot of male C3H/HeJ mice. Four weeks after inoculation, behavioral signs were observed for mechanical allodynia, cold allodynia, and hyperalgesia using a von Frey filament, acetone, and radiant heat, respectively. Bone invasion by the tumor commenced from 7 days after inoculation of tumor cells and was evident from 14 days after inoculation. Cold allodynia but neither mechanical allodynia nor hyperalgesia was observed in mice that received an inoculation into the thigh. On the contrary, mechanical allodynia and cold allodynia, but not hyperalgesia, were developed in mice with an inoculation into the foot. Sometimes, mirror-image pain was developed in these animals. These results suggest that carcinoma cells injected into the foot of mice may develop severe chronic pain related to cancer. This animal model of pain would be useful to elucidate the mechanisms of cancer pain in humans.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
*Behavior, Animal
Bone and Bones/pathology
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/pathology
Cell Line, Tumor
Cold
Disease Models, Animal
Foot
Liver Neoplasms/pathology
Male
Mice
Mice, Inbred C3H
Neoplasm Invasiveness
Neoplasm Transplantation
Neoplasms/*complications
Pain/*etiology/physiopathology/*psychology
Pain Threshold
Physical Stimulation
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Thigh
Figure
Reference
-
1. Portenoy RK, Lesage P. Management of cancer pain. Lancet. 1999. 353:1695–1700.2. Won R, Lee BH, Park S, Kim SH, Park YG, Chung SS. Role of different peripheral components in the expression of neuropathic pain syndrome. Yonsei Med J. 2000. 41:354–361.3. Lee WT, Sohn MK, Ahn SK, Lee JE, Park KA. Studies on the changes of c-fos protein in spinal cord and neurotransmitter in dorsal root ganglion of the rat with an experimental peripheral neuropathy. Yonsei Med J. 2001. 42:30–40.4. Lee YW, Park KA, Lee WT. Effects of MK-801 and morphine on spinal C-Fos expression during the development of neuropathic pain. Yonsei Med J. 2002. 43:370–376.5. Schwei MJ, Honore P, Rogers SD, Lalak-Johnson JL, Finke MP, Ramnaraine ML, et al. Neurochemical and cellular reorganization of the spinal cord in a murine model of bone cancer pain. J Neurosci. 1999. 19:10886–10897.6. Medhurst SJ, Walder K, Bowes M, Kidd BL, Glatt M, Muller M, et al. A rat model of bone cancer pain. Pain. 2002. 96:129–140.7. Milas L, Hunter N, Mason K, Withers HR. Immunologic resistance to pulmonary metastases in C3Hf/Bu mice bearing syngeneic fibrosarcoma of different sizes. Cancer Res. 1974. 34:61–71.8. Lee BH, Won R, Baik EJ, Lee SH, Moon CH. An animal model of neuropathic pain employing injury to the sciatic nerve branches. Neuroreport. 2000. 11:657–661.9. Bonica JJ. Bonica JJ, Liebeskind JC, Albe-Fessard DG, editors. Causalgia and other reflex sympathetic dystrophies. Advances in Pain Research and Therapy. 1979. New York: Raven;141–166.10. Livingston WK. Fields HL, editor. The mirror image. Pain and Suffering. 1998. Seattle: IASP Press;79–85.11. Mitchell SW. Injuries of Nerves and Their Consequences. 1872. Philadelphia: Lippincott.12. Thomas PK. Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, Lambert EH, Bunge R, editors. Clinical features and differential diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral Neuropathy. 1984. Philadelphia: Saunders;1169–1190.13. Attal N, Jazat F, Kayser V, Guilbaud G. Further evidence for pain-related behaviours in a model of unilateral peripheral mononeuropathy. Pain. 1990. 41:235–251.14. Kayser V, Basbaum AI, Guilbaud G. Deafferentation in the rat increase mechanical nociceptive threshold in the innervated limbs. Brain Res. 1990. 508:329–332.15. Seltzer Z, Dubner R, Shir Y. A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain. 1990. 43:205–218.16. Sinnott CJ, Garfield JM, Strichartz GR. Differential efficacy of intravenous lidocaine in alleviating ipsilateral versus contralateral neuropathic pain in the rat. Pain. 1999. 80:521–531.17. Vos BP, Strassman A, Maciewicz RJ. Behavioral evidence of trigeminal neuropathic pain following chronic constriction injury to the rat's infraorbital nerve. J Neurosci. 1994. 14:2708–2723.18. Aloisi AM, Porro CA, Cavazzuti M, Baraldi P, Carli G. 'Mirror pain' in the formalin test: behavioral and 2-deoxyglucose studies. Pain. 1993. 55:267–273.19. Grubb B, Stiller RU, Schaible HG. Dynamic changes in the receptive field properties of spinal cord neurons with ankle input in rats with chronic unilateral inflammation in the ankle region. Exp Brain Res. 1993. 92:441–452.20. Caraceni A, Portenoy RK. An international survey of cancer pain characteristics and syndromes. Pain. 1999. 82:263–274.21. Wacnik PW, Eikmeier LJ, Ruggles TR, Ramnaraine ML, Walcheck BK, Beitz AJ, et al. Functional interactions between tumor and peripheral nerve: morphology, algogen identification, and behavioral characterization of a new murine model of cancer pain. J Neurosci. 2001. 21:9355–9366.22. Cain DM, Wacnik PW, Turner M, Wendelschafer-Crabb G, Kennedy WR, Wilcox GL, et al. Functional interactions between tumor and peripheral nerve: changes in excitability and morphology of primary afferent fibers in a murine model of cancer pain. J Neurosci. 2001. 21:9367–9376.23. Honore P, Rogers SD, Schwei MJ, Salak-Johnson JL, Luger NM, Sabino MC, et al. Murine models of inflammatory, neuropathic and cancer pain each generates a unique set of neurochemical changes in the spinal cord and sensory neurons. Neuroscience. 2000. 98:585–598.24. Luger NM, Honore P, Sabino MAC, Schwei MJ, Rogers SD, Mach DB, et al. Osteoprotegerin diminishes advanced bone cancer pain. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:4038–4047.25. Sabino MAC, Luger NM, Mach DB, Rogers SD, Schwei MJ, Mantyh PW. Different tumors in bone each give rise to a distinct pattern of skeletal destruction, bone cancer-related pain behaviors and neurochemical changes in the central nervous system. Int J Cancer. 2003. 104:550–558.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bile duct ligation of C57BL/6 mice as a model of hepatic encephalopathy
- The Generation and Application of Patient-Derived Xenograft Model for Cancer Research
- Effect of ginsenosides in a mouse model of bone cancer pain
- Incision-induced Pain Behaviors in the DBA/2 Mouse
- Mouse Models of Gastric Carcinogenesis