J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Aug;27(8):857-863. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.857.
Isolation and Characterization of Chorionic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Human Full Term Placenta
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. microkim@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology, College of Life Sciences and Biotechnology, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1714195
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.857
Abstract
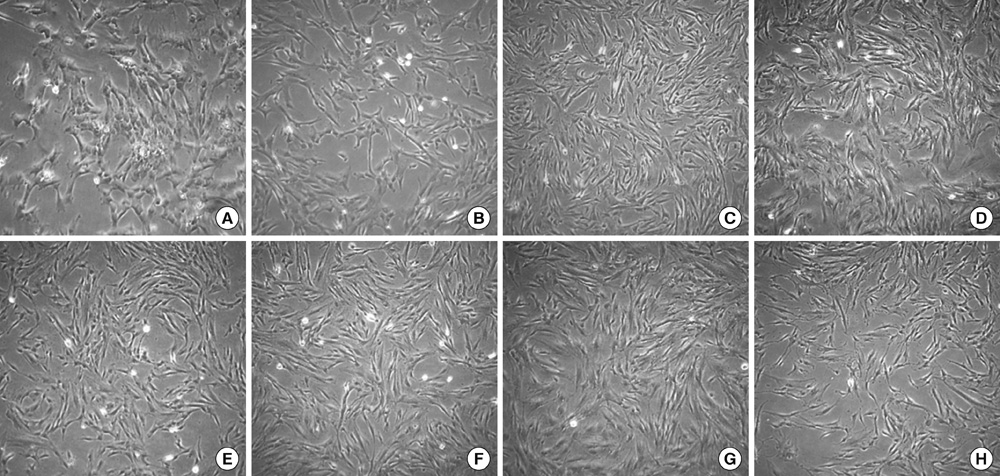
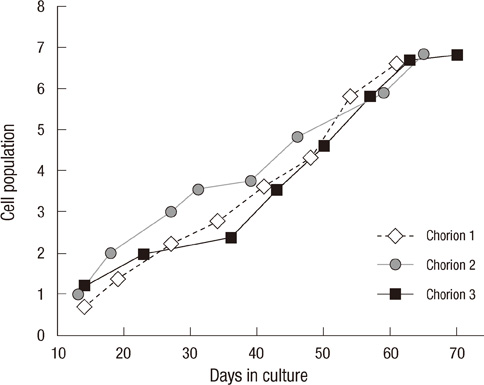
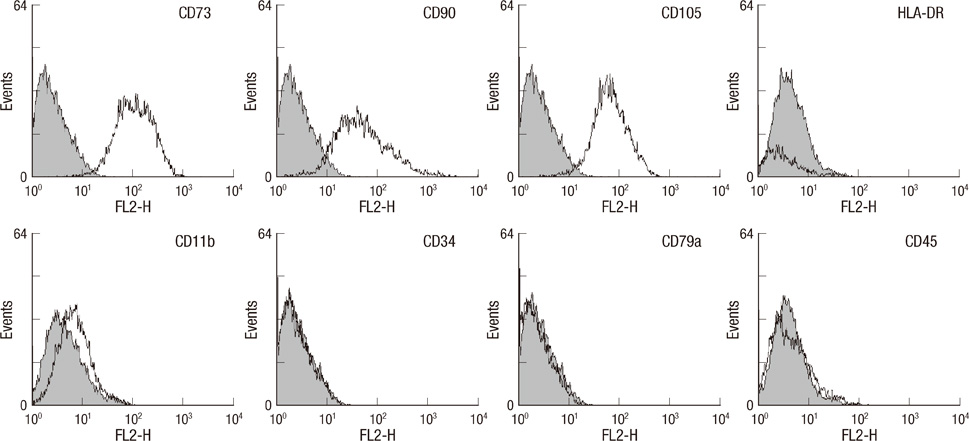
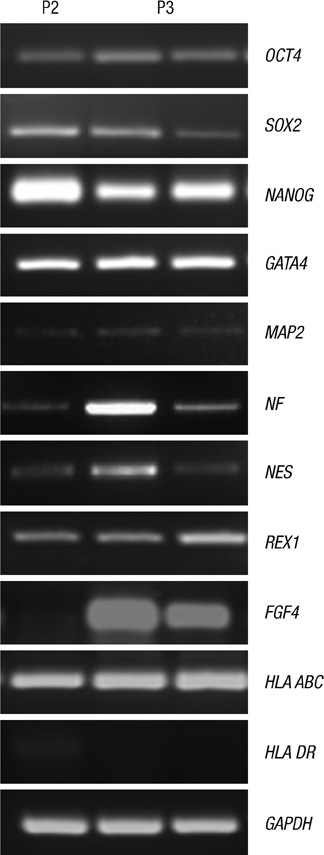
- This study focused on the characterization of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) from the chorion of human full term placenta from 15 donors. Chorionic MSCs revealed homologous fibroblast-like morphology and expressed CD73, CD29, CD105, and CD90. The hematopoietic stem cell markers including HLA DR, CD11b, CD34, CD79a, and CD45 were not expressed. The growth kinetics of their serial passage was steady at the later passages (passage 10). The multilineage capability of chorionic MSCs was demonstrated by successful adipogenic, osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation and associated gene expression. Chorionic MSCs expressed genes associated with undifferentiated cells (NANOG, OCT4, REX1) and cardiogenic or neurogenic markers such as SOX2, FGF4, NES, MAP2, and NF. TERT was negative in all the samples. These findings suggest that chorionic MSCs undifferentiated stem cells and less likely to be transformed into cancer cells. A low HLA DR expression suggests that chorionic MSCs may serve as a great source of stem cells for transplantation because of their immune-privileged status and their immunosuppressive effect. Based on these unique properties, it is concluded that chorionic MSCs are pluripotent stem cells that are probably less differentiated than BM-MSCs, and they have considerable potential for use in cell-based therapies.
MeSH Terms
-
Antigens, CD/genetics/metabolism
Cell Differentiation
Cell Proliferation
Cells, Cultured
Chorion/cytology
Female
Gene Expression Regulation
HLA-DR Antigens/genetics/metabolism
Humans
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/*cytology/metabolism
Placenta/*cytology
Pregnancy
Transcription Factors/genetics/metabolism
Antigens, CD
HLA-DR Antigens
Transcription Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parolini O, Alviano F, Bagnara GP, Gilic G, Bühring HJ, Evangerlista M, Hennerbichler S, Liu B, Magatti M, Mao N, et al. Concise review: isolation and characterization of cells from human term placenta: outcome of the first international workshop on placenta derived stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008. 26:300–311.2. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 22DDCT method. Methods. 2001. 25:402–408.3. Miki T, Lehmann T, Cai H, Stolz DB, Strom SC. Stem cell characteristics of amniotic epithelial cells. Stem Cells. 2005. 23:1549–1559.4. Soncini M, Vertua E, Gibelli L, Zorzi F, Denegri M, Albertini A, Wengler GS, Parolini O. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal cells from human fetal membrane. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007. 1:296–305.5. Kim J, Kang HM, Kim H, Kim MR, Kwon HC, Gye MC, Kang SG, Yang HS, You J. Ex vivo characteristic of human amniotic membrane-derived stem cells. Cloning Stem Cells. 2007. 9:581–594.6. Fariha MM, Chua KH, Tan GC, Tan AE, Hayati AR. Human chorion-derived stem cells: changes in stem cell properties during serial passage. Cytotherapy. 2011. 13:582–593.7. Ilancheran S, Moodley Y, Manuelpillai U. Human fetal membranes: a source of stem cells for tissue regeneration and repair? Placenta. 2009. 30:2–10.8. Le Blanc K. Immunomodulatory effects of fetal and adult mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2003. 5:485–489.9. Kim J, Lee Y, Hwang KJ, Kwon HC, Kim SK, Cho DJ, Kang SG, You J. Human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells have characteristics of multipotent stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2007. 40:75–90.10. Kuo CT, Morrisey EE, Anandappa R, Sigrist K, Lu MM, Parmacek MS, Soudais C, Leiden JM. GATA4 transcription factor is required for ventral morphogenesis and heart tube formation. Genes Dev. 1997. 11:1048–1060.11. Molkentin JD, Lin Q, Duncan SA, Olson EN. Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997. 11:1061–1072.12. Portmann-Lanz CB, Schoeberlein A, Huber A, Sager R, Malek A, Holzgreve W, Surbek DV. Placental mesenchymal stem cells as potential autologous graft for pre- and perinatal neuroregeneration. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006. 194:664–673.13. Lensch MW, Daheron L, Schlaeger TM. Pluripotent stem cells and their niches. Stem Cell Rev. 2006. 2:185–201.14. Kosaka N, Kodama M, Sasaki H, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Takahama Y, Sakamoto H, Kato T, Terada M, Ochiya T. FGF-4 regulates neural progenitor cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. FASEB J. 2006. 20:E623–E629.15. Sjöberg G, Jiang WQ, Ringertz NR, Lendahl U, Sejersen T. Colocalization of nestin and vimentin/desmin in skeletal muscle cells demonstrated by three-dimensional fluorescence digital imaging microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1994. 214:447–458.16. Amit M, Carpenter MK, Inokuma MS, Chiu CP, Harris CP, Waknitz MA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Thomson JA. Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture. Dev Biol. 2000. 227:271–278.17. Sung HJ, Hong SH, Yoo JH, Oh JH, Shin HJ, Choi IY, Ahn KH, Kim SH, Park Y, Kim BS. Stemness evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells from placentas according to developmental stage: comparison to those from adult bone marrow. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1418–1426.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of embryonic stem cell markers in human term placenta
- Isolation and Characterization of Human Chorionic Membranes Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Neural Differentiation
- Concise Review: Differentiation of Human Adult Stem Cells Into Hepatocyte-like Cells In vitro
- Expression of GnRH and GnRH-receptor mRNAs in the Human Placenta
- Adipose Tissue Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells