J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Oct;22(5):820-824. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.820.
Allergic Asthma and Rhinitis Caused by Household Rabbit Exposure: Identification of Serum-Specific IgE and Its Allergens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pulmonology and Allergy, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1713287
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.5.820
Abstract
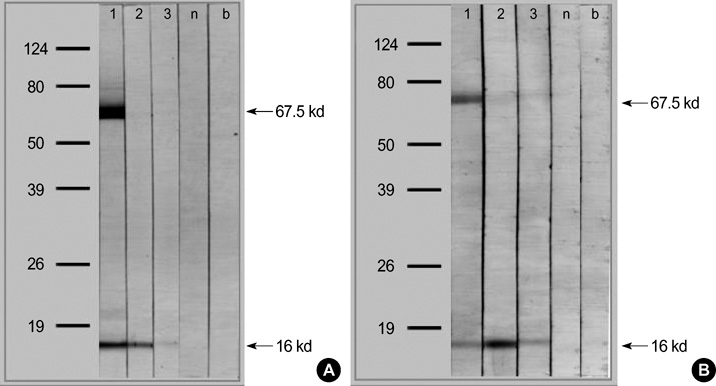
- Although rabbits are common domestic pets, severe respiratory allergic reactions to rabbits in households are unusual. Ory c 1, a 17-kDa glycoprotein found in saliva and fur, has previously been identified as a major rabbit allergen. In this report, we describe the cases of three patients with rabbit allergy who presented with asthma and/or rhinitis while living in households with detectable levels of serum-specific IgE and major IgE binding components. Three patients with rabbit allergy and 18 unexposed nonatopic healthy controls were enrolled. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for serum-specific IgE and IgG4 to rabbit epithelium and inhibition ELISA were performed followed by sodium dodecye sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and IgE immunoblotting. All three patients with rabbit allergy had high serum-specific IgE antibody levels compared with controls. The results of the inhibition ELISA showed significant inhibition with the addition of rabbit epithelium, whereas no significant inhibition was noted with the addition of cat and dog epithelia. Two IgE-binding components with molecular weights of 16 kDa and 67.5 kDa were identified by IgE immunoblotting. In conclusion, rabbit exposure may induce IgE-mediated bronchial asthma and/or rhinitis in domestic settings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Allergens/*blood
Animals
Asthma/*immunology/metabolism
Electrophoresis, Polyacrylamide Gel
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay/methods
Female
Humans
Hypersensitivity/*immunology/metabolism
Hypersensitivity, Immediate/immunology
Immunoblotting
Immunoglobulin E/*blood/*chemistry
Immunoglobulin G/chemistry
Male
Rabbits
Rhinitis/*immunology/metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bush RK, Wood RA, Eggleston PA. Laboratory animal allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 102:99–112.
Article2. Lee JC, Lee KS, Park EC, Kang MH, Kang SY. J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990. 10:71–76.3. Aoyama K, Ueda A, Manda F, Matsushita T, Ueda T, Yamauchi C. Allergy to laboratory animals: an epidemiologic study. Br J Ind Med. 1992. 49:41–47.4. Price JA, Longbottom JL. Allergy to rabbits. II. Identification and characterization of a major rabbit allergen. Allergy. 1988. 43:39–48.5. Warner JA, Longbottom JL. Allergy to rabbits. III. Further identification and characterization of rabbit allergens. Allergy. 1991. 46:481–491.6. Prince E, Zacharisen MC, Kurup VP. Anaphylaxis to rabbit: a case report. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998. 81:272–273.
Article7. Liccardi G, D'Amato G, Canonica GW, Dente B, Passalacqua G. Severe respiratory allergy induced by indirect exposure to rabbit dander: a case report. Allergy. 2004. 59:1237–1238.
Article8. Ohman JL Jr, Lowell FC, Bloch KJ. Allergens of mammalian origin. II. Characterization of allergens extracted from rat, mouse, guinea pig, and rabbit pelts. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975. 55:16–24.9. Baker J, Berry A, Boscato LM, Gordon S, Walsh BJ, Stuart MC. Identification of some rabbit allergens as lipocalins. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001. 31:303–312.
Article10. Stewart GA, Robinson C. Adkinson NF, Yunginger JW, Busse WW, Bochner BS, Holgate ST, Simons FER, editors. Allergen structure and function. Middleton's allergy. Principles and practices. 2003. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby Inc.;585–609.11. Spitzauer S, Pandjaitan B, Söregi G, Mühl S, Ebner C, Kraft D, Valenta R, Rumpold H. IgE cross-reactivities against albumins in patients allergic to animals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995. 96:951–959.
Article12. Hilger C, Kohnen M, Grigioni F, Lehners C, Hentges F. Allergic cross-reactions between cat and pig serum albumin. Study at the protein and DNA levels. Allergy. 1997. 52:179–187.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Allergic Skin Prick Test and FAST System in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis
- A Case of Suspected Occupational Asthma Caused by Rabbit Fur
- Relationship between serum total IgE, specific IgE, and peripheral blood eosinophil count according to specific allergic diseases
- Comparative Study on the Allergy Skin Test and RAST in Allergic Patients
- Relationship of serum vitamin D and interleukin-31 levels to allergic or nonallergic rhinitis in children