J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Aug;20(4):586-590. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.586.
Effect of High Dose Inhaled Glucocorticoids on Quality of Life in Patients with Moderate to Severe Asthma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Respiratory Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. mdcspark@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 1712737
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.586
Abstract
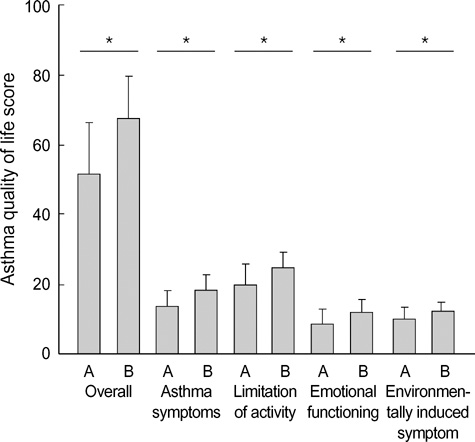
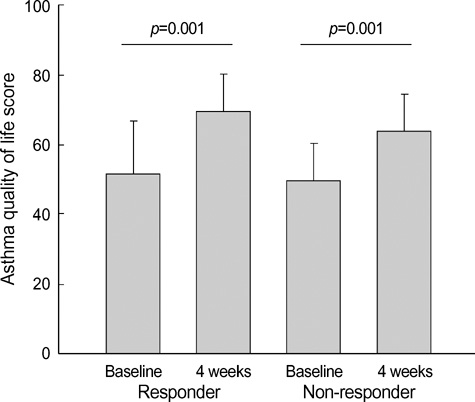
- Asthma is a chronic disorder that can place considerable restrictions on the physical, emotional, and social aspects of the lives of patients. Inhaled glucocorticoids (GCs) are the most effective controller therapy. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of inhaled GCs on quality of life in patients with moderate to severe asthma. Patients completed the asthma quality of life questionnaire (AQLQ) and pulmonary function test at baseline and after 4 wks treatment of GCs. We enrolled 60 patients who had reversibility in FEV1 after 200 microgram of albuterol of 15% or more and/or positive methacholine provocation test, and initial FEV1% predicted less than 80%. All patients received inhaled GCs (fluticasone propionate 1,000 microgram/day) for 4 wks. The score of AQLQ was significantly improved following inhaled GCs (overall 51.9+/-14.3 vs. 67.5+/-12.1, p<0.05). The change from day 1 to day 28 in FEV1 following inhaled GCs was diversely ranged from -21.0% to 126.8%. The improvement of score of AQLQ was not different between at baseline and after treatment of GCs according to asthma severity and GCs responsiveness. Quality of life was improved after inhaled GCs regardless of asthma severity and GCs responsiveness in patients with moderate to severe asthma.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Inhalation
Adult
Asthma/*drug therapy/pathology/physiopathology
Cell Count
Dose-Response Relationship, Drug
Female
Glucocorticoids/administration & dosage/*therapeutic use
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Prospective Studies
*Quality of Life
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Respiratory Function Tests
Skin Tests
Spirometry/methods
Sputum/cytology
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. NHLBI/WHO workshop report. Bethesda, Md: National Institutes of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 2002. NIH publication no. 02-3659. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002. 110:S141–S219.2. Blaiss MS. Outcomes analysis in asthma. JAMA. 1997. 278:1874–1880.
Article3. Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Patrick DL. Measuring health-related quality of life. Ann Intern Med. 1993. 118:622–629.
Article4. Juniper EF. Quality of life in adults and children with asthma and rhinitis. Allergy. 1997. 52:971–977.
Article5. Barnes PJ. Inhaled glucocorticoids for asthma. N Engl J Med. 1995. 332:868–875.
Article6. Kamada AK, Szefler SJ, Martin RJ, Boushey HA, Chinchilli VM, Drazen JM, Fish JE, Israel E, Lazarus SC, Lemanske RF. Issues in the use of inhaled glucocorticoids. The Asthma Clinical Research Network. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996. 153:1739–1748.
Article7. Amirav I, Goren A, Pawlowski NA. What do pediatricians in training know about the correct use of inhalers and spacer devices? J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994. 94:669–675.
Article8. American Thoracic Society. Lung function testing: selection of reference values and interpretative strategies. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 144:1202–1218.9. Standards for the diagnosis and care of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987. 136:225–244.10. Park JW, Cho YS, Lee SY, Nahm DH, Kim YK, Kim DG, Sohn JW, Park JK, Jee YK, Cho YJ, Yoon HJ, Kim MK, Park HS, Choi BW, Choi IS, Park CS, Min KU, Moon HB, Park SH, Lee YK, Kim NS, Hong CS. Multi-center study for the utilization of quality of life questionnaire for adult Korean asthmatics (QLQAKA). J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 20:467–480.11. Juniper EF, Cockcroft DW, Hargreave FE. Histamine and methacholine inhalation tests: A laboratory tidal breathing protocol. 1994. ed 2. Lund: Astra Draco.12. Norzila MZ, Fakes K, Henry RL, Simpson J, Gibson PG. Interleukin-8 secretion and neutrophil recruitment accompanies induced sputum eosinophil activation in children with acute asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:769–774.
Article13. Pizzichini MM, Pizzichini E, Clelland L, Efthimadis A, Mahony J, Hargreave FE. Sputum in severe exacerbation of asthma: Kinetics of inflammatory indices after prednisone treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. 155:1501–1508.14. Park CS, Kim YY, Kang SY. Correlation between RAST and skin test for inhalant offending allergens. J Korean Soc Allergol. 1983. 3:1–9.15. Horn CR, Clark TJ, Cochrane GM. Inhaled therapy reduces morning dips in asthma. Lancet. 1984. I:1143–1145.
Article16. Juniper EF, Kline PA, Vanzieleghem MA, Ramsdale EH, O'Byrne PM, Hargreave FE. Effect of long-term treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide) on airway hyperresponsiveness and clinical asthma in nonsteroid dependent asthmatics. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990. 142:832–836.17. Katz PP, Yelin EH, Eisner MD, Earnest G, Blanc PD. Performance of valued life activities reflected asthma-specific quality of life more than general physical function. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004. 57:259–267.
Article18. Mancuso CA, Peterson MG. Different methods to assess quality of life from multiple follow-ups in a longitudinal asthma study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004. 57:45–54.
Article19. Moy ML, Fuhlbrigge AL, Blumenschein K, Chapman RH, Zillich AJ, Kuntz KM, Paltiel AD, Kitch BT, Weiss ST, Neumann PJ. Association between preference-based health-related quality of life and asthma severity. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004. 92:329–334.
Article20. Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Epstein RS, Ferrie PJ, Jaeschke R, Hiller TK. Evaluation of impairment of health related quality of life in asthma: development of a questionnaire for use in clinical trials. Thorax. 1992. 47:76–83.
Article21. Marks GB, Dunn SM, Woolcock AJ. An evaluation of an asthma quality of life questionnaire as a measure of change in adults with asthma. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993. 46:1103–1111.
Article22. Lim S, Jatakanon A, John M, Gilbey T, O'Connor BJ, Chung KF, Barnes PJ. Effect of inhaled budesonide on lung function and airway inflammation: Assessment by various inflammatory markers in mild asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 159:22–30.23. Laitinen LA, Laitinen A, Haahtela T. A comparative study of the effects of an inhaled corticosteroid, budesonide, and a beta 2-agonist terbutaline on airway inflammation in newly diagnosed asthma: a randomized, double-blind parallel group controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992. 90:32–42.24. Laitinen LA, Laitinen A, Heino M, Haahtela T. Eosinophilic airway inflammation during exacerbation of asthma and its treatment with inhaled corticosteroid. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 143:423–427.
Article25. Toogood JH, Baskerville JC, Jennings B, Lefcoe NM, Johansson SA. Influence of dosing frequency and schedule on the response of chronic asthmatics to the aerosol steroid, budesonide. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982. 70:288–298.
Article26. Holgate ST, Chuchalin AG, Hebert J, Lotvall J, Persson GB, Chung KF, Bousquet J, Kerstjens HA, Fox H, Thirlwell J, Cioppa GD. Efficacy and safety of a recombinant anti-immunoglobulin E antibody (omalizumab) in severe allergic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. 34:632–638.
Article27. Juniper EF, Jenkins C, Price MJ, James MH. Impact of inhaled salmeterol/ fluticasone propionate combination product versus budesonide on the health-related quality of life of patients with asthma. Am J Respir Med. 2002. 1:435–440.28. Banov C, Howland WC 3rd, Lumry WR, Parasuraman B, Uryniak T, Liljas B. Budesonide turbuhaler delivered once daily improves health-related quality of life in adult patients with non-steroid-dependent asthma. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2003. 24:129–136.29. Juniper EF, Svensson K, O'Byrne PM, Barnes PJ, Bauer CA, Lofdahl CG, Postma DS, Pauwels RA, Tattersfield AE, Ullman A. Asthma quality of life during 1 year of treatment with budesonide with or without formoterol. Eur Respir J. 1999. 14:1038–1043.
Article30. Marks GB, Dunn SM, Woolcock AJ. A scale for the measurement of quality of life in adults with asthma. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992. 45:461–472.
Article