J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Aug;20(4):573-578. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.573.
Chestnut as a Food Allergen: Identification of Major Allergens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1712735
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.573
Abstract
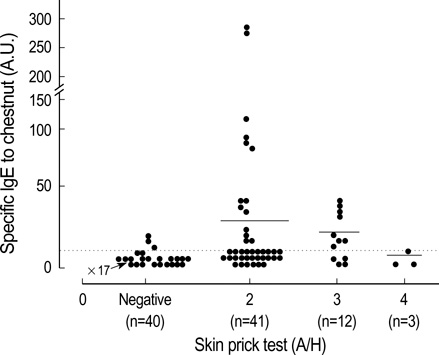
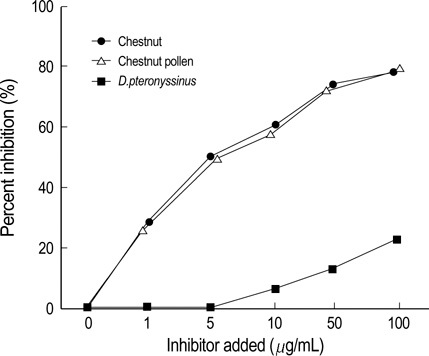
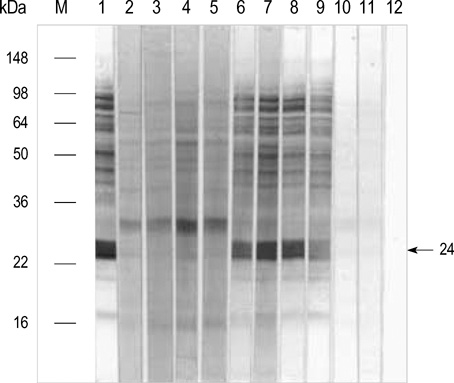
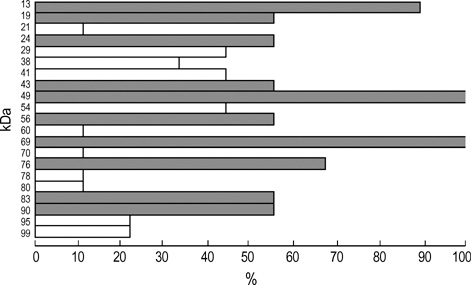
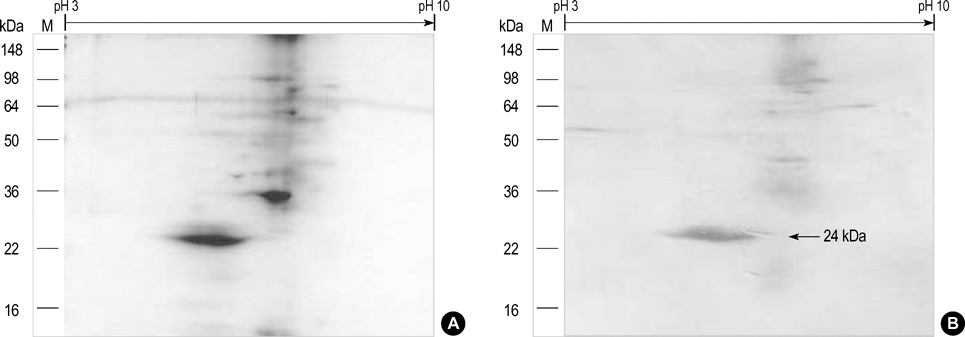
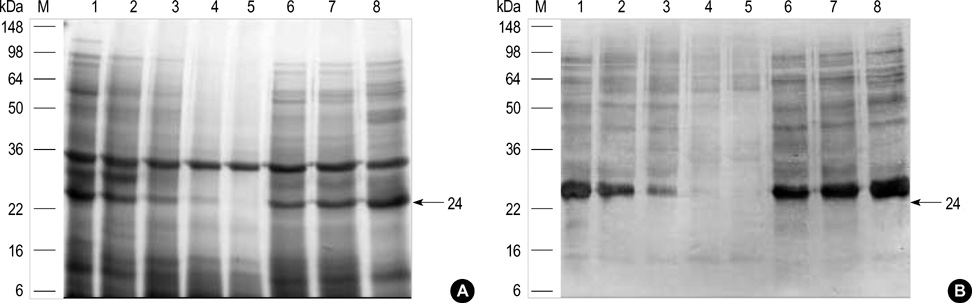
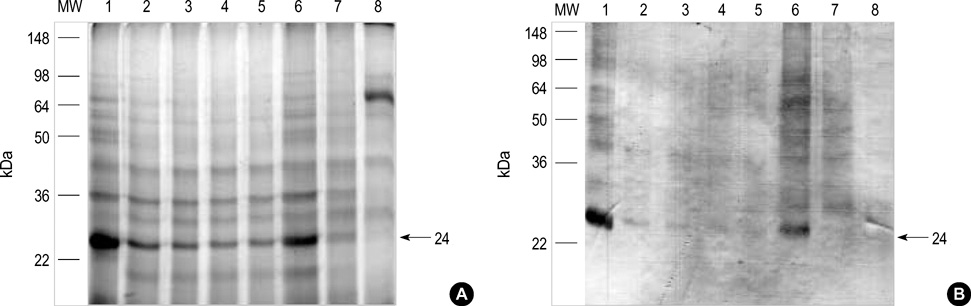
- Chestnut as a Food Allergen: Identification of Major Allergens To evaluate the clinical significance of chestnut as a food allergen in Korea, skin prick test and ELISA were done in 1,738 patients with respiratory allergies. To identify the IgE binding components, IgE-immunoblotting, 2D IgE-immunoblotting and MALDITOF were performed. To observe the effects of digestive enzymes and a boiling treatment, simulated gastric fluid (SGF) and simulated intestinal fluids (SIF) were incubated with chestnut extracts, and IgE-immunoblotting were then repeated. Skin prick test revealed that 56 (3.2%) patients showed more than 2+ of allergen to histamine ratio to chestnut. Among the 21 IgE binding components, 9 bands were found in more than 50% of the sera tested and the 24 kDa protein had the highest binding intensity. The amino acid sequence of the 24 kDa protein (pI 6.3) had homology with legume protein of oak tree. SGF, SIF and boiling treatment were able to suppress the IgE binding components. In conclusion, chestnut ingestion was shown to induce IgE mediated responses with a 3.2% sensitization rate. Twenty one IgE binding components and one new allergen (the 24 kDa protein) were identified. Digestive enzymes and boiling treatment were able to decrease the allergenic potency.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Allergens/analysis/immunology
Amino Acid Sequence
Electrophoresis, Polyacrylamide Gel
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay/methods
Fagaceae/chemistry/*immunology
Food Hypersensitivity/blood/*immunology
Humans
Immunoblotting
Immunoglobulin E/blood/immunology
Plant Extracts/chemistry/immunology
Protein Binding/immunology
Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
Sequence Analysis, Protein
Skin Tests/methods
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim SH, Kang HR, Kim KM, Kim SS, Chang YS, Kim CW, Bahn JW, Kim YK, Cho SH, Park HS, Lee JM, Min KU, Hong CS, Kim NS, Kim YY. The sensitization rates of food allergens in a Korean population: a multi-center study (in Korean). J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 23:502–514.2. Yagame T, Haishima Y, Nakamura A, Osuna H, Ikezawa Z. Digestibility of allergens extracted from natural rubber latex and vegetable foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 106:752–762.3. Rico P, Crespo JF, Feliu A, Rodriguez J. Chestnut allergy: Beyond the latex-fruit syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 113:Suppl 2.4. Astwood JD, Leach JN, Fuchs RL. Stability of food allergens to digestion in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 1996. 14:1269–1273.
Article5. Van Ree R. Clinical importance of non-specific lipid transfer proteins as food allergens. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. 30:910–913.
Article6. FAO/WHO. Evaluation of allergenicity of genetically modified foods. 2001. Rome: FAO;1–26.7. Taylor SL. Protein allergenicity assessment of foods produced through agricultural biotechnology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. 42:99–112.8. Lee SK, Jee YK, Kim YK, Suh JH, Lee MH, Park HS. Identification of IgE binding components of Tetranychus urticae: species-specific and cross-reacting allergens with house dust mite (in Korean). Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 20:879–886.9. Park HS. Allergy skin tests in clinical practice. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001. 21:115–119.10. Kim YK, Park HS, Kim HA, Lee MH, Choi JH, Kim SS, Lee SK, Nahm DH, Cho SH, Min KU, Kim YY. Two-spotted spider mite allergy: immunoglobulin E sensitization and characterization of allergenic components. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002. 89:517–522.
Article11. NCBI BLAST. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/Blast.cgi.12. Roux KH, Teuher SS, Sathe SK. Tree nut allergens. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003. 131:234–244.
Article13. Brehler R, Theissen U, Mohr C, Luger T. Latex-fruit syndrome: frequency of cross-reacting IgE antibodies. Allergy. 1997. 52:404–410.
Article14. Fernandez de Corres L, Moneo I, Munoz D, Bernaola G, Fenandez E, Audicana M, Urrutia I. Sensitization from chestnuts and bananas in patients with urticaria and anaphylaxis from contact with latex. Ann Allergy. 1993. 70:35–39.15. Rodriguez M, Vega F, Garcia MT, Panizo C, Laffond E, Montalvo A, Cuevas M. Hypersensitivity to latex, chestnut, and bananas. Ann Allergy. 1993. 70:31–34.16. Diaz-Perales A, Coliada C, Blanco C, Sanchez-Monge R, Carrilio T, Aragoncillo C, Salcedo G. Class I chitinases with hevein-like domain, but not class II enzyme, are relevant chestnut and avocado allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 102:127–133.17. Blanco C, Diaz-Perales A, Collada C, Sanchez-Monge R, Aragoncillo C, Castillo R, Ortega N, Alvarez M, Carrillo T, Salcedo G. Class I chitinase as potential panallergens involved in the latex-fruit syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999. 103:507–513.18. Sanchez-Monge R, Blanco C, Diaz-Perales A, Collada C, Carrillo T, Aragoncillo C, Salcedo G. Class I chitinase, the panallergens responsible for the latex-fruit syndrome, are induced by ethylene treatment and inactivated by heating. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 106:190–195.19. Blanco C, Carrillo T, Castillo R, Quiralte J, Cuevas M. Latex allergy: clinical features and cross-reactivity with fruits. Ann Allergy. 1994. 73:309–314.20. Chen Z, Posch A, Cremer R, Raulf-Heimsoth M, Baur X. Identification of hevein (Hev b 6.02) in Hevea latex as a major cross-reacting allergen with avocado fruit in patients with latex allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 102:476–481.
Article21. Aalberse RC. Food allergens. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 1997. 4:55–60.
Article22. Hefle SL. The chemistry and biology of food allergens. Food Technol. 1996. 50:86–92.23. Veith S. Allergenic cross-reactivity, food allergy and pollen. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 1997. 4:61–70.24. Diaz-Perales A, Blanco C, Sanchez-Monge R, Varela J, Carrillo T, Salcedo G. Analysis of avocado allergen (Prs a 1) IgE-binding peptides generated by simulated gastric fluid digestion. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 112:1002–1007.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Analysis on Prevalence and Allergen of Food Allergies
- The sensitization rates of food allergens in a Korean population: a multi-center study
- Identification and characterization of shrimp allergens in Korea
- A Study of Pinprick Test with Food Allergens in Urticaria
- Optimization of Allergen Standardization