Korean J Gastroenterol.
2013 Jul;62(1):33-41. 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.1.33.
Benzoxazole Derivative B-98 Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Acute Murine Colitis and the Change of T Cell Profiles in Acute Murine Colitis Model
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea. jassa@ewha.ac.kr
- 2College of Pharmacy, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1711277
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2013.62.1.33
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
The unique role of enzyme 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) in the production of leukotrienes makes it a therapeutic target for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of B-98, a newly synthesized benzoxazole derivatives and a novel 5-LO inhibitor, in a mouse model of IBD induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS).
METHODS
C57BL/6 mice were randomly assigned to four groups: normal control, DSS colitis (DSS+saline), low dose B-98 (DSS+B-98 20 mg/kg) and high dose B-98 (DSS+B-98 100 mg/kg). B-98 was administered with 3% DSS intraperitoneally. The severity of the colitis was assessed via the disease activity index (DAI), colon length, and histopathologic grading. The production of inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 was determined by RT-PCR. Th cells were examined for the proportion of Th1 cell, Th2 cell, Th9 cell, Th17 cell and Treg cell using intracellular cytometry.
RESULTS
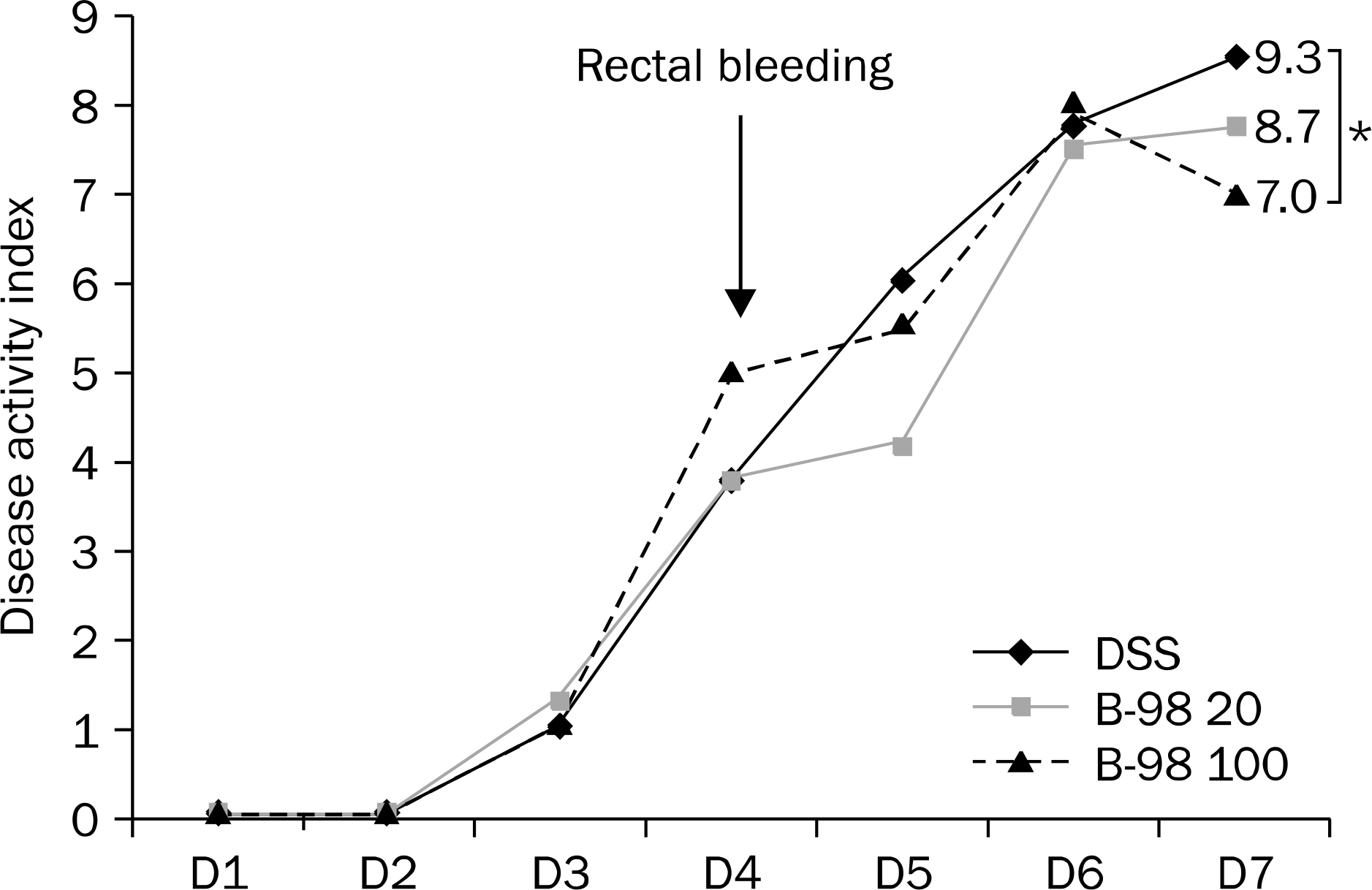
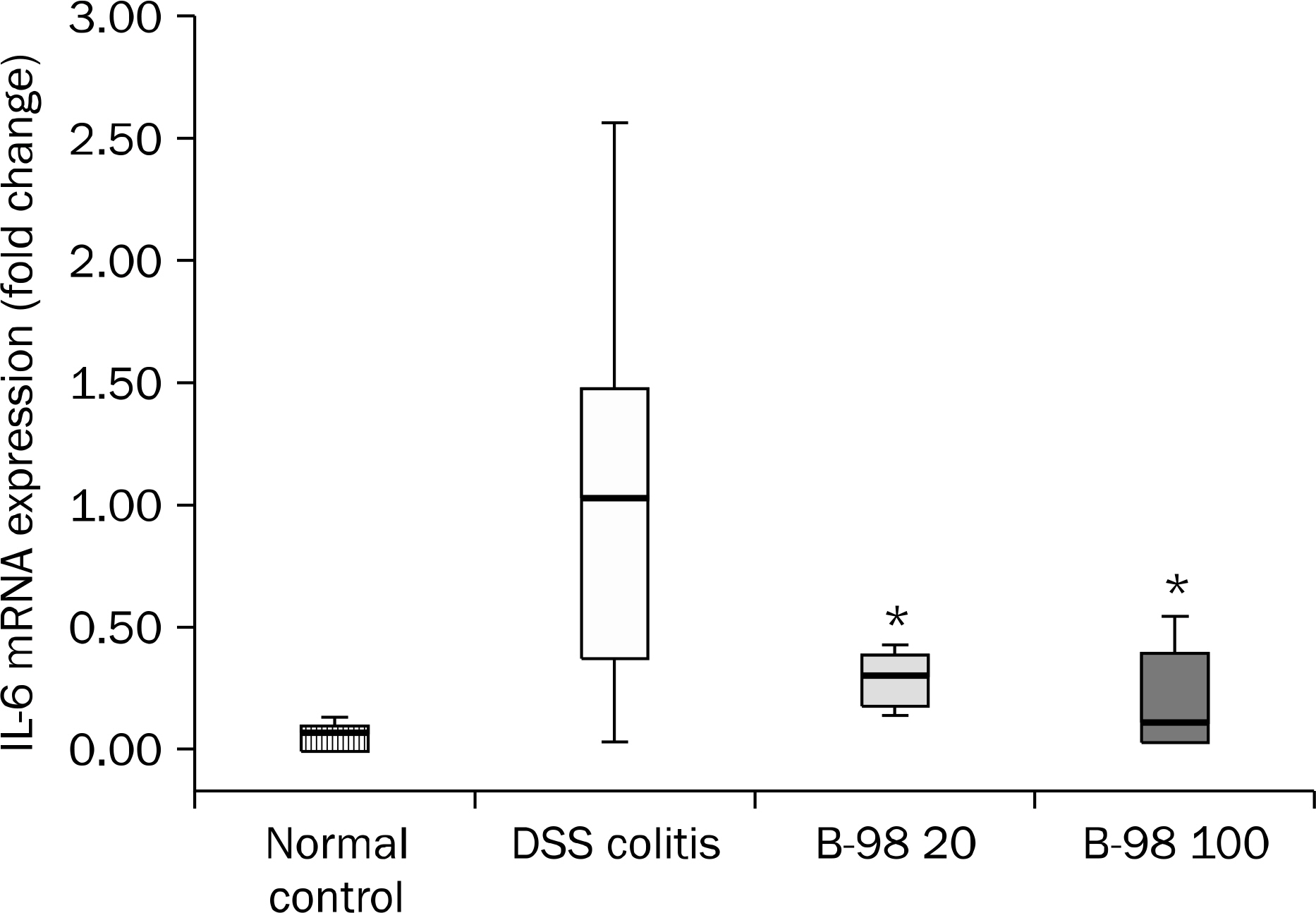
The B-98 group showed lower DAI, less shortening of the colon length and lower histopathologic grading compared with the DSS colitis group (p<0.01). The expression of IL-6 in colonic tissue was significantly lower in the B-98 groups than the DSS colitis group (p<0.05). The cellular profiles revealed that the Th1, Th9 and Th17 cells were increased in the DSS colitis group compared to the B-98 group (p<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
Our results suggest that acute intestinal inflammation is reduced in the group treated with B-98 by Th1, Th9 and Th17 involved cellular immunity.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Animals
Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase/chemistry/metabolism
Benzoxazoles/chemistry/*pharmacology
Colitis/chemically induced/pathology/*prevention & control
Colon/drug effects/pathology/physiology
Dextran Sulfate/toxicity
Disease Models, Animal
Forkhead Transcription Factors/metabolism
Injections, Intraperitoneal
Interleukin-6/genetics/metabolism
Lipoxygenase Inhibitors/chemistry/*pharmacology
Male
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
Severity of Illness Index
T-Lymphocytes/classification/*drug effects/metabolism
Arachidonate 5-Lipoxygenase
Benzoxazoles
Dextran Sulfate
Forkhead Transcription Factors
Interleukin-6
Lipoxygenase Inhibitors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of DA-9601, an extract of
Artemisia asiatica , on aceclofenac-induced acute enteritis
Ju Hwan Kim, Chang Yell Shin, Sun Woo Jang, Dong-Seok Kim, Wonae Lee, Hyung-Gun Kim, Hak Rim Kim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;25(5):439-448. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2021.25.5.439.
Reference
-
References
1. Yang SK, Yun S, Kim JH, et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in the Songpa-Kangdong district, Seoul, Korea, 1986–2005: a KASID study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008; 14:542–549.
Article2. Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:417–429.
Article3. Neurath MF, Finotto S, Glimcher LH. The role of Th1/Th2 polar-ization in mucosal immunity. Nat Med. 2002; 8:567–573.
Article4. Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science. 2006; 314:1461–1463.5. Mudter J, Neurath MF. Il-6 signaling in inflammatory bowel disease: pathophysiological role and clinical relevance. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007; 13:1016–1023.
Article6. Olsen T, Rismo R, Cui G, Goll R, Christiansen I, Florholmen J. TH1 and TH17 interactions in untreated inflamed mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease, and their potential to mediate the inflammation. Cytokine. 2011; 56:633–640.
Article7. Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995; 155:1151–1164.8. Henderson WR Jr. The role of leukotrienes in inflammation. Ann Intern Med. 1994; 121:684–697.
Article9. Dahlén SE, Björk J, Hedqvist P, et al. Leukotrienes promote plasma leakage and leukocyte adhesion in postcapillary venules: in vivo effects with relevance to the acute inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981; 78:3887–3891.10. Rachmilewitz D, Simon PL, Schwartz LW, Griswold DE, Fonda-caro JD, Wasserman MA. Inflammatory mediators of experimental colitis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1989; 97:326–337.
Article11. Boughton-Smith NK, Hawkey CJ, Whittle BJ. Biosynthesis of lip-oxygenase and cyclooxygenase products from [14C]-arachi-donic acid by human colonic mucosa. Gut. 1983; 24:1176–1182.
Article12. Berger W, De Chandt MT, Cairns CB. Zileuton: clinical implications of 5-Lipoxygenase inhibition in severe airway disease. Int J Clin Pract. 2007; 61:663–676.
Article13. Song H, Oh SR, Lee HK, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of benzoxazole derivatives as 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010; 18:7580–7585.
Article14. Stevceva L, Pavli P, Husband A, Ramsay A, Doe WF. Dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis is ameliorated in interleukin 4 deficient mice. Genes Immun. 2001; 2:309–316.
Article15. Kihara N, de la Fuente SG, Fujino K, Takahashi T, Pappas TN, Mantyh CR. Vanilloid receptor-1 containing primary sensory neurones mediate dextran sulphate sodium induced colitis in rats. Gut. 2003; 52:713–719.
Article16. Jang MH, Sougawa N, Tanaka T, et al. CCR7 is critically important for migration of dendritic cells in intestinal lamina propria to mesenteric lymph nodes. J Immunol. 2006; 176:803–810.
Article17. Lauritsen K, Laursen LS, Bukhave K, Rask-Madsen J. Effects of topical 5-aminosalicylic acid and prednisolone on prostaglandin E2 and leukotriene B4 levels determined by equilibrium in vivo dialysis of rectum in relapsing ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1986; 91:837–844.
Article18. Lauritsen K, Laursen LS, Bukhave K, Rask-Madsen J. In vivo effects of orally administered prednisolone on prostaglandin and leucotriene production in ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1987; 28:1095–1099.
Article19. Cuzzocrea S, Rossi A, Mazzon E, et al. 5-Lipoxygenase modulates colitis through the regulation of adhesion molecule expression and neutrophil migration. Lab Invest. 2005; 85:808–822.
Article20. Bertrán X, Mañé J, Fernández-Bañares F, et al. Intracolonic administration of zileuton, a selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, accelerates healing in a rat model of chronic colitis. Gut. 1996; 38:899–904.
Article21. Singh VP, Patil CS, Kulkarni SK. Effect of 5-lipoxygenase inhibition on events associated with inflammatory bowel disease in rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2004; 42:667–673.22. Zarif A, Eiznhamer D, Callaghan C, Doria MI, Broutman L, Keshavarzian A. The effect of a selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, zileuton, on tissue damage in acute colonic inflammation in rats. Inflammation. 1996; 20:217–227.
Article23. Hawkey CJ, Dube LM, Rountree LV, Linnen PJ, Lancaster JF. A trial of zileuton versus mesalazine or placebo in the maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis. The European Zileuton Study Group For Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology. 1997; 112:718–724.
Article24. Holma R, Salmenperä P, Riutta A, Virtanen I, Korpela R, Vapaatalo H. Acute effects of the cys-leukotriene-1 receptor antagonist, montelukast, on experimental colitis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001; 429:309–318.
Article25. Hawthorne AB, Boughton-Smith NK, Whittle BJ, Hawkey CJ. Colorectal leukotriene B4 synthesis in vitro in inflammatory bowel disease: inhibition by the selective 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor BWA4C. Gut. 1992; 33:513–517.
Article26. Ito R, Kita M, ShinYa M, et al. Involvement of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of DSS-induced colitis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008; 377:12–16.
Article27. Leppkes M, Becker C, Ivanov II, et al. RORgamma-expressing Th17 cells induce murine chronic intestinal inflammation via re-dundant effects of IL-17A and IL-17F. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:257–267.28. Alex P, Zachos NC, Nguyen T, et al. Distinct cytokine patterns identified from multiplex profiles of murine DSS and TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009; 15:341–352.
Article29. Stassen M, Schmitt E, Bopp T. From interleukin-9 to T helper 9 cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012; 1247:56–68.
Article30. Mottet C, Uhlig HH, Powrie F. Cutting edge: cure of colitis by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2003; 170:3939–3943.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Therapeutic Efficacy of Tonsil-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-induced Acute Murine Colitis Model
- Th17 Responses Are Not Induced in Dextran Sodium Sulfate Model of Acute Colitis
- Fine Structure of Goblet Cell Regeneration on Experimental Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium
- Histological Study of Experimental Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium
- A glycolipid adjuvant, 7DW8-5, provides a protective effect against colonic inflammation in mice by the recruitment of CD1d-restricted natural killer T cells