Ann Lab Med.
2013 Jul;33(4):274-278. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.4.274.
Analysis of Lyso-Globotriaosylsphingosine in Dried Blood Spots
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Clinical and Translational Genetics, Department of Human Genetics, University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine, USA. obodamer@med.miami.edu
- 2Pharm-analyt Laboratories Inc., Baden, Austria.
- 3University Children's Hospital, Padua, Italy.
- 4National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan.
- 5Lysosomal Storage Disease Unit, Department of Infectious and Pediatric Immunology, Medical and Health Science Center, University of Debrecen, Debrecen, Hungary.
- KMID: 1707235
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.4.274
Abstract
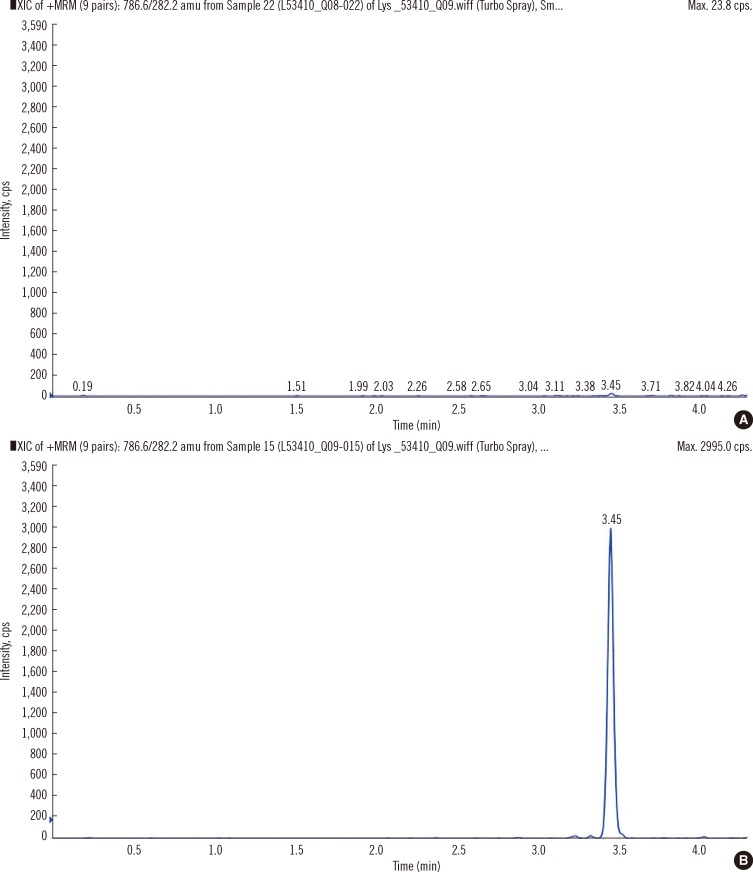
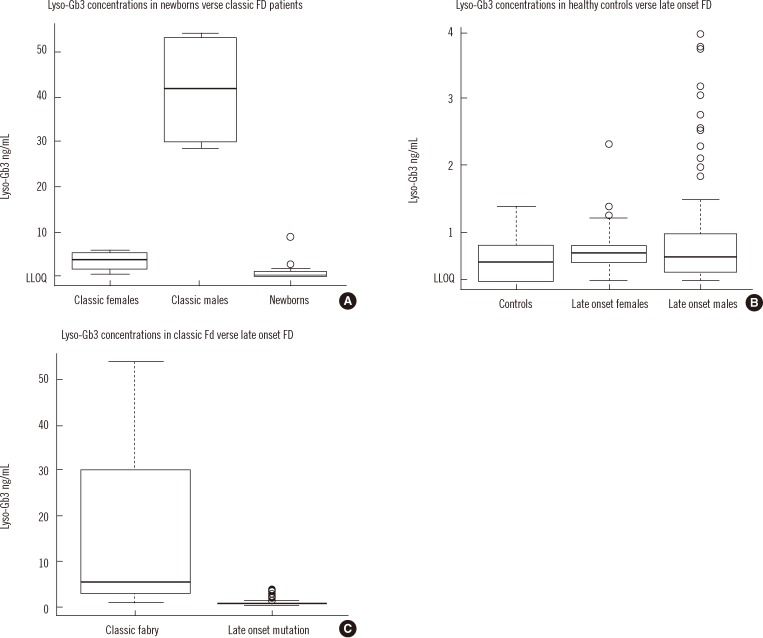
- Recently, lyso-globotriaosylsphingosine (lyso-Gb3) was found to be elevated in plasma of treatment naive male patients and some female patients with Fabry Disease (FD). This study tested whether lyso-Gb3 could be analyzed in dried blood spots (DBS) from filter cards and whether concentrations are elevated in newborn infants with FD. Lyso-Gb3 concentrations were analyzed in DBS following extraction using a novel HPLC-mass spectrometry (MS)/MS method. Lyso-Gb3 levels in DBS were above the lower limit of quantitation (0.28 ng/mL) in 5/17 newborn FD infants (16 males; range: 1.02-8.81 ng/mL), but in none of the newborn controls, in all 13 patients (4 males) with classic FD (range: 2.06-54.1 ng/mL), in 125/159 Taiwanese individuals with symptomatic or asymptomatic FD who carry the late onset alpha-galactosidase A (GLA) mutation c.936+919G>A (IVS4+919G>A) (3.75+/-0.69 ng/mL; range: 0.418-3.97 ng/mL) and in 20/29 healthy controls (0.77+/-0.24 ng/mL; range: 0.507-1.4 ng/mL). The HPLC-MS/MS method for analysis of lyso-Gb3 is robust and yields reproducible results in DBS in patients with FD. However, concentrations of lyso-Gb3 were below the limit of quantitation in most newborn infants with FD rendering this approach not suitable for newborn screening. In addition, most females with the late onset mutation have undetectable lyso-Gb3 concentrations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
2. Gal A, Hughes DA, Winchester B. Toward a consensus in the laboratory diagnostics of Fabry disease - recommendations of a European expert group. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011; 34:509–514. PMID: 21229318.
Article3. Dajnoki A, Fekete G, Keutzer J, Orsini JJ, De Jesus VR, Chien YH, et al. Newborn screening for Fabry disease by measuring GLA activity using tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta. 2010; 411:1428–1431. PMID: 20338160.
Article4. MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH. Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 60 obligate carrier females. J Med Genet. 2001; 38:769–775. PMID: 11732485.
Article5. Fauler G, Rechberger GN, Devrnja D, Erwa W, Plecko B, Kotanko P, et al. Rapid determination of urinary globotriaosylceramide isoform profiles by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry using stearoyl-d35-globotriaosylceramide as internal standard. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2005; 19:1499–1506. PMID: 15880667.
Article6. Paschke E, Fauler G, Winkler H, Schlagenhauf A, Plecko B, Erwa W, et al. Urinary total globotriaosylceramide and isoforms to identify women with Fabry disease: a diagnostic test study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011; 57:673–681. PMID: 21186071.
Article7. Rombach SM, Dekker N, Bouwman MG, Linthorst GE, Zwinderman AH, Wijburg FA, et al. Plasma globotriaosylsphingosine: diagnostic value and relation to clinical manifestations of Fabry disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010; 1802:741–748. PMID: 20471476.
Article8. Aerts JM, Groener JE, Kuiper S, Donker-Koopman WE, Strijland A, Ottenhoff R, et al. Elevated globotriaosylsphingosine is a hallmark of Fabry disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:2812–2817. PMID: 18287059.
Article9. Kalliokoski RJ, Kalliokoski KK, Penttinen M, Kantola I, Leino A, Viikari JS, et al. Structural and functional changes in peripheral vasculature of Fabry patients. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006; 29:660–666. PMID: 16906474.
Article10. Hwu WL, Chien YH, Lee NC, Chiang SC, Dobrovolny R, Huang AC, et al. Newborn screening for Fabry disease in Taiwan reveals a high incidence of the later-onset GLA mutation c.936+919G>A (IVS4+919G>A). Hum Mutat. 2009; 30:1397–1405. PMID: 19621417.11. Adam BW, Alexander JR, Smith SJ, Chace DH, Loeber JG, Elvers LH, et al. Recoveries of phenylalanine from two sets of dried-blood-spot reference materials: prediction from hematocrit, spot volume, and paper matrix. Clin Chem. 2000; 46:126–128. PMID: 10620584.
Article12. Chace DH, Adam BW, Smith SJ, Alexander JR, Hillman SL, Hannon WH. Validation of accuracy-based amino acid reference materials in dried-blood spots by tandem mass spectrometry for newborn screening assays. Clin Chem. 1999; 45:1269–1277. PMID: 10430794.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Advances in the use of dried blood spots on filter paper to monitor kidney disease
- Frequency of Fabry disease in chronic kidney disease patients including patients on renal replacement therapy in Korea
- Analysis of the Stability of Urea in Dried Blood Spots Collected and Stored on Filter Paper
- Lyso-globotriaosylsphingosine induces endothelial dysfunction via autophagy-dependent regulation of necroptosis
- Rapid DNA Extraction from Dried Blood Spots on Filter Paper: Potential Applications in Biobanking