Korean J Radiol.
2013 Jun;14(3):525-531. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.3.525.
Digital Tomosynthesis of the Chest: Comparison of Patient Exposure Dose and Image Quality between Standard Default Setting and Low Dose Setting
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 135-710, Korea. mjchung@skku.edu
- 2Department of Radiology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang 431-070, Korea.
- KMID: 1705470
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.3.525
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To determine the optimum low dose (LD) digital tomosynthesis (DT) setting, and to compared the image quality of the LD DT with that of the standard default (SD) DT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nine DT settings, by changing tube voltage, copper filter, and dose ratio, were performed for determining the LD setting. Among combinations of DT setting, a condition providing the lowest radiation dose was determined. Eighty artificial nodules less than 1 cm in diameter (subcentimeter nodules: 40, micronodules less than 4 mm: 40) were attached to a Styrofoam and a diaphragm of the phantom. Among these, 38 nodules were located at the periphery of the lung (thin area) and 42 nodules were located at the paravertebral or sub-diaphragmatic area (thick area). Four observers counted the number of nodules detected in the thick and thin areas. The detection sensitivity in SD and LD settings were calculated separately. Data were analyzed statistically.
RESULTS
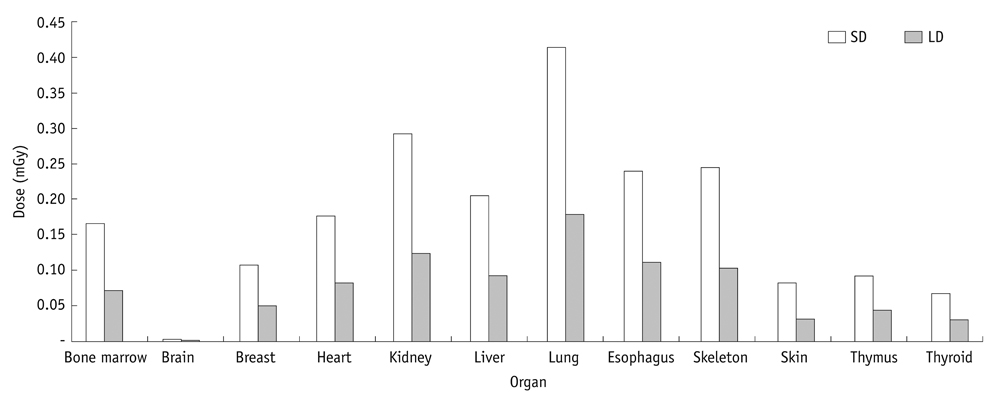
The lowest LD setting was a combination of 100 kVp, 0.3 mm additional copper filter, and a 1 : 5 dose ratio. The effective dose for the LD and SD settings were 62 microSv and 140 microSv, separately. A 56.7% dose reduction was achieved in the LD setting compared with the SD setting. Detection sensitivities were not different between the SD and the LD settings except between observers 1 and 2 for the detection of micronodules in the thick area.
CONCLUSION
LD DT can be effective in nodule detection bigger than 4 mm without a significant decrease in image quality compared with SD DT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dobbins JT 3rd, Godfrey DJ. Digital x-ray tomosynthesis: current state of the art and clinical potential. Phys Med Biol. 2003. 48:R65–R106.2. Vikgren J, Zachrisson S, Svalkvist A, Johnsson AA, Boijsen M, Flinck A, et al. Comparison of chest tomosynthesis and chest radiography for detection of pulmonary nodules: human observer study of clinical cases. Radiology. 2008. 249:1034–1041.3. Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:2277–2284.4. Hall EJ, Brenner DJ. Cancer risks from diagnostic radiology. Br J Radiol. 2008. 81:362–378.5. McCollough CH, Primak AN, Braun N, Kofler J, Yu L, Christner J. Strategies for reducing radiation dose in CT. Radiol Clin North Am. 2009. 47:27–40.6. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP. 2007. 37:1–332.7. James TD, McAdams HP, Song JW, Li CM, Godfrey DJ, DeLong DM, et al. Digital tomosynthesis of the chest for lung nodule detection: interim sensitivity results from an ongoing NIH-sponsored trial. Med Phys. 2008. 35:2554–2557.8. Quaia E, Baratella E, Cioffi V, Bregant P, Cernic S, Cuttin R, et al. The value of digital tomosynthesis in the diagnosis of suspected pulmonary lesions on chest radiography: analysis of diagnostic accuracy and confidence. Acad Radiol. 2010. 17:1267–1274.9. Sabol JM. A Monte Carlo estimation of effective dose in chest tomosynthesis. Med Phys. 2009. 36:5480–5487.10. Båth M, Svalkvist A, von Wrangel A, Rismyhr-Olsson H, Cederblad A. Effective dose to patients from chest examinations with tomosynthesis. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2010. 139:153–158.11. Svalkvist A, Båth M. Simulation of dose reduction in tomosynthesis. Med Phys. 2010. 37:258–269.12. Hamer OW, Sirlin CB, Strotzer M, Borisch I, Zorger N, Feuerbach S, et al. Chest radiography with a flat-panel detector: image quality with dose reduction after copper filtration. Radiology. 2005. 237:691–700.13. Dobbins JT 3rd, Samei E, Chotas HG, Warp RJ, Baydush AH, Floyd CE Jr, et al. Chest radiography: optimization of X-ray spectrum for cesium iodide-amorphous silicon flat-panel detector. Radiology. 2003. 226:221–230.14. MacMahon H, Austin JH, Gamsu G, Herold CJ, Jett JR, Naidich DP, et al. Guidelines for management of small pulmonary nodules detected on CT scans: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 2005. 237:395–400.15. National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011. 365:395–409.16. Dobbins JT 3rd, McAdams HP. Chest tomosynthesis: technical principles and clinical update. Eur J Radiol. 2009. 72:244–251.17. Carmichael JHE, Maccia C, Moores BM, Oestmann JW, Schibilla H, Teunen D, et al. EUR 16260 - European Guidelines on Quality Criteria for Diagnostic Radiographic Images. 1996. Brussels: European Communities.18. Kim EY, Chung MJ, Lee HY, Koh WJ, Jung HN, Lee KS. Pulmonary mycobacterial disease: diagnostic performance of low-dose digital tomosynthesis as compared with chest radiography. Radiology. 2010. 257:269–277.19. Kim EY, Chung MJ, Choe YH, Lee KS. Digital tomosynthesis for aortic arch calcification evaluation: performance comparison with chest radiography with CT as the reference standard. Acta Radiol. 2012. 53:17–22.20. Yoo JY, Chung MJ, Choi B, Jung HN, Koo JH, Bae YA, et al. Digital tomosynthesis for PNS evaluation: comparisons of patient exposure and image quality with plain radiography. Korean J Radiol. 2012. 13:136–143.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparative Study of Image Quality and Radiation Dose with Changes in Tube Voltage and Current for a Digital Chest Radiography
- Storage Phosphor Digital Radiography in Portable Chest Imaging: Comparison of Image Quality with Conventional Film-Screen System with Variation of mAs
- Digital tomography in the diagnosis of a posterior pneumothorax in the intensive care unit
- Radiation Dose Reduction without Compromise to Image Quality by Alterations of Filtration and Focal Spot Size in Cerebral Angiography
- Relationship of Image Quality and Radiation Dose for Chest Radiography in the Medical Institutions for Pneumoconiosis: A Comparison to the Korean Diagnostic Reference Level