J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Feb;62(2):131-137. 10.3348/jksr.2010.62.2.131.
A Comparative Study of Image Quality and Radiation Dose with Changes in Tube Voltage and Current for a Digital Chest Radiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Korea. sungdw@paran.com
- KMID: 2208950
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.62.2.131
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: High-voltage techniques applicable for analog radiographs are usually used in digital radiographs. We compared the image quality of the different exposure conditions to produce conditions of high image quality and low radiation dose.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
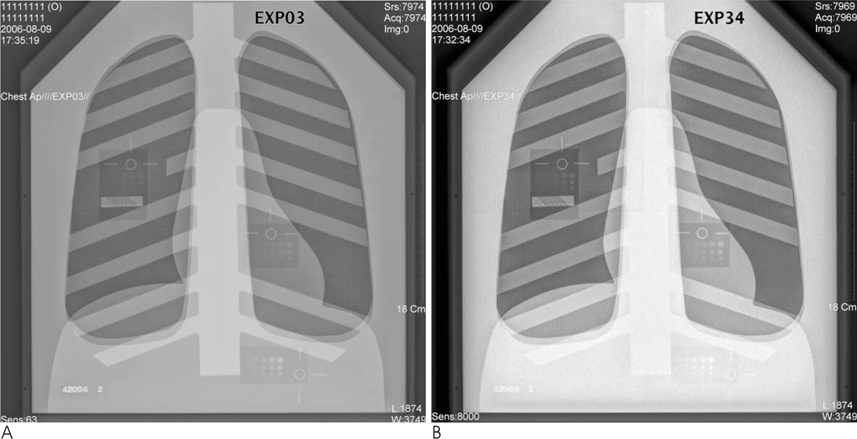
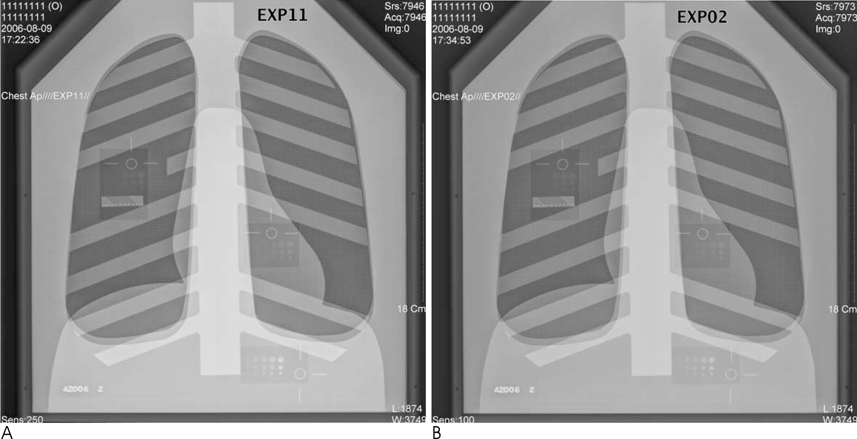
The tube voltage ranged from 70 to 133 kV, whereas the tube current ranged from 2 to 6.3 mAs. The digital radiograph images of a chest phantom were obtained at each setting. We measured the radiation doses of each condition, and counted the visible test objects. The numbers of objects for each condition were compared with the standards used at our institution.
RESULTS
The standard settings were set at 133 kVp and 2 or 4 mAs. Compared to the image quality at 133 kVp and 2 mAs, the radiation dose was lowest at a setting of 109 kVp and 2 mAs. Compared to the image quality of 133 kVp and 4 mAs, the radiation dose was lowest at 109 kVp and 4 mAs.
CONCLUSION
The results of our study suggest that radiation dose can be reduced without compromising image quality by a low-voltage technique in digitial radiography.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berrington de González A, Darby S. Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays: estimates for the UK and 14 other countries. Lancet. 2004; 363:345–351.2. Pohlit W. Radiation biology risk of imaging procedures. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd. 1986; 134:364–369.3. Willis CE. Strategies for dose reduction in ordinary radiographic examinations using CR and DR. Pediatr Radiol. 2004; 34:Suppl 3. S196–S200.4. Peters SE, Brennan PC. Digital radiography: are the manufacturers' settings too high? Optimization of the Kodak digital radiography system with aid of the computed radiography dose index. Eur Radiol. 2002; 12:2381–2387.5. Huda W, Sajewicz AM, Ogden KM, Dance DR. Experimental investigation of the dose and image quality characteristics of a digital mammography imaging system. Med Phys. 2003; 30:442–448.6. Gkanatsios NA, Huda W, Peters KR. Effect of radiographic techniques (kVp and mAs) on image quality and patient doses in digital subtraction angiography. Med Phys. 2002; 29:1643–1650.7. Bankier AA, Schaefer-Prokop C, De Maertelaer V, Tack D, Jaksch P, Klepetko W, et al. Air Trapping: Comparison of Standard-Dose and Simulated Low-Dose Thin-Section CT Techniques. Radiology. 2007; 242:898–906.8. Neofotistou V, Tsapaki V, Kottou S, Schreiner-Karoussou A, Vano E. Does digital imaging decrease patient dose? A pilot study and review of the literature. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005; 117:204–210.9. Bacher K, Smeets P, Bonnarens K, De Hauwere A, Verstraete K, Thierens H. Dose reduction in patients undergoing chest imaging: digital amorphous silicon flat-panel detector radiography versus conventional film-screen radiography and phosphor-based computed radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 181:923–929.10. Kroft LJ, Veldkamp WJ, Mertens BJ, van Delft JP, Geleijns J. Detection of simulated nodules on clinical radiographs: dose reduction at digital posteroanterior chest radiography. Radiology. 2006; 241:392–398.11. Strotzer M, Gmeinwieser JK, Völk M, Fründ R, Seitz J, Feuerbach S. Detection of simulated chest lesions with normal and reduced radiation dose: comparison of conventional screen-film radiography and a flat-panel X-ray detector based on amorphous silicon. Invest Radiol. 1998; 33:98–103.12. Petrone TJ, Steidley KD, Appleby A, Christman E, Haughey F. X-ray beam energy, scatter, and radiation risk in chest radiography. Health Phys. 1996; 70:488–497.13. Hintenlang KM, Williams JL, Hintenlang DE. A survey of radiation dose associated with pediatric plain-film chest X-ray examinations. Pediatr Radiol. 2002; 32:771–777.14. Chotas HG, Floyd CE Jr, Johnson GA, Ravin CE. Quality Control Phantom for Digital Chest Radiography. Radiology. 1997; 202:111–116.15. Mattoon JS. Digital radiography. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2006; 19:123–132.16. Van Soldt RT, Zweers D, van den Berg L, Geleijns J, Jansen JT, Zoetelief J. Survey of posteroanterior chest radiography in The Netherlands: patient dose and image quality. Br J Radiol. 2003; 76:398–405.17. Sandborg M, Tingberg A, Ullman G, Dance DR, Alm Carlsson G. Comparison of clinical and physical measures of image quality in chest and pelvis computed radiography at different tube voltages. Med Phys. 2006; 33:4169–4175.18. Reissberg S, Hoeschen C, Kästner A, Theus U, Fiedler R, Krause U, Döhring W. First clinical experience with a full-size, flat-panel detector for imaging the peripheral skeletal system. Rofo. 2001; 173:1048–1052.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Optimizing Imaging Quality and Radiation Dose by the Age-Dependent Setting of Tube Voltage in Pediatric Chest Digital Radiography
- Relationship of Image Quality and Radiation Dose for Chest Radiography in the Medical Institutions for Pneumoconiosis: A Comparison to the Korean Diagnostic Reference Level
- Abdominal Digital Radiography with a Novel Post-Processing Technique: Phantom and Patient Studies
- Combined Use of Automatic Tube Voltage Selection and Current Modulation with Iterative Reconstruction for CT Evaluation of Small Hypervascular Hepatocellular Carcinomas: Effect on Lesion Conspicuity and Image Quality
- ROC Analysis of Simulated Chest Lesions for Computed Radiography and Digital Radiography at Various Tube Voltages