Acute Crit Care.
2024 May;39(2):323-326. 10.4266/acc.2021.01802.
Digital tomography in the diagnosis of a posterior pneumothorax in the intensive care unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, University Hospital Brussels, Jette, Belgium
- 2Department of Radiology, University Hospital Brussels, Jette, Belgium
- 3Radiology Solutions R&D, Agfa NV, Mortsel, Belgium
- 4Department of Intensive Care Medicine, University Hospital Brussels, Jette, Belgium
- KMID: 2557250
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2021.01802
Abstract
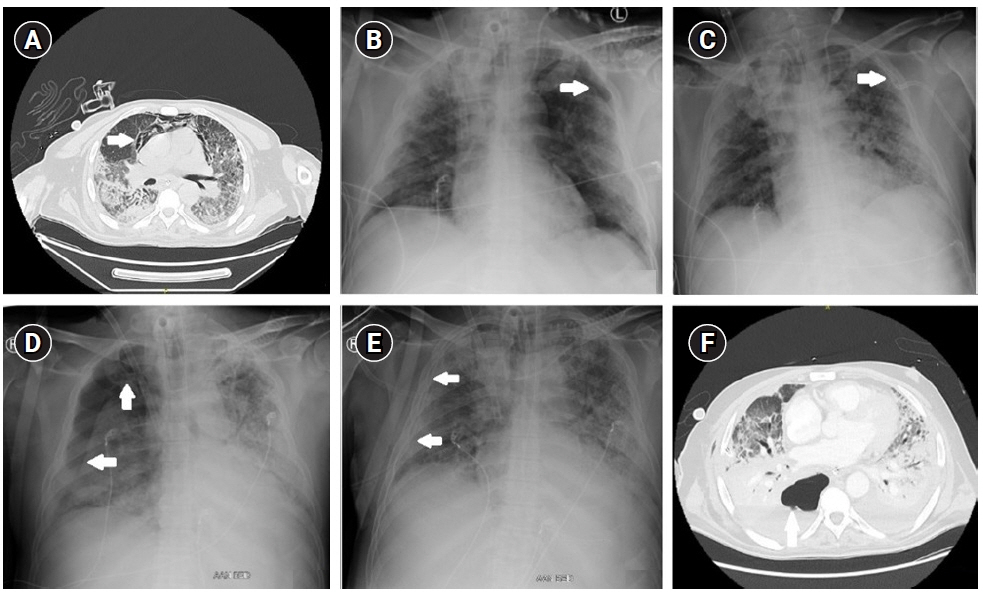
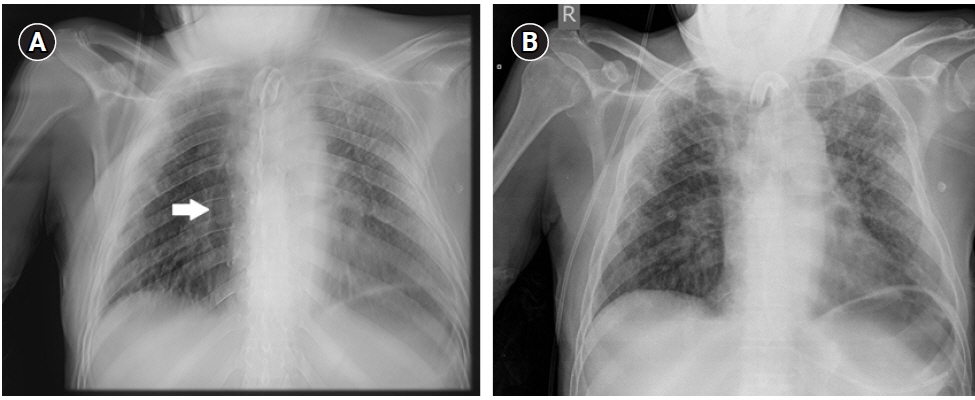
- Portable chest radiography is a valuable tool in the intensive care unit. However, the supine position causes superposition of anatomical structures resulting in less reliable detection of certain abnormalities. Recently, a portable digital tomosynthesis (pDTS) prototype with a modified motorized x-ray device was developed. We aimed to compare the diagnostic value of pDTS to standard bedside chest radiography in the diagnosis of a posterior pneumothorax. A modified motorized x-ray device was developed to perform 15 radiographic projections while translating the x-ray tube 25 cm (10 cm ramp up and 15 cm during x-ray exposure) with a total radiation dose of 0.54 mSv. This new technique of pDTS was performed in addition to standard bedside chest x-ray in a patient with a confirmed posterior hydropneumothorax. The images were compared with the standard bedside chest x-ray and computed tomography (CT) images by two experienced radiologists. The posterior hydropneumothorax previously identified with CT was visible on tomosynthesis images but not with standard bedside imaging. Combining the digital tomosynthesis technique with the portable x-ray machine could increase the diagnostic value of bedside chest radiography for the diagnosis of posterior pneumothoraces while avoiding intrahospital transport and limiting radiation exposure compared to CT.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Strange C. Pleural complications in the intensive care unit. Clin Chest Med. 1999; 20:317–27.
Article2. Wilson H, Ellsmere J, Tallon J, Kirkpatrick A. Occult pneumothorax in the blunt trauma patient: tube thoracostomy or observation? Injury. 2009; 40:928–31.
Article3. Kelly AM, Weldon D, Tsang AY, Graham CA. Comparison between two methods for estimating pneumothorax size from chest X-rays. Respir Med. 2006; 100:1356–9.
Article4. Cant J, Snoeckx A, Behiels G, Parizel PM, Sijbers J. Can portable tomosynthesis improve the diagnostic value of bedside chest X-ray in the intensive care unit? A proof of concept study. Eur Radiol Exp. 2017; 1:20.
Article5. Dobbins JT 3rd, McAdams HP, Godfrey DJ, Li CM. Digital tomosynthesis of the chest. J Thorac Imaging. 2008; 23:86–92.
Article6. Mettler FA Jr, Mahesh M, Bhargavan-Chatfield M, Chambers CE, Elee CE, Frush DP, et al. Patient exposure from radiologic and nuclear medicine procedures in the united states: procedure volume and effective dose for the period 2006-2016. Radiology. 2020; May. 295:418–27.
Article7. Kollef MH. Risk factors for the misdiagnosis of pneumothorax in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1991; 19:906–10.
Article8. Ding W, Shen Y, Yang J, He X, Zhang M. Diagnosis of pneumothorax by radiography and ultrasonography: a meta-analysis. Chest. 2011; 140:859–66.
Article9. Fanara B, Manzon C, Barbot O, Desmettre T, Capellier G. Recommendations for the intra-hospital transport of critically ill patients. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R87.
Article10. Krishnan S, Moghekar A, Duggal A, Yella J, Narechania S, Ramachandran V, et al. Radiation exposure in the medical ICU: predictors and characteristics. Chest. 2018; 153:1160–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Subcutaneous Emphysema and Pneumothorax Occurred during Patient Transfer to Intensive Care Unit: A Case Report
- Risk Factors for Cognitive Impairment in Intensive Care Unit Survivors
- Pneumothorax and pulmonary air leaks as ventilator-induced injuries in COVID-19
- Mechanical ventilation-associated pneumothorax presenting with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in patients with acute respiratory failure
- Characteristics of Pneumothorax in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit