J Clin Neurol.
2006 Jun;2(2):126-133. 10.3988/jcn.2006.2.2.126.
Cognitive Effects of Low-dose Topiramate Compared with Oxcarbazepine in Epilepsy Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. sppark@mail.knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1700745
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2006.2.2.126
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Low-dose topiramate (TPM) monotherapy has recently been found effective for seizure control in newly diagnosed epilepsy. In higher dosages, TPM has been associated with relatively high rates of adverse cognitive effects; similar side effects have been seen after rapid titration or polytherapy. However, its cognitive effects during low-dose monotherapy have not been established. We evaluated the cognitive effects of low-dose TPM compared with oxcarbazepine (OXC), a drug that does not appear to affect cognitive function.
METHODS
Cognitive tests and subjective complaints of 30 patients with low-dose TPM monotherapy (50-200 mg/day) were retrospectively compared with those of 30 patients with OXC monotherapy at 1 year of medication. The two groups did not differ with respect to epilepsy-relevant variables, nor on baseline neuropsychological tests.
RESULTS
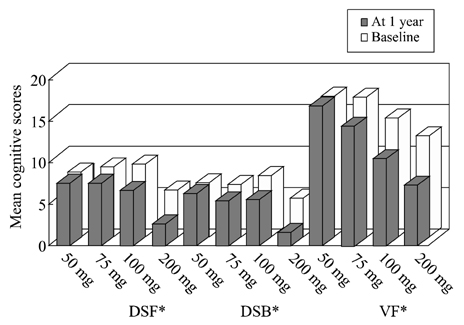
The TPM group showed a significant difference in the performance of delayed word recall (P<0.05), backward digit span (P<0.01), and verbal fluency (P<0.05) compared with the OXC group. The TPM group showed worse performances of digit span and verbal fluency. The OXC group showed better performances of delayed word recall. The incidence of cognitive complaints was higher in the TPM group (50%) than in the OXC group (20%) (P<0.05). These cognitive effects shown in the TPM group were dose-related. The cognitive dysfunction was trivial with patients taking 50 mg/day TPM.
CONCLUSIONS
Even at low-dose, TPM has a negative effect on working memory and verbal fluency compared with OXC. It can be demonstrated at 1 year of treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cognitive Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs
Sung-Pa Park, Soon-Hak Kwon
J Clin Neurol. 2008;4(3):99-106. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.3.99.
Reference
-
1. Motamedi G, Meador K. Epilepsy and cognition. Epilepsy Behav. 2003. 4:Suppl 2. S25–S38.
Article2. Aldenkamp AP, De Krom MD, Reijs R. Newer antiepileptic drugs and cognitive issues. Epilepsia. 2003. 44:Suppl 4. 21–29.
Article3. Ortinski P, Meador KJ. Cognitive side effects of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsy Behav. 2004. 5:Suppl 1. S60–S65.
Article4. Gilliam FG, Veloso F, Bomhof MA, Gazda SK, Biton V, Ter Bruggen JP, et al. A dose-comparison trial of topiramate as monotherapy in recently diagnosed partial epilepsy. Neurology. 2003. 60:196–201.
Article5. Privitera MD, Brodie MJ, Mattson RH, Chadwick DW, Neto W, Wang S. Topiramate, carbamazepine and valproate monotherapy: double-blind comparison in newly diagnosed epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2003. 107:165–175.
Article6. Bootsma HP, Coolen F, Aldenkamp AP, Arends J, Diepman I, Hulsman J, et al. Topiramate in clinical practice: long-term experience in patients with refractory epilepsy referred to a tertiary epilepsy center. Epilepsy Behav. 2004. 5:380–387.
Article7. Tatum WO 4th, French JA, Faught E, Morris GL 3rd, Liporace J, Kanner A, et al. Postmarketing experience with topiramate and cognition. Epilepsia. 2001. 42:1134–1140.
Article8. Aldenkamp AP, Baker G, Mulder OG, Chadwick D, Cooper P, Doelman J, et al. A multicenter, randomized clinical study to evaluate the effect on cognitive function of topiramate compared with valproate as add-on therapy to carbamazepine in patients with partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia. 2000. 41:1167–1178.
Article9. Thompson PJ, Baxendale SA, Duncan JS, Sander JW. Effects of topiramate on cognitive function. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000. 69:636–641.
Article10. Meador KJ, Loring DW, Hulihan JF, Kamin M, Karim R. Differential cognitive and behavioral effects of topiramate and valproate. Neurology. 2003. 60:1483–1488.
Article11. Mula M, Trimble MR, Thompson P, Sander JW. Topiramate and word-finding difficulties in patients with epilepsy. Neurology. 2003. 60:1104–1107.
Article12. Lee S, Sziklas V, Andermann F, Farnham S, Risse G, Gustafson M, et al. The effects of adjunctive topiramate on cognitive function in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2003. 44:339–347.
Article13. Kockelmann E, Elger CE, Helmstaedter C. Significant improvement in frontal lobe associated neuropsychological functions after withdrawal of topiramate in epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res. 2003. 54:171–178.
Article14. Fritz N, Glogau S, Hoffmann J, Rademacher M, Elger CE, Helmstaedter C. Efficacy and cognitive side effects of tiagabine and topiramate in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2005. 6:373–381.
Article15. Beydoun A, Sachdeo RC, Rosenfeld WE, Krauss GL, Sessler N, Mesenbrink P, et al. Oxcarbazepine monotherapy for partial-onset seizures: a multicenter, double-blind, clinical trial. Neurology. 2000. 54:2245–2251.
Article16. Saber A, Møller A, Dam M, Smed A, Arlien-Soborg P, Buchman J, et al. Cognitive function and anticonvulsant therapy: effect of monotherapy in epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 1995. 92:19–27.
Article17. Aikia M, Kalviainen R, Sivenius J, Halonen T, Riekkinen PJ. Cognitive effects of oxcarbazepine and phenytoin monotherapy in newly diagnosed epilepsy: one year follow-up. Epilepsy Res. 1992. 11:199–203.
Article18. Park SP, Hwang YH, Kim JI, Kim JY, Kwon SH, Jung BW, et al. Cognitive function in epileptic patients treated with oxcarbazepine: neuropsychologic test and event-related potential. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2002. 20:27–33.19. Williams JM. Memory Assessment Scales Professional Manual. 1991. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.20. Wechsler D. Wechsler Memory Scale-Revised Manual. 1987. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.21. Reitan RM, Wolfson D. The Halstead-Reitan Neuropsychological Test Battery: Theory and Clinical Interpretation. 1993. 2nd edn. Tucson, AZ: Neuropsychology Press.22. Goodglass H, Kaplan E, Barresi B. Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination-Third Edition (BDAE-3). 2000. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.23. Aldenkamp AP. Cognitive and behavioural assessment in clinical trials: when should they be done? Epilepsy Res. 2001. 45:155–157.
Article24. Thompson P. Cognitive and behavioural assessment in clinical trials: when should they be done? Epilepsy Res. 2001. 45:159–161.
Article25. Bourgeois BFD. Determining the effects of antiepileptic drugs on cognitive function in pediatric patients with epilepsy. J Child Neurol. 2004. 19:Suppl 1. S15–S24.
Article26. Arroyo S, Dodson WE, Privitera MD, Glauser TA, Naritoku DK, Dlugo DJ, et al. Randomized dose-controlled study of topiramate as first-line therapy in epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand. 2005. 112:214–222.
Article27. Lin KM, Poland RE, Lesser IM. Ethnicity and psychopharmacology. Cult Med Psychiatry. 1986. 10:151–165.
Article28. Silberstein SD, Ben-Menachem E, Shank RP, Wiegand F. Topiramate monotherapy in epilepsy and migraine prevention. Clin Ther. 2005. 27:154–165.29. Curran HV, Java R. Memory and psychomotor effects of oxcarbazepine in healthy human volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1993. 44:529–533.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cognitive Effects of Newer Antiepileptic Drugs
- Safety and Efficacy of Topiramate Monotherapy in Children with Recent-onset Seizures
- Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Language Abilities in Benign Epilepsy of Childhood with Centrotemporal Spikes
- Cognitive and Behavioral Problems and the Effectiveness of Topiramate Once per Day in the Control of Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spikes
- Low-dose, Once-a-day Treatment of Topiramate in Benign Childhood Epilepsy with Centrotemporal Spikes