J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Jun;14(2):118-124. 10.4078/jkra.2007.14.2.118.
The Expression of Toll-like Receptors in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea. ksimd@pusan.ac.kr
- 3Research Institute, College of Medicine, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1526428
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2007.14.2.118
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the expression of toll-like receptor (TLR)-2, 4 and 9 in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs).
Methods
The expression of TLR-2, 4 and 9 was measured by real-time RT-PCR and immunohistochemical stain (IHS) from muscle tissues in patients with IIMs and controls.
Results
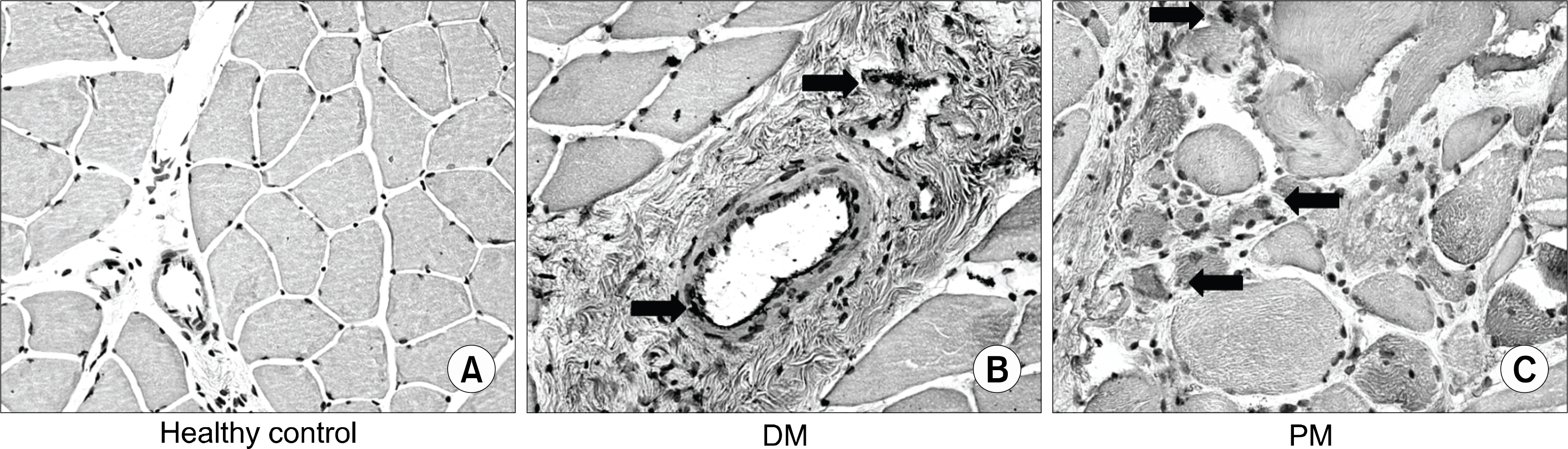
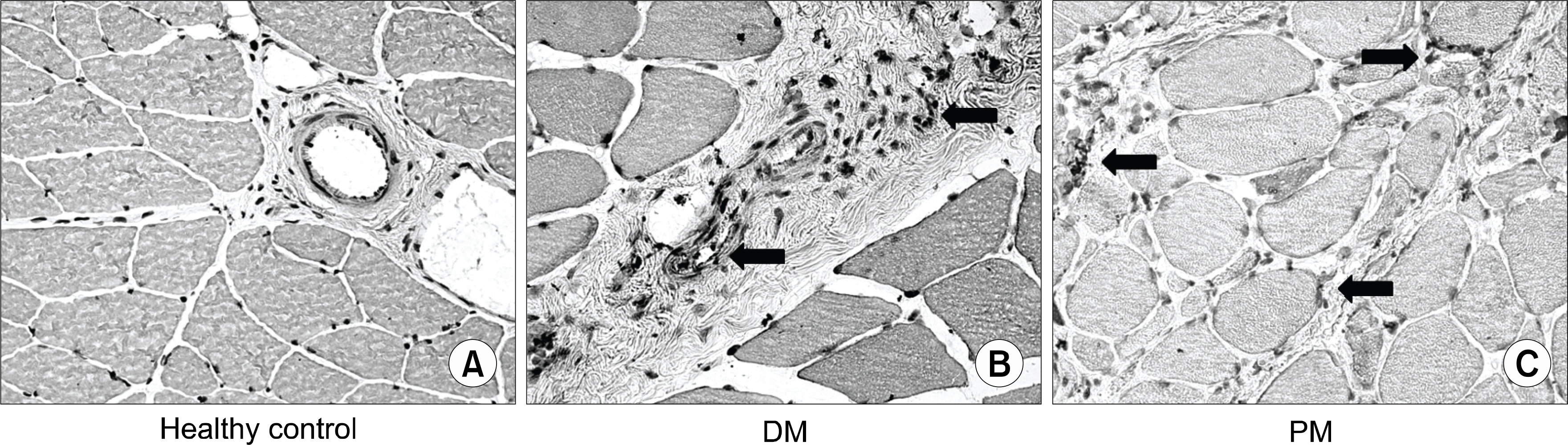
The expression levels of TLR-2, 4 and 9 in IIMs were significantly higher than controls. TLR-2, 4 and 9 were mainly expressed on sarcolemma of muscle fibers, perimysial vascular endothelium and infiltrating inflammatory cells in dermatomyositis, whereas, they were mainly expressed on sarcolemma of muscle fibers, destructed muscle fibers, and enodmysial infiltrating inflammatory cells in polymyositis.
Conclusion
TLR-2, 4 and 9 were highly expressed in muscle tissue of IIMs. These results suggest that TLR-2, 4 and 9 play a role in pathogenesis of IIMs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Kanneboyina N. Update on immunopathgenesis in inflammatory myopathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001. 13:461–8.2). Anderem A., Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000. 406:782–7.
Article3). Anderson KV. Toll signaling pathways in the innate immune response. Curr ᄋpin Immunol. 2000. 12:13–9.
Article4). Elias T., Yehuda S. Toll-like receptors and their role in the development of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity. 2004. 37:183–8.
Article5). Bohan A., Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975. 292:344–7.6). Bohan A., Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975. 292:403–7.7). Lee EY., Yim JJ., Lee HS., Lee YJ., Lee EB., Song YW. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in intron II of human Toll-like receptor 2 gene and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Immunogenet. 2006. 33:211–5.
Article8). Kilding R., Akil M., Till S., Amos R., Winfield J., Iles MM, et al. A biologically important single nucleotide polymorphism within the toll-like receptor-4 gene is not associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. 21:340–2.9). Sanches E., ᄋrozco G., Lopez-Nevot MA., Jimenez-Alonso J., Martin J. Polymorphisms of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 genes in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens. 2004. 63:54–7.
Article10). Hur JW., Shin HD., Park BL., Kim LH., Kim SY., Bae SC. Association study of Toll-like receptor 9 gene polymorphism in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Tissue Antigens. 2005. 65:266–70.
Article11). Seibl R., Birchler T., Loeliger S., Hossle JP., Gay RE., Saurenmann T, et al. Expression and regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Am J Pathol. 2003. 162:1221–7.
Article12). Radstake TR., Roelofs MF., Jenniskens YM., Appers-Walgreen B., van Riel PL., Barrera P, et al. Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 via interferon-gamma. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:3856–65.13). Iwahashi M., Yamamura M., Aita T., ᄋkamoto A., Ueno A., ᄋgawa N, et al. Expression of Toll-like receptor 2 on CD 16+ blood monocytes and synovial tissue macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:1457–67.14). Papadimitraki ED., Choulaki C., Koutala E., Bertsias G., Tsatsanis C., Gergianaki I, et al. Expansion of toll-like receptor 9-expressing B cells in active systemic lupus erythematosus: implications for the induction and maintenance of the autoimmune process. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. 54:3601–11.
Article15). Briani C., Doria A., Sarzi-Puttini P., Dalakas MC. Update on idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Autoimmunity. 2006. 39:161–70.
Article16). Gaston JS. Heat shock proteins and arthritis-new readers start here. Autoimmunity. 1997. 26:33–42.17). Prakken BJ., van der Zee R., Anderton SM., van Kooten PJ., Kuis W., van Eden W. Peptide-induced nasal tolerance for a mycobacterial heat shock protein 60 T cell epitope in rats suppresses both adjunvant arthritis and nonmicrobially induced experimental arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997. 94:3284–9.18). Li M., Carpio DF., Zheng Y., Bruzzo P., Singh V., ᄋuaaz F, et al. An essential role of the NF-kappa B/Toll-like receptor pathway in induction of inflammatory and tissue-repair gene expression by necrotic cells. J Immunol. 2001. 166:7128–35.19). Leadbetter EA., Rifkin IR., Hohlbaum AM., Beaudette BC., Shlomchik MJ., Marshak-Rothstein A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature. 2002. 416:603–7.
Article20). Bosisio D., Polentarutti N., Sironi M., Bernasconi S., Miyake K., Webb GR, et al. Stimulation of toll-like receptor 4 expression in human mononuclear phagocytes by interferon-δ: a molecular basis for priming and synergism with bacterial lipopolysac-charide. Blood. 2004. 99:3427–31.
Article21). Schroder K., Swee MJ., Hume DA. Signal integration between IFN δ and TLR signalling pathways in macrophages. Immunobiology. 2006. 211:511–24.22). Rycke LD., Vandooren B., Kruithof E., Keyser FD., Veys Em., Baeten D. Tumor ncreosis factor α blockade treatment down-modulates the increased systemic and local expresssion of toll-like receptor 2 and toll-like receptor 4 in spondyloarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:2146–58.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Do Toll-like Receptors Play a New Role as a Biomarker of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
- The Expression of Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) in Cultured Human Skin Fibroblast is Modulated by Histamine
- Lipopolysaccharide: Basic Biochemistry, Intracellular Signaling, and Physiological Impacts in the Gut
- Activation of Toll-like Receptors 1, 2, 4, 5, and 7 on Human Melanocytes Modulate Pigmentation
- Systematic Analysis of Translocator Protein 18 kDa (TSPO) Ligands on Toll-like Receptors-mediated Pro-inflammatory Responses in Microglia and Astrocytes